J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Feb;23(1):117-121. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.117.
Compound Nerve Action Potential of Common Peroneal Nerve and Sural Nerve Action Potential in Common Peroneal Neuropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hkkwon@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1786856
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.117
Abstract
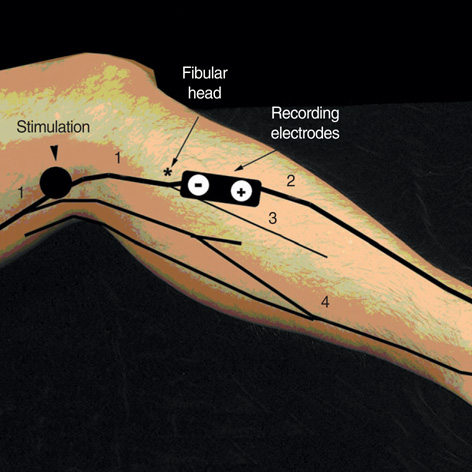
- To enhance the accuracy for determining the precise localization, the findings of the compound nerve action potentials (CNAPs) of the common peroneal nerve (CPN) were investigated in patients with common peroneal mononeuropathy (CPM) in the knee, and the sural sensory nerve action potentials (SNAPs) were also analyzed. Twenty-five patients with CPM in the knee were retrospectively reviewed. The findings of the CNAPs of the CPN recorded at the fibular neck and the sural SNAPs were analyzed. The lesion was localized at the fibular head (abnormal CNAPs) and at or distal to the fibular head (normal CNAPs). Seven patients were diagnosed as having a lesion at or distal to the fibular neck, and 18 cases were diagnosed as having a fibular head lesion. The sural SNAPs were normal in all the cases of lesion at or distal to the fibular neck. Among 18 cases of fibular head lesion, the sural SNAPs were normal in 7 patients: two cases of conduction block and 5 cases of mild axon loss. Eleven patients showed abnormal sural SNAPs. Of those, 9 cases were severe axon loss lesions and 2 patients were diagnosed as having severe axon loss with conduction block. The recording of the CNAPs may enhance precise localization of CPM in the knee. Moreover, the sural SNAPs could be affected by severe axonal lesion at the fibular head.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wilbourn AJ. AAEE case report #12: Common peroneal mononeuropathy at the fibular head. Muscle Nerve. 1986. 9:825–836.
Article2. Goldner JC, Thomas JE. Foot drop. GP. 1969. 40:89–96.3. Lee HJ. Compound nerve action potential of common peroneal nerve recorded at fibular neck: its clinical usefulness. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2001. 80:108–112.4. Devi S, Lovelace RL, Duarte N. Proximal peroneal nerve conduction velocity: recording from anterior tibialis and peroneus brevis muscles. Ann Neurol. 1977. 2:116–119.5. Singh N, Behse F, Buchthal F. Electrophysical study of peroneal palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974. 37:1202–1213.6. DeLisa JA, Lee HJ, Baran EM, Lai KS, Spielholz N. Manual of nerve conduction and clinical neurophysiology. 1994. 3rd ed. New York: Raven Press;118–127.7. Campbell WW. AAEM Course D: Fundamentals in electrodiagnostic medicine: electromyograhy and conduction studies in the diagnosis and management of entrapment syndromes. 1993. 37–40.8. Robinson LR. Johnson EW, Pease WS, editors. Entrapment neuropathies and focal neuropathies. Practical Electromyography. 1997. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;262–267.9. Haymaker W, Woodhall B. Peripheral nerve injuries, Principles of diagnosis. 1953. Philadelphia & London: WE Saunders Co;287–30.10. Netter FH. The Ciba collection of medical illumstrations: Musculoskeletal system. Part I Anatomy, physiology and metabolic disorders. 1987. Summit, New Jersey: Ciba-Geigy;82.11. Lee HJ, Delisa JA. Nerve conduction study and surface anatomy for needle electromyography. 2005. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;78–79.12. Dumitru D. Dumitru D, editor. Focal peripheral neuropathies. Electrodiagnostic Medicine. 1996. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus;898–904.
Article13. Berry H, Richardson PM. Common peroneal nerve palsy: a clinical and electrophysiological review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976. 39:1162–1171.
Article14. Sunderland S. Nerve and Nerve Injuries. 1978. 2nd ed. Baltimore: WB Saunders;925–991.15. Stewart JD, Aguayo AJ. Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Lambert EH, Bunge R, editors. Compression and entrapment neuropathies. Peripheral Neuropathy. 1984. 1st ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;1435–1457.16. Katirji MB, Wilbourn AJ. Common peroneal mononeuropathy: a clinical and electrophysiologic study of 116 lesions. Neurology. 1988. 38:1723–1728.
Article17. Kanakamedala RV, Hong CZ. Peroneal nerve entrapment at the knee localized by short segment stimulation. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1989. 68:116–122.
Article18. Brown WF, Yates SK. Percutaneous localization of conduction abnormalities in human entrapment neuropathies. Can J Neurol Sci. 1982. 9:391–400.
Article19. Kim CH, Jung HY, Kim MO, Lee CJ. The relative contributions of the medial sural and peroneal communicating nerves to the sural nerve. Yonsei Med J. 2006. 47:415–422.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Common Peroneal Nerve Injuries
- The Diasgnostic Usefulness of Mean F-wave Latency in Diabetic Polyneuropathy
- Common Peroneal Nerve Palsy after Lithotomy Position: Two case reports
- Clinical and Electrophysiological Findings in the Four Cases of Anterior Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Significance of Amplitude and Area Ratio of Compound Muscle Action Potential in Diagnosis of Diabetic Neuropathy