Korean J Radiol.
2016 Apr;17(2):245-254. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.2.245.
Sonographic Findings of Common Musculoskeletal Diseases in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 02447, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul 02447, Korea. francesca@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul 05278, Korea.
- KMID: 2360210
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.2.245
Abstract
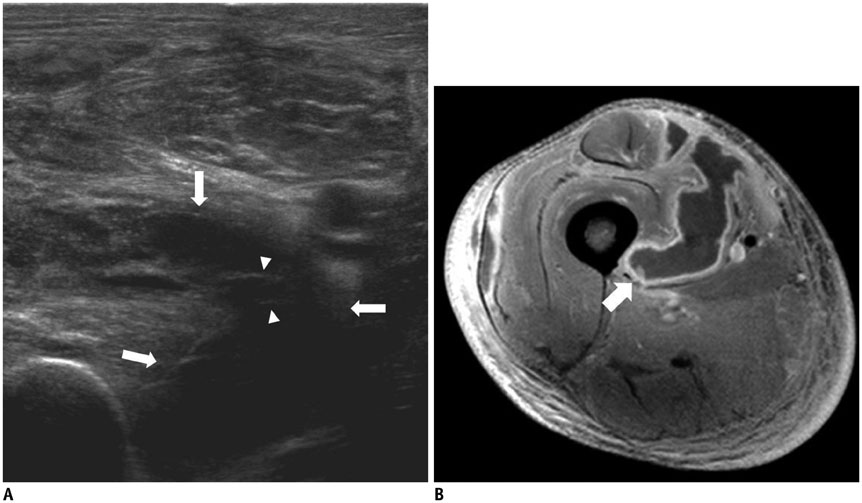
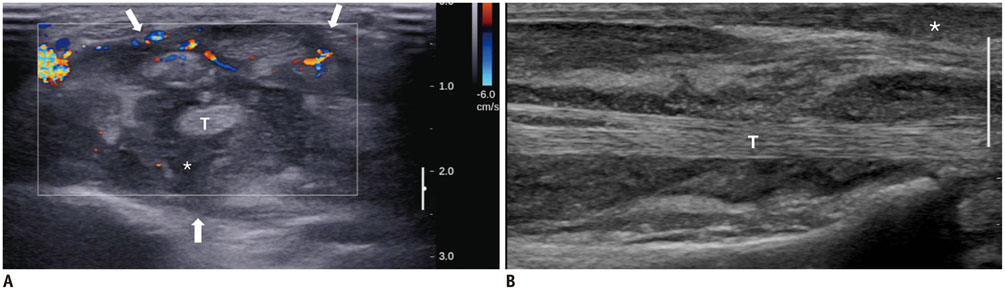
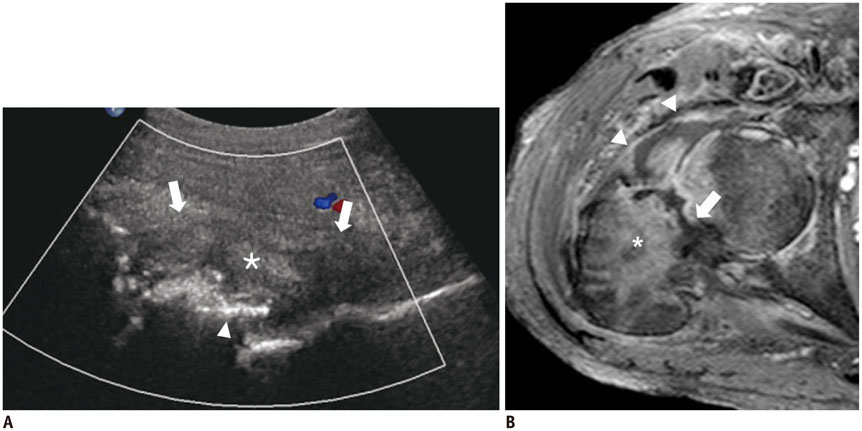
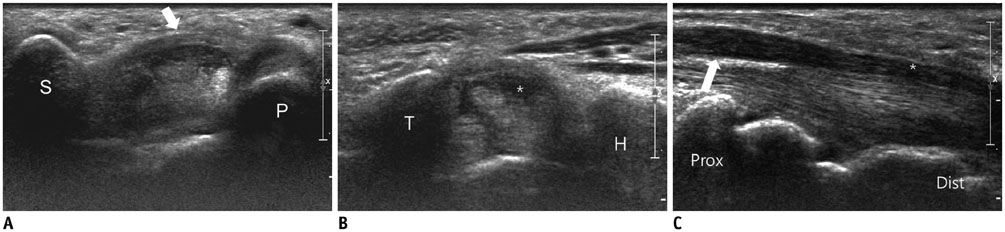
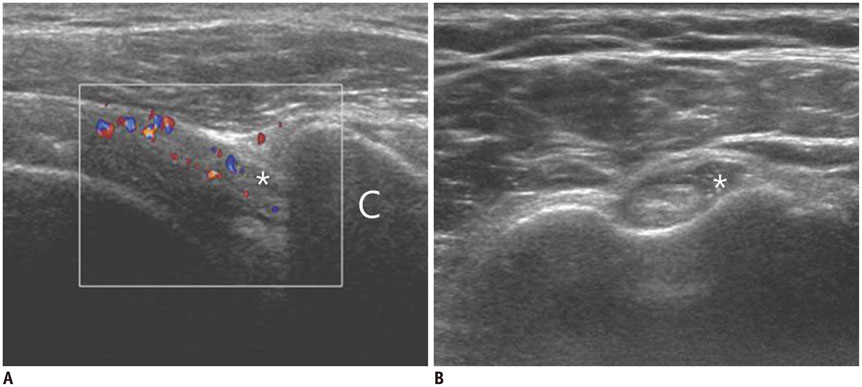
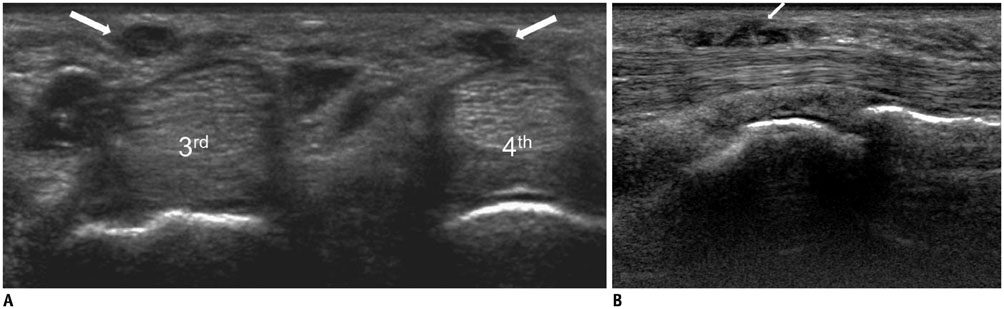
- Diabetes mellitus (DM) can accompany many musculoskeletal (MSK) diseases. It is difficult to distinguish the DM-related MSK diseases based on clinical symptoms alone. Sonography is frequently used as a first imaging study for these MSK symptoms and is helpful to differentiate the various DM-related MSK diseases. This pictorial essay focuses on sonographic findings of various MSK diseases that can occur in diabetic patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Cellulitis/ultrasonography
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/*complications
Diabetic Neuropathies/ultrasonography
Female
Humans
Male
Musculoskeletal Diseases/complications/*diagnosis/ultrasonography
Pyomyositis/microbiology/ultrasonography
Tenosynovitis/microbiology/ultrasonography
Vascular Diseases/ultrasonography
Figure
Reference
-
1. Joshi N, Caputo GM, Weitekamp MR, Karchmer AW. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1906–1912.2. Casqueiro J, Casqueiro J, Alves C. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus: a review of pathogenesis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 16:Suppl 1. S27–S36.3. Chau CL, Griffith JF. Musculoskeletal infections: ultrasound appearances. Clin Radiol. 2005; 60:149–159.4. Turecki MB, Taljanovic MS, Stubbs AY, Graham AR, Holden DA, Hunter TB, et al. Imaging of musculoskeletal soft tissue infections. Skeletal Radiol. 2010; 39:957–971.5. Patel SR, Olenginski TP, Perruquet JL, Harrington TM. Pyomyositis: clinical features and predisposing conditions. J Rheumatol. 1997; 24:1734–1738.6. Bosshardt TL, Henderson VJ, Organ CH Jr. Necrotizing soft-tissue infections. Arch Surg. 1996; 131:846–852. discussion 852-8547. Wongworawat MD, Holtom P, Learch TJ, Fedenko A, Stevanovic MV. A prolonged case of Mycobacterium marinum flexor tenosynovitis: radiographic and histological correlation, and review of the literature. Skeletal Radiol. 2003; 32:542–545.8. Bellapianta JM, Ljungquist K, Tobin E, Uhl R. Necrotizing fasciitis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009; 17:174–182.9. Bureau NJ, Ali SS, Chhem RK, Cardinal E. Ultrasound of musculoskeletal infections. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 1998; 2:299–306.10. Andras A, Ferket B. Screening for peripheral arterial disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; 4:CD010835.11. Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA. 2002; 287:2570–2581.12. Gibbons GW, Shaw PM. Diabetic vascular disease: characteristics of vascular disease unique to the diabetic patient. Semin Vasc Surg. 2012; 25:89–92.13. Pectasides M, Kalva SP. Diabetes revealed: multisystem danger. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:274–286.14. Schäberle W. Ultrasonography in Vascular Diagnosis: A Therapy-Oriented Textbook and Atlas. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;2011. p. 258.15. Al-Aly Z. Medial vascular calcification in diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: the role of inflammation. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2007; 7:1–6.16. David Smith C, Gavin Bilmen J, Iqbal S, Robey S, Pereira M. Medial artery calcification as an indicator of diabetic peripheral vascular disease. Foot Ankle Int. 2008; 29:185–190.17. Liu KH, Chu WC, Kong AP, Choi Ko GT, Ma RC, Chan JW, et al. US assessment of medial arterial calcification: a sensitive marker of diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular complications. Radiology. 2012; 265:294–302.18. Puttemans T, Nemery C. Diabetes: the use of color Doppler sonography for the assessment of vascular complications. Eur J Ultrasound. 1998; 7:15–22.19. Thakkar RS, Del Grande F, Thawait GK, Andreisek G, Carrino JA, Chhabra A. Spectrum of high-resolution MRI findings in diabetic neuropathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 199:407–412.20. Tan PL, Teh J. MRI of the diabetic foot: differentiation of infection from neuropathic change. Br J Radiol. 2007; 80:939–948.21. Jones EA, Manaster BJ, May DA, Disler DG. Neuropathic osteoarthropathy: diagnostic dilemmas and differential diagnosis. Radiographics. 2000; 20 Spec No:S279–S293.22. Baker JC, Demertzis JL, Rhodes NG, Wessell DE, Rubin DA. Diabetic musculoskeletal complications and their imaging mimics. Radiographics. 2012; 32:1959–1974.23. Bianchi S, Baert AL, Abdelwahab IF, Derchi LE, Martinoli C, Rizzatto G, et al. Ultrasound of the musculoskeletal system. Heidelberg: Springer;2007. p. 862.24. Schweitzer ME, Daffner RH, Weissman BN, Bennett DL, Blebea JS, Jacobson JA, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria on suspected osteomyelitis in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Radiol. 2008; 5:881–886.25. Fitzgibbons PG, Weiss AP. Hand manifestations of diabetes mellitus. J Hand Surg Am. 2008; 33:771–775.26. Resnick D, Kransdorf M. Bone and Joint Imaging. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2005. p. 625–629.27. Thomsen NO, Cederlund R, Rosén I, Björk J, Dahlin LB. Clinical outcomes of surgical release among diabetic patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: prospective follow-up with matched controls. J Hand Surg Am. 2009; 34:1177–1187.28. Mallouhi A, Pülzl P, Trieb T, Piza H, Bodner G. Predictors of carpal tunnel syndrome: accuracy of gray-scale and color Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 186:1240–1245.29. Huang YP, Fann CY, Chiu YH, Yen MF, Chen LS, Chen HH, et al. Association of diabetes mellitus with the risk of developing adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: a longitudinal population-based followup study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013; 65:1197–1202.30. Jacobson JA. Musculoskeletal ultrasound: focused impact on MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:619–627.31. Papatheodorou A, Ellinas P, Takis F, Tsanis A, Maris I, Batakis N. US of the shoulder: rotator cuff and non-rotator cuff disorders. Radiographics. 2006; 26:e23.32. Murphey MD, Ruble CM, Tyszko SM, Zbojniewicz AM, Potter BK, Miettinen M. From the archives of the AFIP: musculoskeletal fibromatoses: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2009; 29:2143–2173.33. Khashan M, Smitham PJ, Khan WS, Goddard NJ. Dupuytren’s disease: review of the current literature. Open Orthop J. 2011; 5:Suppl 2. 283–288.34. Créteur V, Madani A, Gosset N. [Ultrasound imaging of Dupuytren’s contracture]. J Radiol. 2010; 91:687–691.35. Ryzewicz M, Wolf JM. Trigger digits: principles, management, and complications. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31:135–146.36. Kim HR, Lee SH. Ultrasonographic assessment of clinically diagnosed trigger fingers. Rheumatol Int. 2010; 30:1455–1458.37. Delaney-Sathy LO, Fessell DP, Jacobson JA, Hayes CW. Sonography of diabetic muscle infarction with MR imaging, CT, and pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 174:165–169.38. Trujillo-Santos AJ. Diabetic muscle infarction: an underdiagnosed complication of long-standing diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:211–215.39. Parmar MS. Diabetic muscle infarction. BMJ. 2009; 338:b2271.