Healthc Inform Res.
2017 Jan;23(1):25-34. 10.4258/hir.2017.23.1.25.
Action Research on Development and Application of Internet of Things Services in Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Management, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. klee@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2368982
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2017.23.1.25
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Services based on the Internet of Things (IoT) technologies have emerged in various business environments. To enhance health service quality and maximize benefits, this study applied an IoT technology based on NFC and iBeacon as an omni-channel service for patient care in hospitals.
METHODS
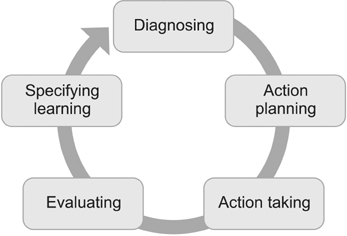
Application of the IoT technology based on NFC and iBeacon was conducted in a general hospital during August 2015 through June 2016, and the development and evaluation results were aligned to an action research framework. The five phases in the action research included diagnosing, planning action, taking action, evaluating action, and specifying learning phases.
RESULTS
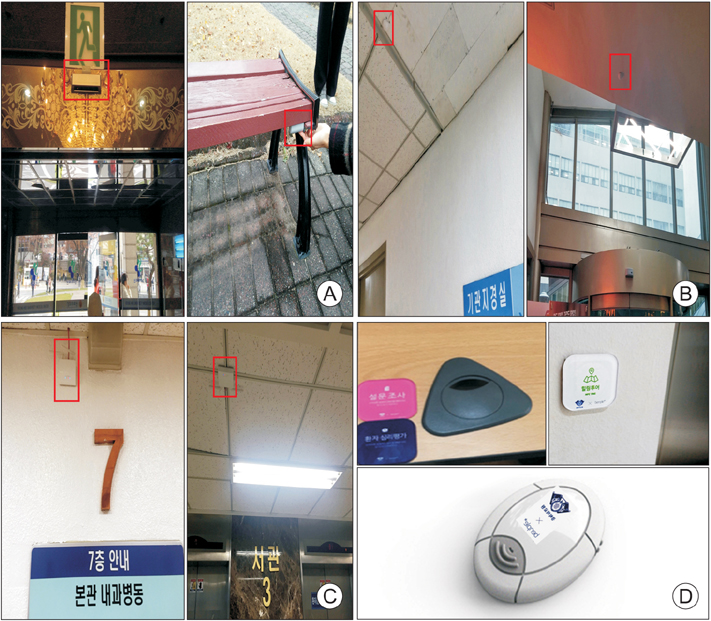
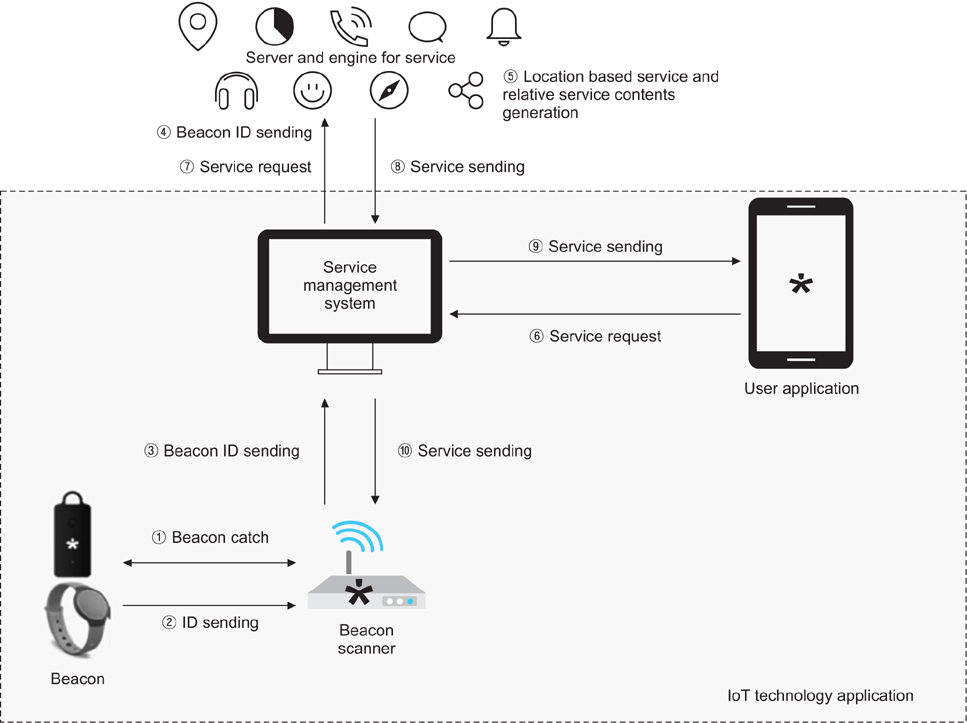
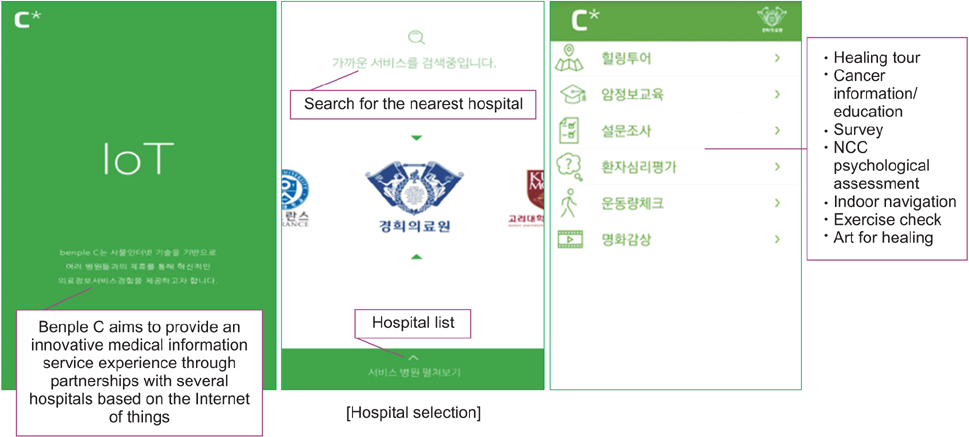
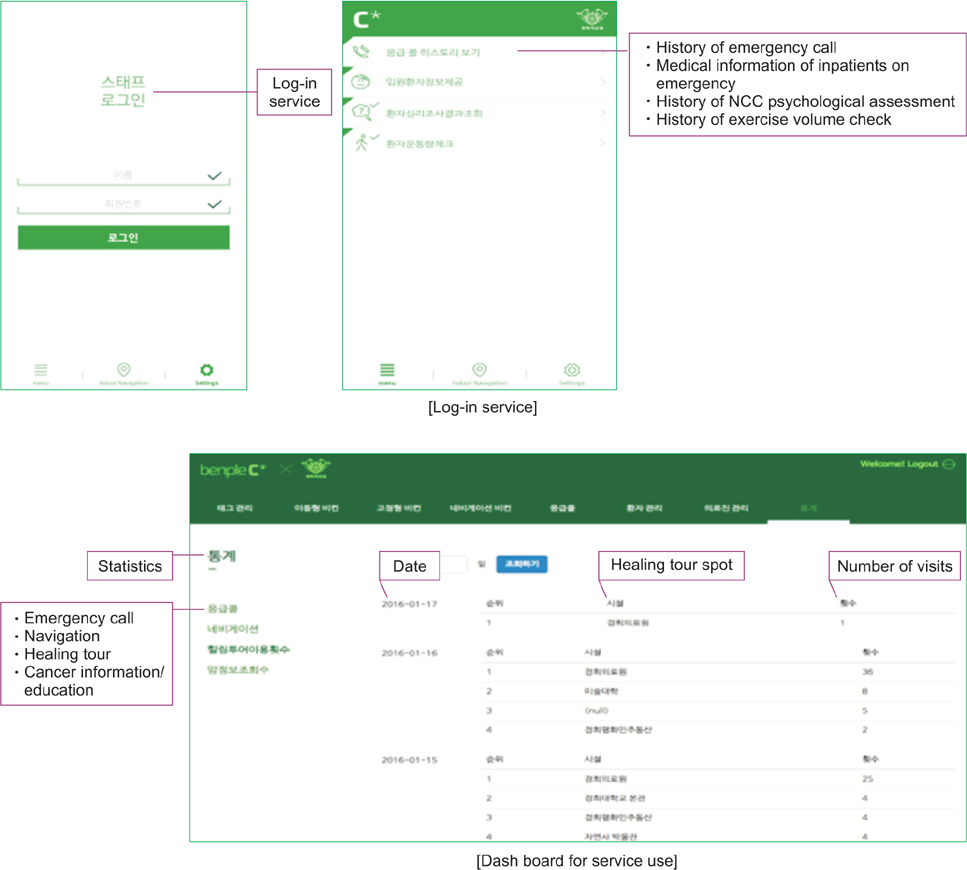
During the first two phases, problems of functional operations in a hospital were diagnosed and eight service models were designed by using iBeacon and NFC to solve the problems. Service models were applied to the hospital by installing beacons, wearable beacons, beacon scanners, and NFC tags during the third phase. During the fourth and fifth phases, the roles and benefits of stakeholders participating in the service models were evaluated, and issues and knowledge of the whole application process were derived and summarized from technological, economic, social and legal perspectives, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
From an action research perspective, IoT-based healthcare services were developed and verified. IoT-based services enable the hospital to acquire lifelog data for precision medicine and ultimately be able to go one step closer to precision medical care. The derived service models could provide patients more enhanced healthcare services and improve the work efficiency and effectiveness of the hospital.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
How to Sustain Smart Connected Hospital Services: An Experience from a Pilot Project on IoT-Based Healthcare Services
Arum Park, Hyejung Chang, Kyoung Jun Lee
Healthc Inform Res. 2018;24(4):387-393. doi: 10.4258/hir.2018.24.4.387.Privacy Enhanced Healthcare Information Sharing System for Home-Based Care Environments
Daniel Agbesi Dzissah, Joong-Sun Lee, Hiroyuki Suzuki, Mie Nakamura, Takashi Obi
Healthc Inform Res. 2019;25(2):106-114. doi: 10.4258/hir.2019.25.2.106.
Reference
-
1. Golubnitschaja O, Costigliola V. Predictive, preventive and personalised medicine as the medicine of the future: anticipatory scientific innovation and advanced medical services. In : Nadin M, editor. Anticipation and medicine. Cham: Springer International Publishing;2017. p. 69–85.2. Swedberg C. Brigham and Women's Hospital tests NFC RFID for patient bedsides. Hauppauge (NY): RFID Journal;2013. cited at 2016 Dec 30. Available from: http://www.rfidjournal.com/articles/view?10511/2.3. Clark S. 50,000 Dutch nurses now using NFC phones [Internet]. Cardiff: NFC World;2011. cited at 2016 Dec 30. Available from: https://www.nfcworld.com/2011/09/06/39716/50000-dutch-nurses-now-using-nfcphones/.4. Institute of Medicine. Health IT and patient safety: building safer systems for better care. Washington (DC): National Academies Press;2011.5. Meterko M, Mohr DC, Young GJ. Teamwork culture and patient satisfaction in hospitals. Med Care. 2004; 42(5):492–498.
Article6. Gaylin DS, Moiduddin A, Mohamoud S, Lundeen K, Kelly JA. Public attitudes about health information technology, and its relationship to health care quality, costs, and privacy. Health Serv Res. 2011; 46(3):920–938.
Article7. Bhattacharya D, Canul M, Knight S. Case study: impact of the physical web and BLE beacons. In : Proceedings of the 50th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences; 2017 Jan 4-7; Waikoloa Village: HI;p. 4262–4265.8. Han H, Park A, Chung N, Lee KJ. A near field communication adoption and its impact on Expo visitors' behavior. Int J Inf Manag. 2016; 36(6):1328–1339.
Article9. Deloitte. The omnichannel opportunity: unlocking the power of the connected consumer [Internet]. London: Deloitte;2014. cited at 2016 Dec 30. Available from: https://www2.deloitte.com/uk/en/pages/consumer-business/articles/unlocking-the-power-of-the-connected-consumer.html.10. Griffiths GH, Howard A. Balancing clicks and bricks-strategies for multichannel retailers. J Glob Bus Issues. 2008; 2(1):69–76.11. Lee KJ, Choi MH, Kwon SH, Jeon JH. A study on NFC technology utilization and application cases in museum/gallery. J Arts Cult Manag. 2013; 6(1):29–51.12. Muller-Lankenau C, Wehmeyer K, Klein S. Strategic channel alignment: an analysis of the configuration of physical and virtual marketing channels. Inf Syst e-Bus Manag. 2006; 4(2):187–216.
Article13. Regalado A. It's all e-commerce now [Internet]. Big Sandy (TX): MIT Technology Review;2013. cited at 2016 Dec 30. Available from: https://www.technologyreview.com/s/520786/its-all-e-commerce-now/#comments/.14. Verhoef PC, Kannan PK, Inman JJ. From multi-channel retailing to omni-channel retailing: introduction to the special issue on multi-channel retailing. J Retail. 2015; 91(2):174–181.15. Peltola S, Vainio H, Nieminen M. Key factors in developing omnichannel customer experience with Finnish retailers. In : Nah FF, Tan CH, editors. HCI in business. Cham: Springer International Publishing;2015. p. 335–346.16. Baburoglu ON, Ravn I. Normative action research. Organ Stud. 1992; 13(1):19–34.17. Baskerville RL, Wood-Harper AT. A critical perspective on action research as a method for information systems research. In : Willcocks LP, Sauer C, Lacity MC, editors. Enacting research methods in information systems. Cham: Springer International Publishing;2016. p. 169–190.18. Susman GI, Evered RD. An assessment of the scientific merits of action research. Adm Sci Q. 1978; 25(4):582–603.
Article19. Timmers P. Business models for electronic markets. Electron Mark. 1998; 8(2):3–8.
Article20. Yao W, Chu CH, Li Z. The adoption and implementation of RFID technologies in healthcare: a literature review. J Med Syst. 2012; 36(6):3507–3525.
Article21. National Cancer Center. Recommendations for distress management in cancer patients [Internet]. Ilsan, Korea: National Cancer Center;2008. cited at 2016 Dec 30. Available from: http://www.cancer.go.kr/2010/04/22/Recommendations_Distress_Management_version1.pdf.22. Lin CC, Lin PY, Lu PK, Hsieh GY, Lee WL, Lee RG. A healthcare integration system for disease assessment and safety monitoring of dementia patients. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2008; 12(5):579–586.
Article23. Lai CL, Fang K, Chien SW. Enhanced monitoring of tuberculosis patients by using RFID technologies. Int J Mob Commun. 2010; 8(2):244–256.
Article24. Iadanza E, Dori F. Custom active RFID solution for children tracking and identifying in a resuscitation ward. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009; 2009:5223–5226.
Article25. Greengard S. RFID: cure for counterfeit drugs? [Internet]. Hauppauge (NY): RFID Journal;2003. cited at 2016 Dec 30. Available from: http://www.rfidjournal.com/articles/view?611.26. Glabman M. Room for tracking. RFID technology finds the way. Mater Manag Health Care. 2004; 13(5):26–28. 31–34. 36 passim27. Azevedo SG, Ferreira JJ. Radio frequency identification: a case study of healthcare organisations. Int J Secur Netw. 2010; 5(2-3):147–155.
Article28. Huang PJ, She CC, Chang P. The development of a Patient-Identification-Oriented Nursing Shift Exchange Support System using wireless RFID PDA techniques. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2005; 2005:990.29. Jaffe R, Nash RA, Ash R, Schwartz N, Corish R, Born T, et al. Healthcare transparency: opportunity or mirage. J Manag Dev. 2006; 25(10):981–995.
Article30. Kim SJ, Kim NS. An approach about implementation and use of one-stop healthcare service system using RFID technology. In : Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT); 2006 Feb 20-22; Phoenix Park, Korea. p. 339–344.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Internet of Things: An Overview and its Applications in Aviation
- Development Scenario of Dietary Intake Survey Using Internet of Things (IoT)
- Book Review: The Internet of Healthy Things
- Service-Oriented Security Framework for Remote Medical Services in the Internet of Things Environment
- Utilization of Internet-based Medical Information Services and Hospital Selection among Health Care Consumers: Internet Survey