J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Sep;52(3):257-260.
Retroperitoneal Spinal Extradural Arachnoid Cyst Combined with Congenital Hemivertebrae
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Spine and Spinal Cord Institute, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kuhsu@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
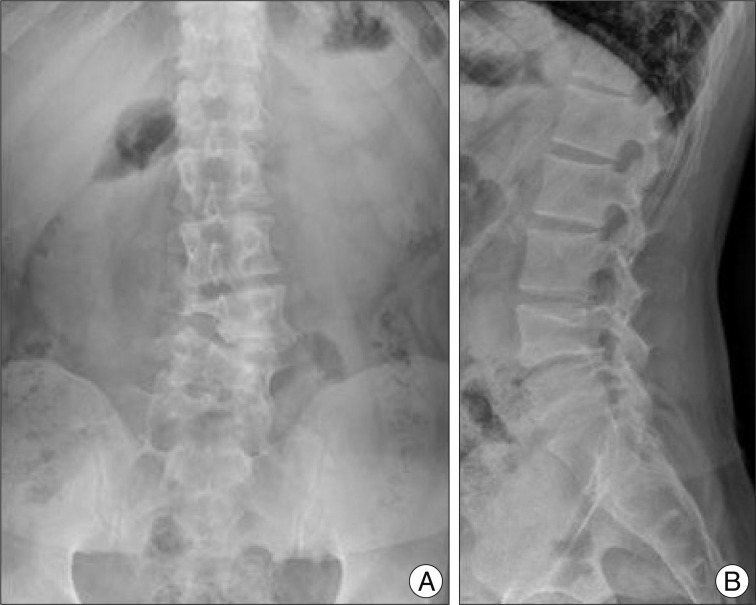
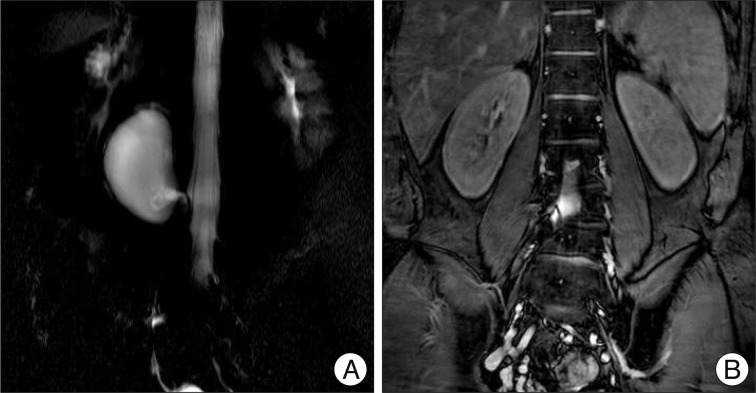
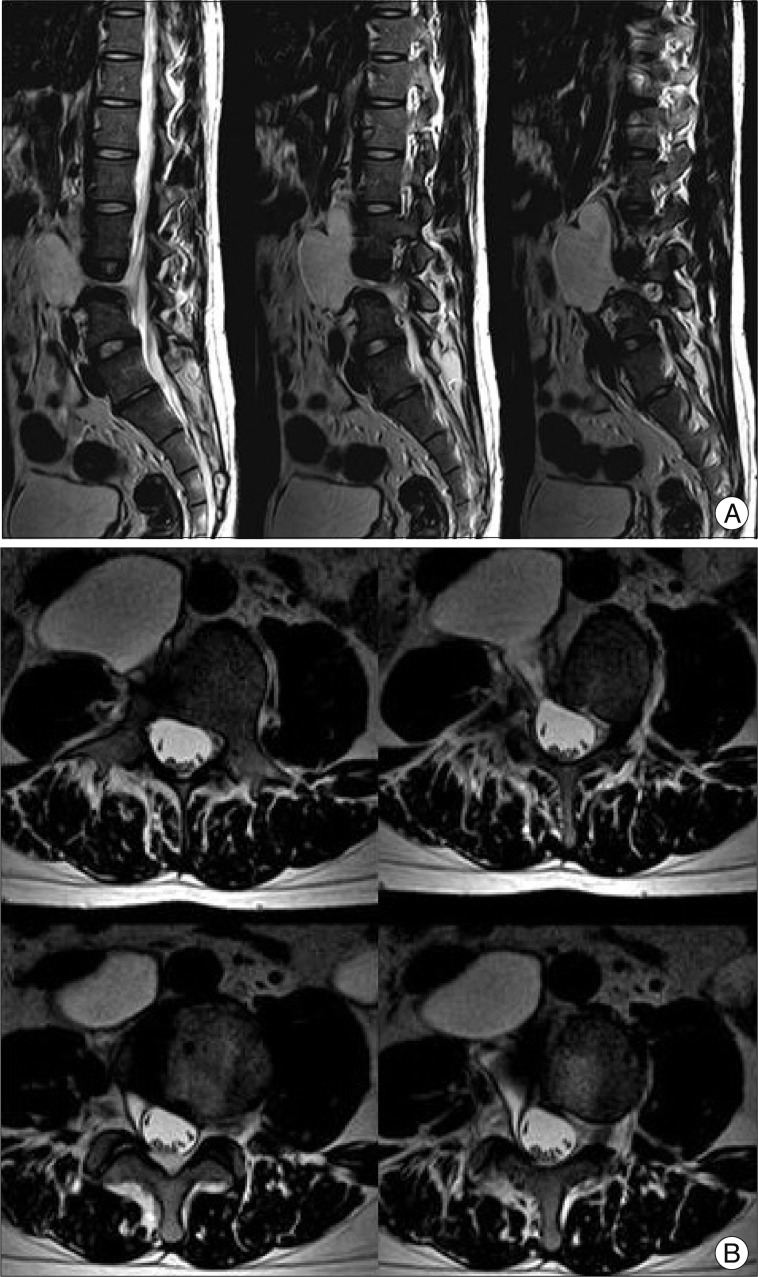
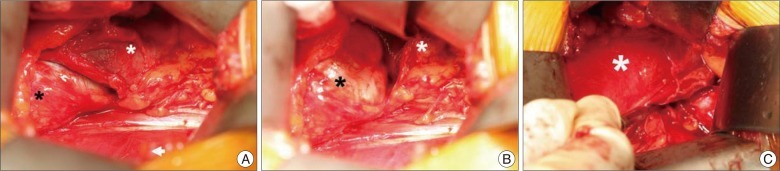
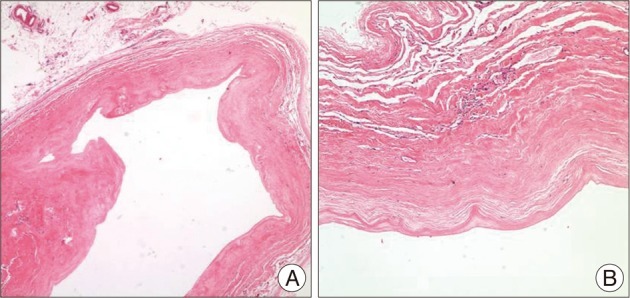
- Spinal extradural arachnoid cysts usually cause symptoms related to spinal cord or nerve root compression. Here, we report an atypical presentation of a spinal extradural arachnoid cyst combined with congenital hemivertebra which was presented as a retroperitoneal mass that exerted mass effects to the abdominal organs. On image studies, the communication between the cystic pedicle and the spinal arachnoid space was indistinct. Based on our experience and the literature of the pathogenesis, we planned anterior approach for removal of the arachnoid cyst in order to focus on mass removal rather than ligation of the fistulous channel. In our estimation this was feasible considering radiologic findings and also essential for the symptom relief. The cyst was totally removed with the clogged 'thecal sac-side' end of the cystic pedicle. The patient was free of abdominal discomfort by one month after the surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi JY, Kim SH, Lee WS, Sung KH. Spinal extradural arachnoid cyst. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006; 148:579–585. discussion 585. PMID: 16505968.
Article2. Cloward RB. Congenital spinal extradural cysts : case report with review of literature. Ann Surg. 1968; 168:851–864. PMID: 5684190.3. Gortvai P. Extradural cysts of the spinal canal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963; 26:223–230. PMID: 13949360.
Article4. Kulkarni AG, Goel A, Thiruppathy SP, Desai K. Extradural arachnoid cysts : a study of seven cases. Br J Neurosurg. 2004; 18:484–488. PMID: 15799150.5. Lake PA, Minckler J, Scanlan RL. Spinal epidural cyst : theories of pathogenesis. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1974; 40:774–778. PMID: 4826604.6. Liu JK, Cole CD, Kan P, Schmidt MH. Spinal extradural arachnoid cysts : clinical, radiological, and surgical features. Neurosurg Focus. 2007; 22:E6. PMID: 17608349.7. Mao HQ, Yang HL, Geng DC, Bao ZH, Tang TS. Spinal extradural arachnoid cyst following percutaneous vertebroplasty. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(Suppl 2):S206–S210. PMID: 20835874.
Article8. McCrum C, Williams B. Spinal extradural arachnoid pouches. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1982; 57:849–852. PMID: 7143073.9. Nabors MW, Pait TG, Byrd EB, Karim NO, Davis DO, Kobrine AI, et al. Updated assessment and current classification of spinal meningeal cysts. J Neurosurg. 1988; 68:366–377. PMID: 3343608.
Article10. Neo M, Koyama T, Sakamoto T, Fujibayashi S, Nakamura T. Detection of a dural defect by cinematic magnetic resonance imaging and its selective closure as a treatment for a spinal extradural arachnoid cyst. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:E426–E430. PMID: 15454723.
Article11. Rohrer DC, Burchiel KJ, Gruber DP. Intraspinal extradural meningeal cyst demonstrating ball-valve mechanism of formation. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1993; 78:122–125. PMID: 8416228.
Article12. Sakellaridis N, Panagopoulos D, Mahera H. Sacral epidural noncommunicating arachnoid cyst. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 6:473–478. PMID: 17542517.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Retroperitoneal Hematoma after Excision of Lumbar Extradural Arachnoid Cyst: Case Report
- Septated Extradural Arachnoid Cyst in Thoracolumbar Spine Causing Myelopathy
- Extradural Spinal Arachnoid Cyst as a Cause of Cauda Equina Syndrome in a Child
- Multiple Extradural Arachnoid Cyst : A Case Report
- Huge Thoracolumbar Extradural Arachnoid Cyst