J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2016 Dec;21(4):238-242. 10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.4.238.
Nodular Melanoma on the Tip of the Thumb
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic Surgery, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Chungnam, Korea. jaheagu@gmail.com
- KMID: 2364216
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.4.238
Abstract
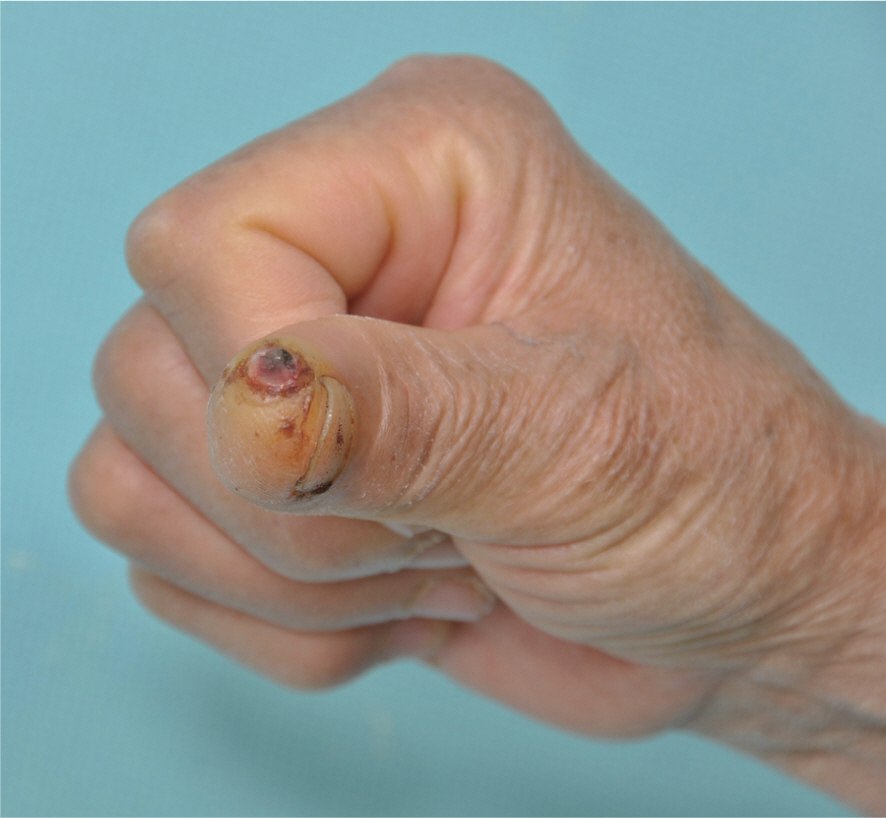
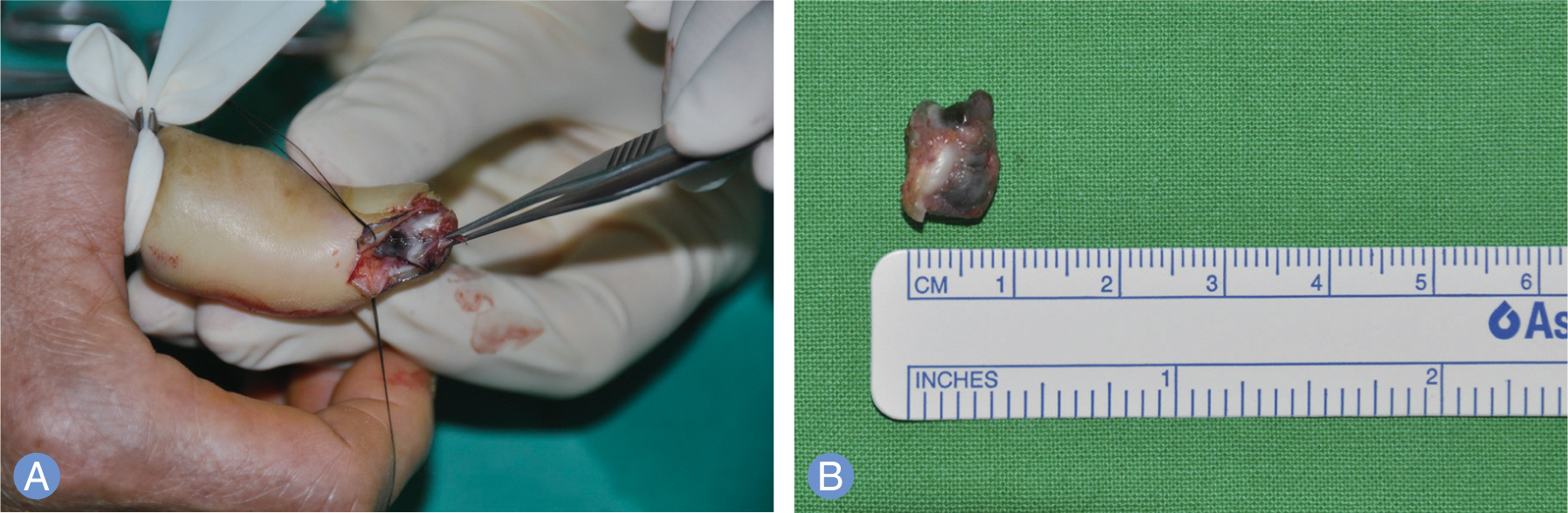
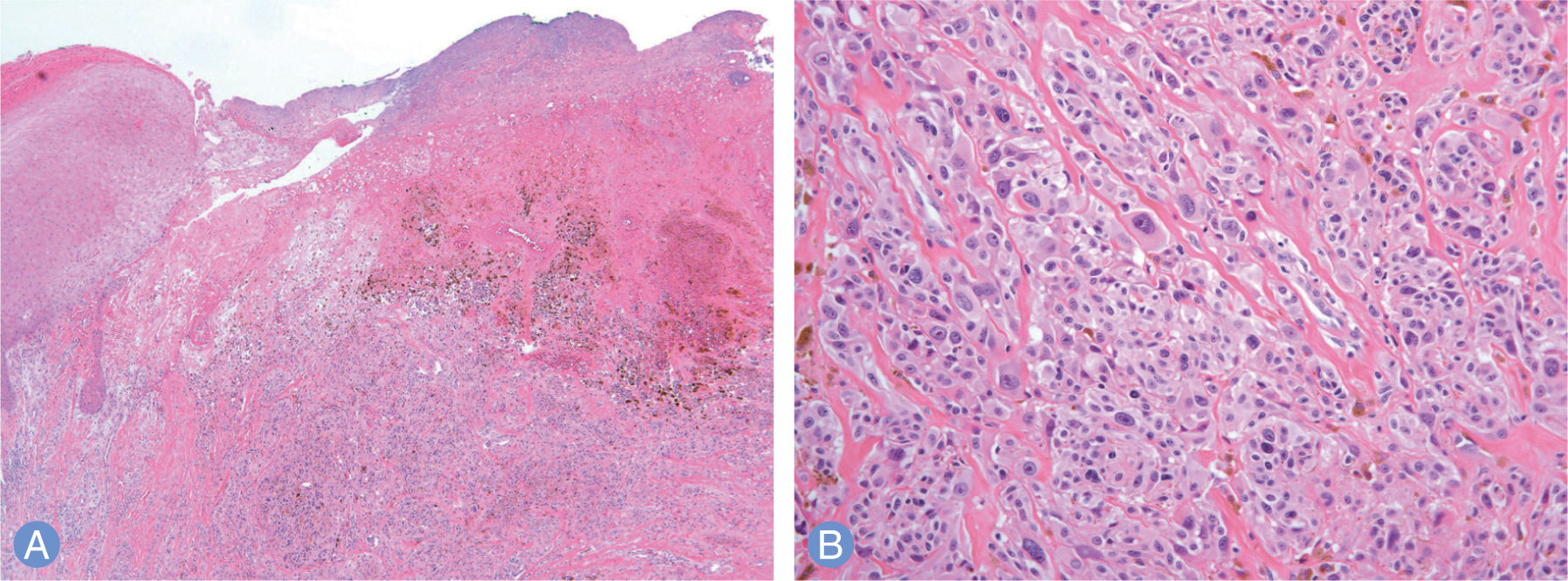
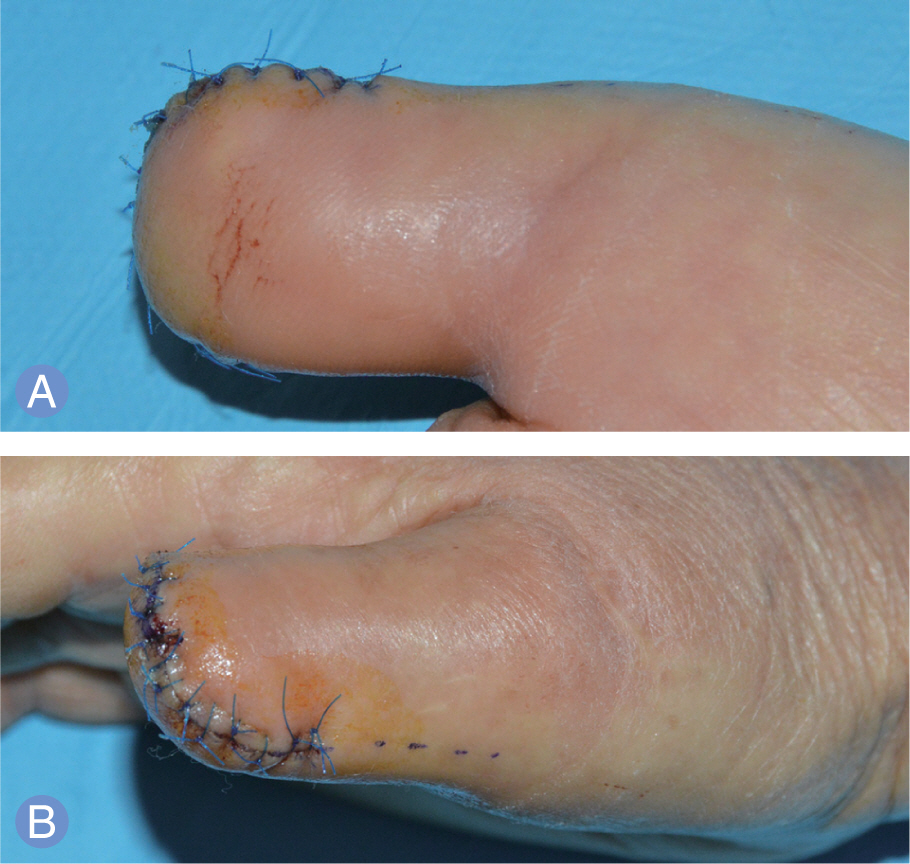
- Nodular type malignant melanoma is uncommon in fingers. In previous publications, treatment, diagnosis and case reports of subungal melanoma is often, however fingertip lesion was not focused. A 64-year-old woman who had a non-healing red and dark colored nodular mass with ulceration over the finger tip in the right thumb visited our clinics. Biopsy results was malignant melanoma then we performed amputation surgery of distal phalanx. Lymph node biopsy and resection margin was negative for melanoma. Chemotherapy was administered immediately. After 5 months, pulmonary nodular lesion was found and diagnosed as metastatic malignant melanoma by the wedge resection surgery. The patient is treated for additional chemotherapy consistently and disease free for 2 years. Nodular type melanoma of the finger is uncommon and it could be presented as ulceration and amelanotic nodular mass. Therefore we recommend biopsy to diagnose correctly if there are chronic non healing lesions on the fingers.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yang Z, Xie L, Huang Y, et al. Clinical features of malignant melanoma of the finger and therapeutic efficacies of different treatments. Oncol Lett. 2011; 2:811–5.
Article2. Situm M, Buljan M, Kolic M, Vucic M. Melanoma: clinical, dermatoscopical, and histopathological morphological characteristics. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2014; 22:1–12.3. Furukawa H, Tsutsumida A, Yamamoto Y, et al. Melanoma of thumb: retrospective study for amputation levels, surgical margin and reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007; 60:24–31.
Article4. Kato T, Suetake T, Sugiyama Y, Tabata N, Tagami H. Epidemiology and prognosis of subungual melanoma in 34 Japanese patients. Br J Dermatol. 1996; 134:383–7.
Article5. Kuchelmeister C, Schaumburg-Lever G, Garbe C. Acral cutaneous melanoma in caucasians: clinical features, histopathology and prognosis in 112 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2000; 143:275–80.
Article6. Kozlow JH, Rees RS. Surgical management of primary disease. Clin Plast Surg. 2010; 37:65–71.
Article