J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Apr;31(4):502-509. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.502.
Bone Scintigraphy in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Is There Additional Value of Bone Scintigraphy with Blood Pool Phase over Conventional Bone Scintigraphy?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. yychoi@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine and the Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363687
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.502
Abstract
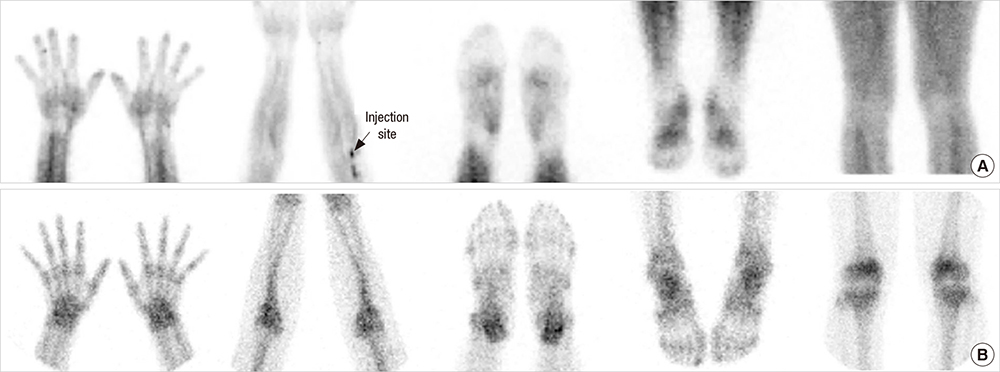
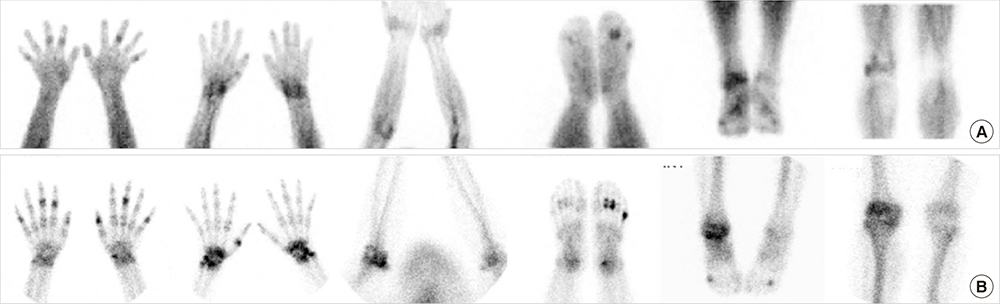
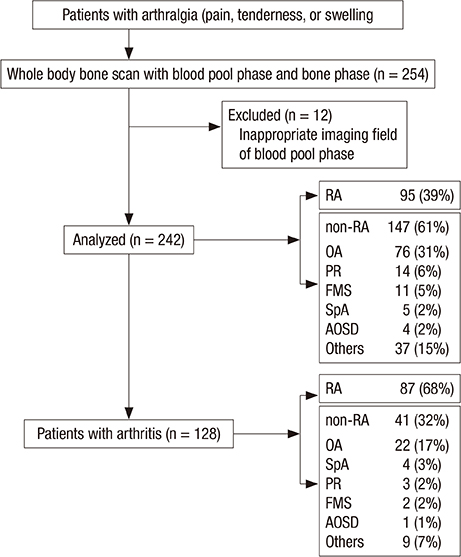
- We aimed to investigate the value of bone scintigraphy with additional blood pool phase (BSBP), compared with conventional bone scintigraphy (CBS), in the assessment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A total of 242 patients (43 males, 199 females; 14-78 years) with arthralgia, and underwent BSBP were retrospectively analyzed. On the first physical examination, active arthritis was found in 128 of the 242 patients. Clinical diagnosis was made by a rheumatologist on the basis of the 1987 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria, which are considered to be the gold standard. The diagnostic performances and prognostic value of BSBP and CBS were analyzed in the total patients with arthralgia and in the patients with arthritis. The sensitivity of BSBP (84.2%, 80/95) were significantly higher than that of CBS (74.8%, 72/95) in the patients with arthralgia (P = 0.039). When BSBP was interpreted with the results of elevated/positive anti-CCP antibody, its accuracy over CBS also became significantly higher (86.0%, 208/242 vs. 83.1%, 201/242 respectively, P = 0.021). The diagnostic odds ratio of BSBP positivity was higher than CBS positivity in the patients with arthralgia (26.0, 12.9-52.4 vs. 21.1, 10.8-41.3) and with arthritis (12.0, 4.9-29.4 vs. 10.0, 4.2-23.4). Both BSBP and CBS appear to provide acceptable accuracy and comparable diagnostic performance for diagnosis of RA. However, in the patients with arthralgia, BSBP was found to be more sensitive than CBS and more accurate when interpreted with the result of anti-CCP antibody. This could help physicians diagnose RA in daily clinical practice.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Arthralgia/complications
Arthritis, Rheumatoid/complications/*diagnosis
Autoantibodies/blood
Bone and Bones/diagnostic imaging
Female
*Gated Blood-Pool Imaging
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Odds Ratio
Peptides, Cyclic/immunology
Positron-Emission Tomography
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Sensitivity and Specificity
Technetium/chemistry
*Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Young Adult
Autoantibodies
Peptides, Cyclic
Technetium
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Nuclear Medicine Imaging in Rheumatic Diseases
Yun Young Choi, Ji Young Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2017;24(1):4-13. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.4.Bone scintigraphy in patients with pain
Seung Hyeon Shin, Seong Jang Kim
Korean J Pain. 2017;30(3):165-175. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2017.30.3.165.
Reference
-
1. Grassi W, De Angelis R, Lamanna G, Cervini C. The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Radiol. 1998; 27:Suppl 1. S18–24.2. Ziff M. General mechanisms of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Schweiz Akad Med Wiss. 1979; 35:275–281.3. Kim JY, Cho SK, Han M, Choi YY, Bae SC, Sung YK. The role of bone scintigraphy in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis according to the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:204–209.4. Papathanassiou D, Bruna-Muraille C, Jouannaud C, Gagneux-Lemoussu L, Eschard JP, Liehn JC. Single-photon emission computed tomography combined with computed tomography (SPECT/CT) in bone diseases. Joint Bone Spine. 2009; 76:474–480.5. Berná L, Torres G, Diez C, Estorch M, Martínez-Duncker D, Carrió I. Technetium-99m human polyclonal immunoglobulin G studies and conventional bone scans to detect active joint inflammation in chronic rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Nucl Med. 1992; 19:173–176.6. de Bois MH, Arndt JW, van der Velde EA, Pauwels EK, Breedveld FC. Joint scintigraphy for quantification of synovitis with 99mTc-labelled human immunoglobulin G compared to late phase scintigraphy with 99mTc-labelled diphosphonate. Br J Rheumatol. 1994; 33:67–73.7. Gerasimou G, Moralidis E, Papanastasiou E, Liaros G, Aggelopoulou T, Triantafyllidou E, Lytras N, Settas L, Gotzamani-Psarrakou A. Radionuclide imaging with human polyclonal immunoglobulin (Tc-HIG) and bone scan in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and serum-negative polyarthritis. Hippokratia. 2011; 15:37–42.8. Masaoka S. Evaluation of arterial obstructive leg and foot disease by three-phase bone scintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med. 2001; 15:281–287.9. Stumpe KD, Nötzli HP, Zanetti M, Kamel EM, Hany TF, Görres GW, von Schulthess GK, Hodler J. FDG PET for differentiation of infection and aseptic loosening in total hip replacements: comparison with conventional radiography and three-phase bone scintigraphy. Radiology. 2004; 231:333–341.10. Hoskinson JJ, Daniel GB, Patton CS. Indium-111-chloride and three-phase bone scintigraphy: a comparison for imaging experimental osteomyelitis. J Nucl Med. 1991; 32:67–75.11. Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31:315–324.12. Zeidler H. The need to better classify and diagnose early and very early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2012; 39:212–217.13. Nishimura K, Sugiyama D, Kogata Y, Tsuji G, Nakazawa T, Kawano S, Saigo K, Morinobu A, Koshiba M, Kuntz KM, et al. Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2007; 146:797–808.14. Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, de Jong BA, Berglin E, Hallmans G, Wadell G, Stenlund H, Sundin U, van Venrooij WJ. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48:2741–2749.15. Aggarwal R, Liao K, Nair R, Ringold S, Costenbader KH. Anti-citrullinated peptide antibody assays and their role in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 61:1472–1483.16. Goldring MB, Otero M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011; 23:471–478.17. Hayashi D, Roemer FW, Katur A, Felson DT, Yang SO, Alomran F, Guermazi A. Imaging of synovitis in osteoarthritis: current status and outlook. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 41:116–130.18. Sellam J, Berenbaum F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010; 6:625–635.19. Zochling J, Smith EU. Seronegative spondyloarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010; 24:747–756.20. Ozgul A, Yasar E, Arslan N, Balaban B, Taskaynatan MA, Tezel K, Baklaci K, Ozgüven MA, Kalyon TA. The comparison of ultrasonographic and scintigraphic findings of early arthritis in revealing rheumatoid arthritis according to criteria of American College of Rheumatology. Rheumatol Int. 2009; 29:765–768.21. Thairu N, Kiriakidis S, Dawson P, Paleolog E. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in arthritis in 2011: learning the lessons of the colorectal cancer experience. Angiogenesis. 2011; 14:223–234.22. Kong X, Zhang Y, Liu C, Guo W, Li X, Su X, Wan H, Sun Y, Lin N. Anti-angiogenic effect of triptolide in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting angiogenic cascade. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e77513.23. Klett R, Grau K, Puille M, Matter HP, Lange U, Steiner D, Bauer R. Comparison of HIG scintigraphy and bloodpool scintigraphy using HDP in arthritic joint disease. Nucl Med (Stuttg). 2000; 39:33–37.24. van der Lubbe PA, Arndt JW, Calame W, Ferreira TC, Pauwels EK, Breedveld FC. Measurement of synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis with technetium 99m labelled human polyclonal immunoglobulin G. Eur J Nucl Med. 1991; 18:119–123.25. Bøyesen P, Haavardsholm EA, Ostergaard M, van der Heijde D, Sesseng S, Kvien TK. MRI in early rheumatoid arthritis: synovitis and bone marrow oedema are independent predictors of subsequent radiographic progression. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:428–433.26. Haavardsholm EA, Bøyesen P, Østergaard M, Schildvold A, Kvien TK. Magnetic resonance imaging findings in 84 patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: bone marrow oedema predicts erosive progression. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008; 67:794–800.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Usefulness of Uptake Ratio of Three Phase Bone Scintigraphy in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome after a Stroke
- Implications of Three-Phase Bone Scintigraphy for the Diagnosis of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
- Applying Pix2pix to Translate Hyperemia in Blood Pool Image into Corresponding Increased Bone Uptake in Delayed Image in Three‑Phase Bone Scintigraphy
- Acute Rhabdomyolysis : Importance of MRI and Bone Scintigraphy
- Uterine Doughnut by Intrauterine Device-induced Photon Attenuation on Three-Phase Bone Scintigraphy: Artifact