J Korean Soc Transplant.
2016 Sep;30(3):133-137. 10.4285/jkstn.2016.30.3.133.
Asymptomatic Common Iliac Artery Stenosis as a Cause of Renal Allograft Dysfunction and Uncontrolled Hypertension
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea. amorfati00@gmail.com
- KMID: 2354637
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2016.30.3.133
Abstract
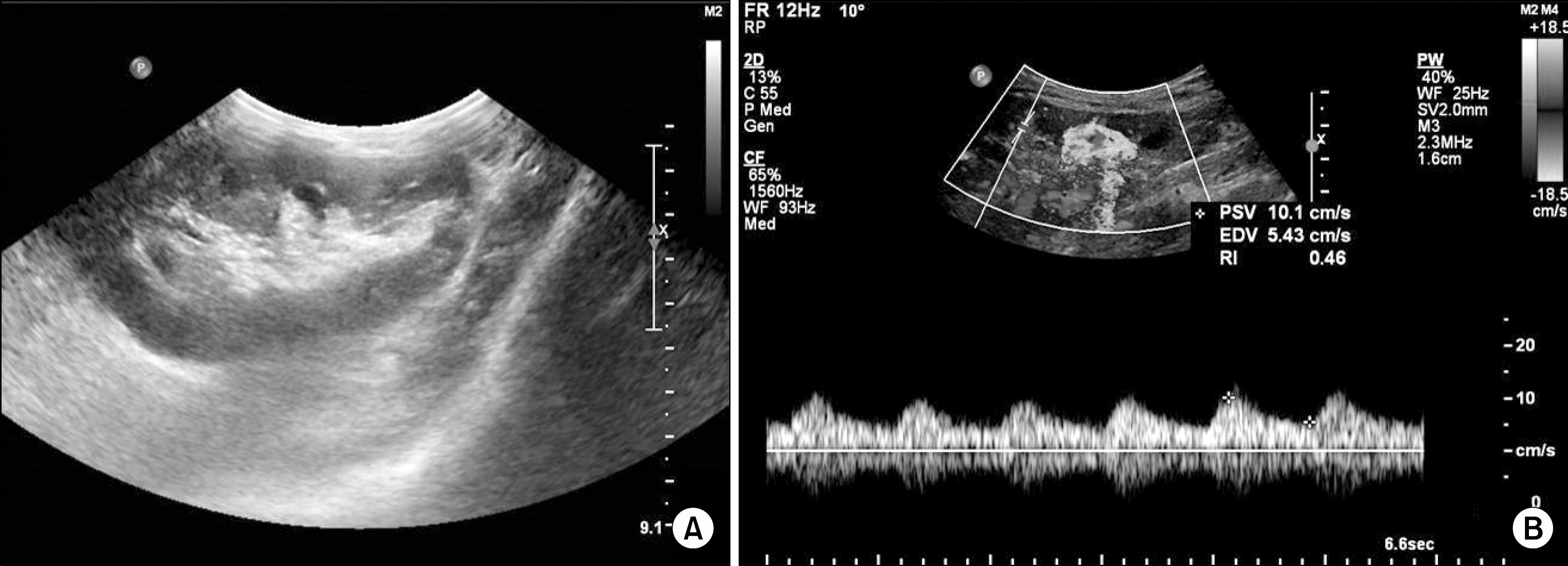
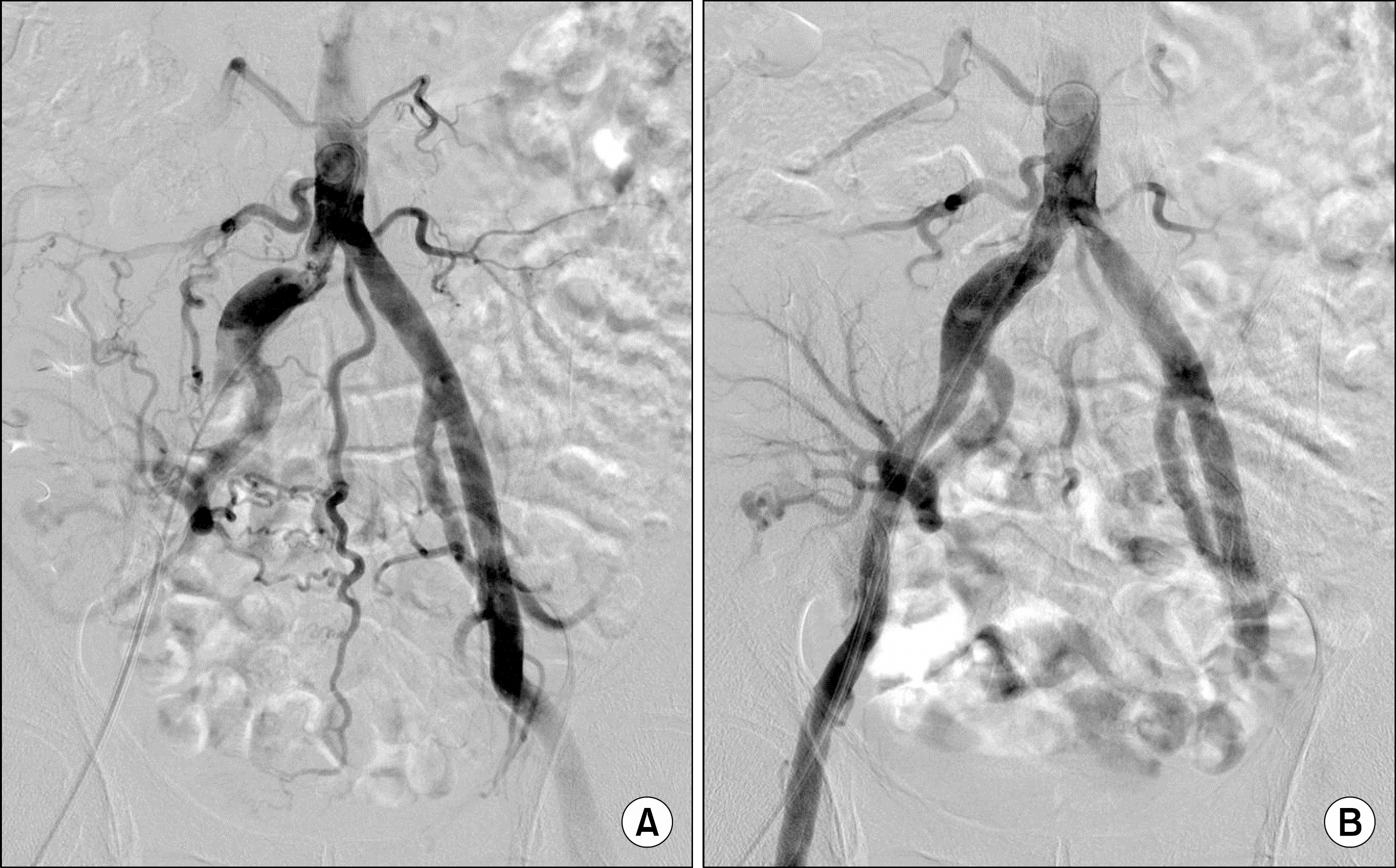
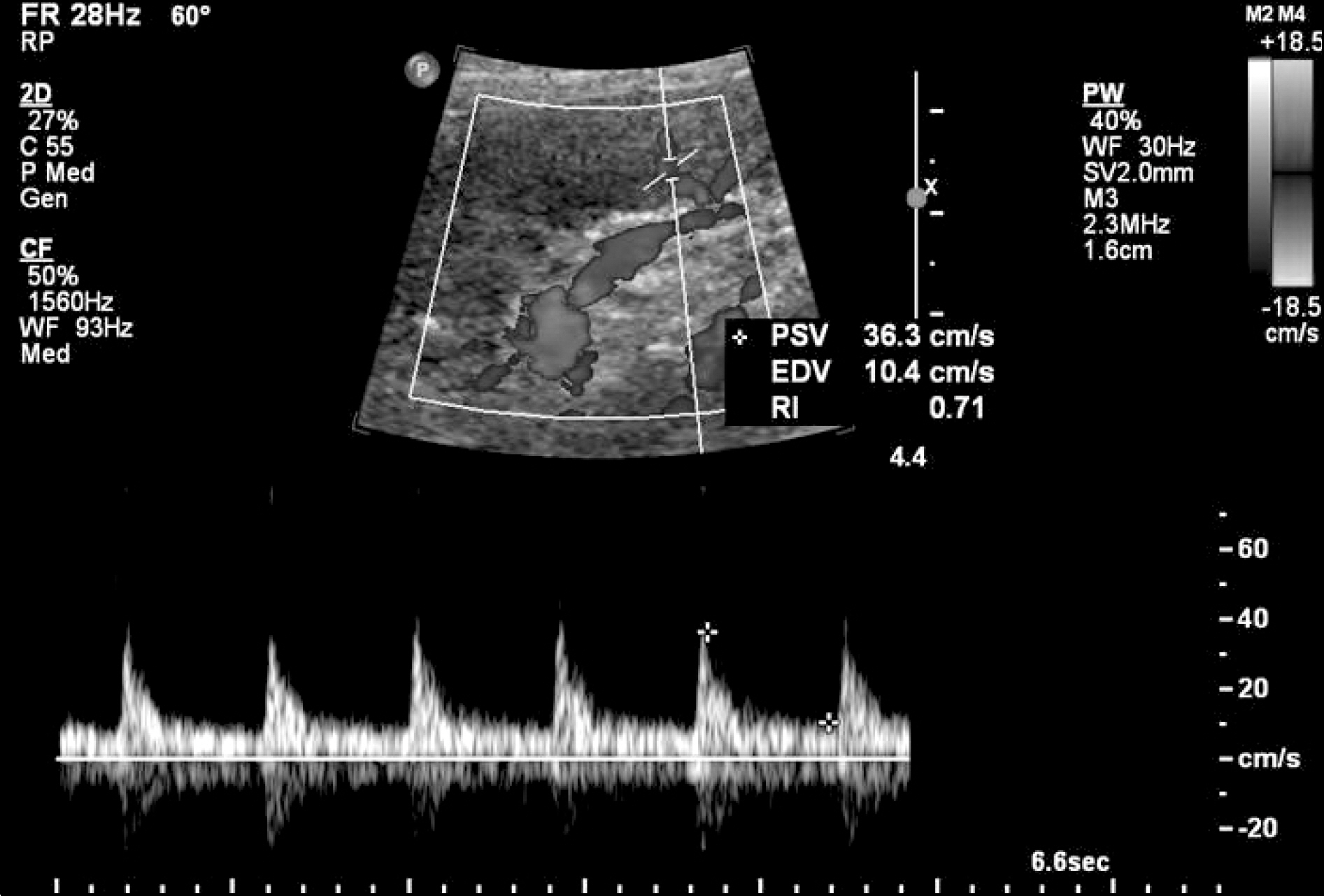
- Occlusive disease of the iliac segment, proximal to the transplant artery (prox-TRAS), in kidney transplant recipients is a rare complication. Prox-TRAS, located in the common iliac artery, is extremely rare in these patients. Herein, we present an interesting case of a common iliac artery stenosis that manifested as decreased allograft function and uncontrolled blood pressure without other typical clinical symptoms. The patient was successfully treated with percutaneous luminal angioplasty and stent insertion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Lacombe M. Arterial stenosis complicating renal allotransplantation in man: a study of 38 cases. Ann Surg. 1975. 181:283–8.2). Merkus JW., van Asten WN., Hoitsma AJ., Buskens FG., Koene RA., Skotnicki SH. Iliac artery stenosis after kidney transplantation. Acta Chir Belg. 1993. 93:242–8.3). Aslam S., Salifu MO., Ghali H., Markell MS., Friedman EA. Common iliac artery stenosis presenting as renal allograft dysfunction in two diabetic recipients. Transplantation. 2001. 71:814–7.
Article4). Weigele JB. Iliac artery stenosis causing renal allograft-mediated hypertension: angiographic diagnosis and treatment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991. 157:513–5.
Article5). Polytimi L., Sofia G., Paris P. Close to transplant renal artery stenosis and percutaneous transluminal treatment. J Transplant. 2011. 2011:219109.
Article6). Becker BN., Odorico JS., Becker YT., Leverson G., McDermott JC., Grist T, et al. Peripheral vascular disease and renal transplant artery stenosis: a reappraisal of transplant renovascular disease. Clin Transplant. 1999. 13:349–55.
Article7). Voiculescu A., Hollenbeck M., Plum J., Hetzel GR., Modder U., Pfeiffer T, et al. Iliac artery stenosis proximal to a kidney transplant: clinical findings, duplex-sonographic criteria, treatment, and outcome. Transplantation. 2003. 76:332–9.
Article8). Pappas P., Zavos G., Kaza S., Leonardou P., Theodoropoulou E., Bokos J, et al. Angioplasty and stenting of arterial stenosis affecting renal transplant function. Transplant Proc. 2008. 40:1391–6.
Article9). Voiculescu A., Schmitz M., Hollenbeck M., Braasch S., Luther B., Sandmann W, et al. Management of arterial stenosis affecting kidney graft perfusion: a single-centre study in 53 patients. Am J Transplant. 2005. 5:1731–8.
Article10). Ghorbani A., Shirazi AS., Sametzadeh M., Mansoori P., Taheri A. Relation of resistive and pulsatility indices with graft function after renal transplant. Exp Clin Transplant. 2012. 10:568–72.
Article11). Sommerville RS., Jenkins J., Walker P., Olivotto R. 3-D magnetic resonance angiography versus conventional angiography in peripheral arterial disease: pilot study. ANZ J Surg. 2005. 75:373–7.
Article12). Bruno S., Remuzzi G., Ruggenenti P. Transplant renal artery stenosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. 15:134–41.13). Dourado R., Goncalves Pde A., Almeida M., Weigert A., Bruges M., Gaspar A, et al. Peripheral artery disease: a cause of refractory hypertension after renal transplantation. Rev Port Cardiol. 2008. 27:353–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Aortoiliac Occlusive Disease as a Cause of Allograft Kidney Dysfunction and Refractory Hypertension
- Transaxillary Renal Artery Angioplasty and Stenting in a Single-Kidney Patient with Leriches Syndrome
- A Case of Renovascular Hypertension Controlled by Renal Artery Embolization
- Results of Renal Allograft in Recipient with Iliac Endarterectomy
- Pheochromocytoma and Renal Artery Stenosis