Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Aug;40(4):702-709. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.4.702.
Shoulder Disease Patterns of the Wheelchair Athletes of Table-Tennis and Archery: A Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. braddom@nate.com
- KMID: 2356656
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.4.702
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the shoulder disease patterns for the table-tennis (TT) and archery (AR) wheelchair athletes via ultrasonographic evaluations.
METHODS
A total of 35 wheelchair athletes were enrolled, made up of groups of TT (n=19) and AR (n=16) athletes. They were all paraplegic patients and were investigated for their wheelchair usage duration, careers as sports players, weekly training times, the Wheelchair User's Shoulder Pain Index (WUSPI) scores and ultrasonographic evaluation. Shoulders were divided into playing arm of TT, non-playing arm of TT, bow-arm of AR, and draw arm of AR athletes. Shoulder diseases were classified into five entities of subscapularis tendinopathy, supraspinatus tendinopathy, infraspinatus tendinopathy, biceps long head tendinopathy, and subacromial-subdeltoid bursitis. The pattern of shoulder diseases were compared between the two groups using the Mann-Whitney and the chi-square tests
RESULTS
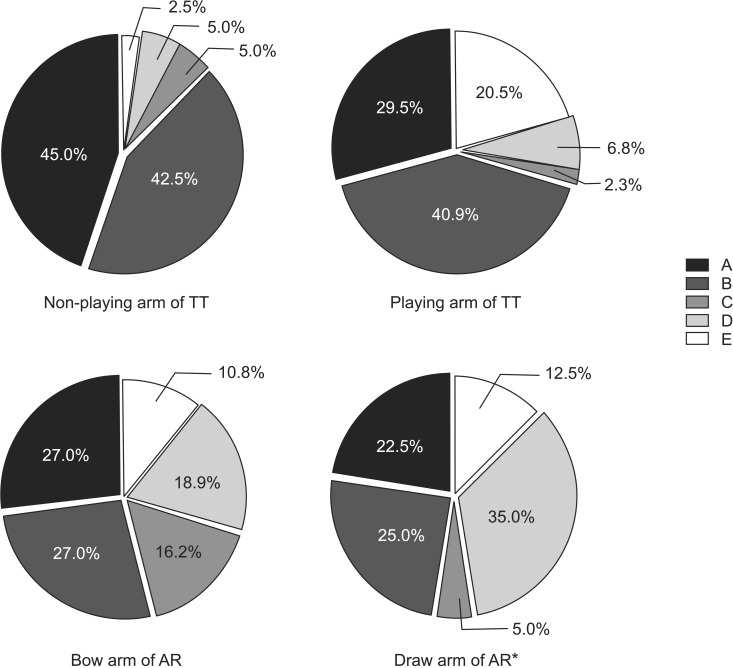
WSUPI did not significantly correlate with age, wheelchair usage duration, career as players or weekly training times for all the wheelchair athletes. For the non-playing arm of TT athletes, there was a high percentage of subscapularis (45.5%) and supraspinatus (40.9%) tendinopathy. The percentage of subacromial-subdeltoid bursitis showed a tendency to be present in the playing arm of TT athletes (20.0%) compared with their non-playing arm (4.5%), even though this was not statistically significant. Biceps long head tendinopathy was the most common disease of the shoulder in the draw arm of AR athletes, and the difference was significant when compared to the non-playing arm of TT athletes (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
There was a high percentage of subscapularis and supraspinatus tendinopathy cases for the non-playing arm of TT wheelchair athletes, and a high percentage of biceps long head tendinopathy for the draw arm for the AR wheelchair athletes. Consideration of the biomechanical properties of each sport may be needed to tailor specific training for wheelchair athletes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korean Statistical Information Service [Internet]. Daejeon: Korean Statistical Information Service;c2015. cited 2016 Jul 22. Available from: http://kosis.kr/.2. McCasland LD, Budiman-Mak E, Weaver FM, Adams E, Miskevics S. Shoulder pain in the traumatically injured spinal cord patient: evaluation of risk factors and function. J Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 12:179–186. PMID: 16891921.3. Akbar M, Brunner M, Ewerbeck V, Wiedenhofer B, Grieser T, Bruckner T, et al. Do overhead sports increase risk for rotator cuff tears in wheelchair users? Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015; 96:484–488. PMID: 25449196.
Article4. Korea Paralympic Committee [Internet]. Seoul: Korea Paralympic Committee;c2015. cited 2016 Jul 22. Available from: http://www.koreanpc.kr/.5. Iino Y, Kojima T. Kinetics of the upper limb during table tennis topspin forehands in advanced and intermediate players. Sports Biomech. 2011; 10:361–377. PMID: 22303787.
Article6. Pieper HG, Quack G, Krahl H. Impingement of the rotator cuff in athletes caused by instability of the shoulder joint. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 1993; 1:97–99. PMID: 8536016.
Article7. Park JY, Oh KS, Yoo HY, Lee JG. Case report: Thoracic outlet syndrome in an elite archer in full-draw position. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471:3056–3060. PMID: 23430722.
Article8. Naraen A, Giannikas KA, Livesley PJ. Overuse epiphyseal injury of the coracoid process as a result of archery. Int J Sports Med. 1999; 20:53–55. PMID: 10090463.
Article9. Lin JJ, Hung CJ, Yang CC, Chen HY, Chou FC, Lu TW. Activation and tremor of the shoulder muscles to the demands of an archery task. J Sports Sci. 2010; 28:415–421. PMID: 20432134.
Article10. Webborn N, Van de Vliet P. Paralympic medicine. Lancet. 2012; 380:65–71. PMID: 22770458.
Article11. Webborn N, Emery C. Descriptive epidemiology of Paralympic sports injuries. PM R. 2014; 6(8 Suppl):S18–S22. PMID: 25134748.
Article12. van der Woude LH, Bouten C, Veeger HE, Gwinn T. Aerobic work capacity in elite wheelchair athletes: a cross-sectional analysis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 81:261–271. PMID: 11953543.13. Brose SW, Boninger ML, Fullerton B, McCann T, Collinger JL, Impink BG, et al. Shoulder ultrasound abnormalities, physical examination findings, and pain in manual wheelchair users with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008; 89:2086–2093. PMID: 18996236.
Article14. Lim KB, Yoo J, Lee HJ, Lee JH, Kwon YG. Evaluation of pain and ultrasonography on shoulder in poliomyelitis wheelchair basketball players. Korean J Sports Med. 2014; 32:20–26.
Article15. Kondric M, Matkovic BR, Furjan-Mandic G, Hadzic V, Dervisevic E. Injuries in racket sports among Slovenian players. Coll Antropol. 2011; 35:413–417. PMID: 21755712.16. Akbar M, Balean G, Brunner M, Seyler TM, Bruckner T, Munzinger J, et al. Prevalence of rotator cuff tear in paraplegic patients compared with controls. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:23–30. PMID: 20048092.
Article17. Fischer CA, Weber MA, Neubecker C, Bruckner T, Tanner M, Zeifang F. Ultrasound vs. MRI in the assessment of rotator cuff structure prior to shoulder arthroplasty. J Orthop. 2015; 12:23–30. PMID: 25829757.
Article18. Bae H. Sports for the disabled: history and the classification. Hanyang Med Rev. 2009; 29:94–106.19. Korea Para Table Tennis Association [Internet]. Seoul: Korea Para Table Tennis Association;c2015. cited 2016 Jul 22. Available from: http://tt.kosad.or.kr/.20. Korea Disabled Archery Association [Internet]. Seoul: Korea Disabled Archery Association;c2015. cited 2016 Jul 22. Available from: http://archery.kosad.kr/.21. Curtis KA, Roach KE, Applegate EB, Amar T, Benbow CS, Genecco TD, et al. Reliability and validity of the Wheelchair User's Shoulder Pain Index (WUSPI). Paraplegia. 1995; 33:595–601. PMID: 8848314.
Article22. Corazza A, Orlandi D, Fabbro E, Ferrero G, Messina C, Sartoris R, et al. Dynamic high-resolution ultrasound of the shoulder: how we do it. Eur J Radiol. 2015; 84:266–277. PMID: 25466650.
Article23. Rutten MJ, Jager GJ, Blickman JG. From the RSNA refresher courses: US of the rotator cuff: pitfalls, limitations, and artifacts. Radiographics. 2006; 26:589–604. PMID: 16549619.24. Kerr J, Borbas P, Meyer DC, Gerber C, Buitrago Tellez C, Wieser K. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair in the weight-bearing shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015; 24:1894–1899. PMID: 26163283.
Article25. Shinohara H, Urabe Y, Maeda N, Xie D, Sasadai J, Fujii E. Does shoulder impingement syndrome affect the shoulder kinematics and associated muscle activity in archers? J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2014; 54:772–779. PMID: 25350034.26. Kim HB, Kim SH, So WY. The relative importance of performance factors in Korean archery. J Strength Cond Res. 2015; 29:1211–1219. PMID: 25226316.
Article27. Wylie EJ, Chakera TM. Degenerative joint abnormalities in patients with paraplegia of duration greater than 20 years. Paraplegia. 1988; 26:101–106. PMID: 3412779.
Article28. Fullerton HD, Borckardt JJ, Alfano AP. Shoulder pain: a comparison of wheelchair athletes and nonathletic wheelchair users. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2003; 35:1958–1961. PMID: 14652488.
Article29. Cooper RA, De Luigi AJ. Adaptive sports technology and biomechanics: wheelchairs. PM R. 2014; 6(8 Suppl):S31–S39. PMID: 25134750.
Article30. Edmonds EW, Dengerink DD. Common conditions in the overhead athlete. Am Fam Physician. 2014; 89:537–541. PMID: 24695599.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Study on the Injury and Rehabilitation of Racket Athletes with Disabilities
- The Characteristics of Shoulder Muscles in Archery Athletes
- Survey and Sonographic Evaluation of Shoulder Musculoskeletal Pain in Korean Junior Elite Tennis Players: A Pilot Study
- Effects of Lower Trapezius Strengthening Exercise on Shoulder Pain, Function and Archery Performance in Elite Archers
- Microinstability of the Shoulder