Korean J Women Health Nurs.
2016 Dec;22(4):264-274. 10.4069/kjwhn.2016.22.4.264.
Development of a Breastfeeding Effectiveness Scale (BES)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Changshin University, Changwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, Masan University, Changwon, Korea. minnung@masan.ac.kr
- 3College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2364629
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2016.22.4.264
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to develop and evaluate breastfeeding effectiveness scale to measure effectiveness of breastfeeding for mothers in the early postpartum period.
METHODS
A conceptual framework was constructed from properties of effective breastfeeding (Yang and Seo, 2011), and item construction was derived from literature review and analysis of the data along with interviews with breastfeeding mothers. Content validity was tested by experts. Each item was scored on a five-point Likert scale. The preliminary questionnaire was administered to 248 breastfeeding mothers. Data were analyzed using item analysis, factor analysis, Pearson correlation coefficients, and Cronbach's α.
RESULTS
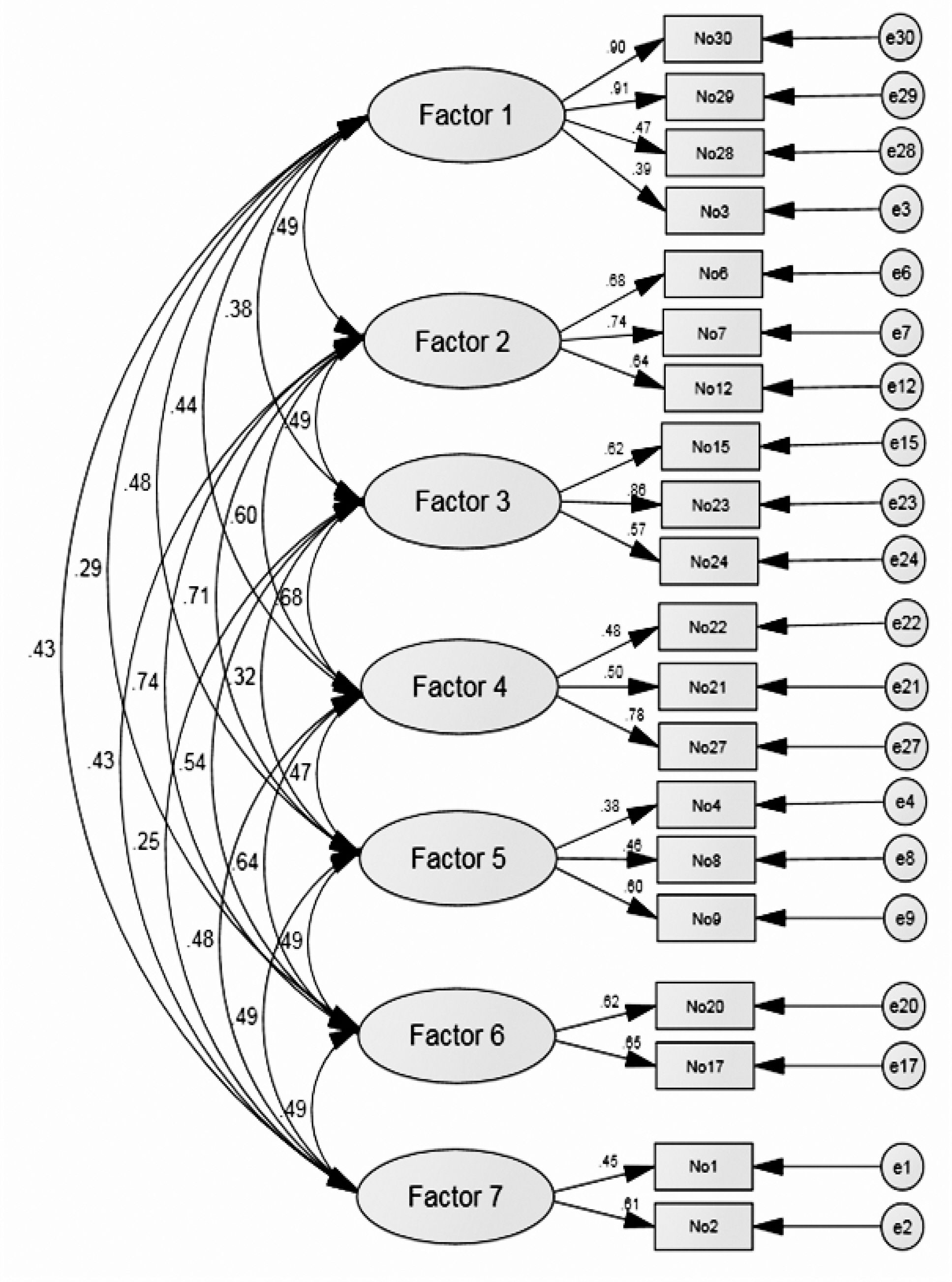
From the factor analysis, 20 items in seven factors were derived. The factors were identified as mother's satisfaction, suckling, assurance of milk quantity, infant's satisfaction, latching on, infant's feeding desire, and breastfeeding positioning. The seven factors explained 65.1% of total variance, Cronbach's α of the total items was .83 and the factors ranged from .44 to .75.
CONCLUSION
Results of this study suggest that breastfeeding effectiveness scale is a reliable and valid instrument to measure breastfeeding effectiveness of mothers in the early postpartum period.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Breastfeeding Adaptation Scale-Short Form for mothers at 2 weeks postpartum: construct validity, reliability, and measurement invariance
Sun-Hee Kim
Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2020;26(4):326-335. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2020.11.10.
Reference
-
1. Cooke M, Sheehan A, Schmied V. A Description of the relationship between breastfeeding experiences, breastfeeding satisfaction, and weaning in the first 3 months after birth. Journal of Human Lactation. 2003; 19(2):145–146.
Article2. Kronborg H, Vaeth M. How are effective breastfeeding technique and pacifier use related to breastfeeding problems and breastfeeding duration? Birth. 2009; 36(1):34–42.
Article3. Shrago L, Bocar D. The infant's contribution to breastfeeding. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing. 1990; 19(3):209–215.
Article4. Mulford C. The Mother-Baby Assessment(MBA): An “Apgar score" for breastfeeding. Journal of Human Lactation. 1992; 8(2):79–82.5. Jensen D, Wallace S, Kelsay P. LATCH: A breastfeeding charting system and documentation tool. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing. 1994; 23(1):27–32.
Article6. Mulder PJ, Johnson TS. The beginning breastfeeding survey: Measuring mother's perceptions of breastfeeding effectiveness during the postpartum hospitalization. Research in Nursing & Health. 2010; 33(4):329–344.
Article7. Mulder PJ. A concept analysis of effective breastfeeding. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing. 2006; 35(3):332–339.
Article8. Yang HJ, Seo JM. Concept analysis of effective breastfeeding. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2011; 17(4):317–327.
Article9. Jeong GH. Effect of the nursing intervention program on promoting the breastfeeding practice in primipara [dissertation]. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;1997. p. 1–133.10. Lee EJ. The effect of prenatal breastfeeding education on breastfeeding practice and retention of knowledge [master's thesis]. Daegu: Keimyung University;1997. p. 1–60.11. Kim SH. Development of a breast feeding adaptation scale. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2009; 39(2):259–269.12. Kim YM, Park YS. A study on the development of the Korean breastfeeding empowerment scale. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2004; 10(4):360–367.
Article13. Dennis CL. The breastfeeding self-efficacy scale: Psychometric assessment of the short form. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing. 2003; 32(6):734–744.
Article14. Matthews MK. Developing an instrument to assess infant breastfeeding behaviour in the early neonatal period. Midwifery. 1998; 4(4):154–165.
Article15. Johnson TS, Mulder PJ, Strube K. Mother-infant breastfeeding progress tool: a guide for education and support of the breastfeeding dyad. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing. 2007; 36(4):319–327.
Article16. Leff EW, Jefferis SC, Gagne MP. The development of the maternal breastfeeding evaluation scale. Journal of Human Lactation. 1994; 10(2):105–111.
Article17. Lee EO, Im NY, Park HA, Lee IS, Kim JI, Bae JY, et al. Nursing research and statistical analysis. 1st ed.Seoul: Soomoonsa;2009. p. 1–733.18. Stevens J. Applied multivariate statistics for the social sciences. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;1996. p. 1–659.19. Yang HJ, Seo JM. A structural model for primiparas' breastfeeding behavior. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2013; 43(3):399–408.
Article20. Lee HS, Im JH. Structural equation modeling with AMOS 18.0/19.0. 1st ed.Seoul: Jiphyeonjae;2011. p. 1–319.21. Pett MA, Lackey NR, Sullivan JJ. Making sense of factor analysis: The use of factor analysis for instrument development in health care research. California: Sage publication;2003. p. 1–348.22. Kim SK, Kim YK, Kim HR, Park CS, Shon SK, Choi YJ, et al. The 2012 national survey on fertility, family health and welfare in Korea. Research report. Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2012. Report No.:. p. 2012–54.23. Netsu Y. Breast management. 2nd ed.Kim YR. translator. Seoul: Knowledge and creative;2007. 25.24. Streiner DL. Starting at the beginning: An introduction to coefficient alpha and internal consistency. Journal of Personality Assessment. 2003; 80(1):99–103.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on the Development of the Korean Breastfeeding Empowerment Scale
- Concept Analysis of Effective Breastfeeding
- A Survey on the Feeding Practices of Women for the Development of a Breastfeeding Education Program: Breastfeeding Knowledge and Breastfeeding Rates
- A Study on the Relationship between Breastfeeding Empowerment and Self-confidence in the Maternal Role of Breastfeeding Mothers
- A Study about Breastfeeding Knowledge, Attitude and Problem of Breastfeeding in Early Postpartum Period and Breastfeeding Practice