J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Jun;55(6):809-816.
Clinical Outcomes of Cataract Surgery with Correction of Corneal Spherical Aberration
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. docchoi@hanmail.net
- 2Seoul National University Hospital Healthcare System Gangnam Center, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate preoperative and postoperative spherical aberrations after cataract surgery based on selecting spherical or aspheric intraocular lens (IOL) according to preoperative corneal aberration.
METHODS
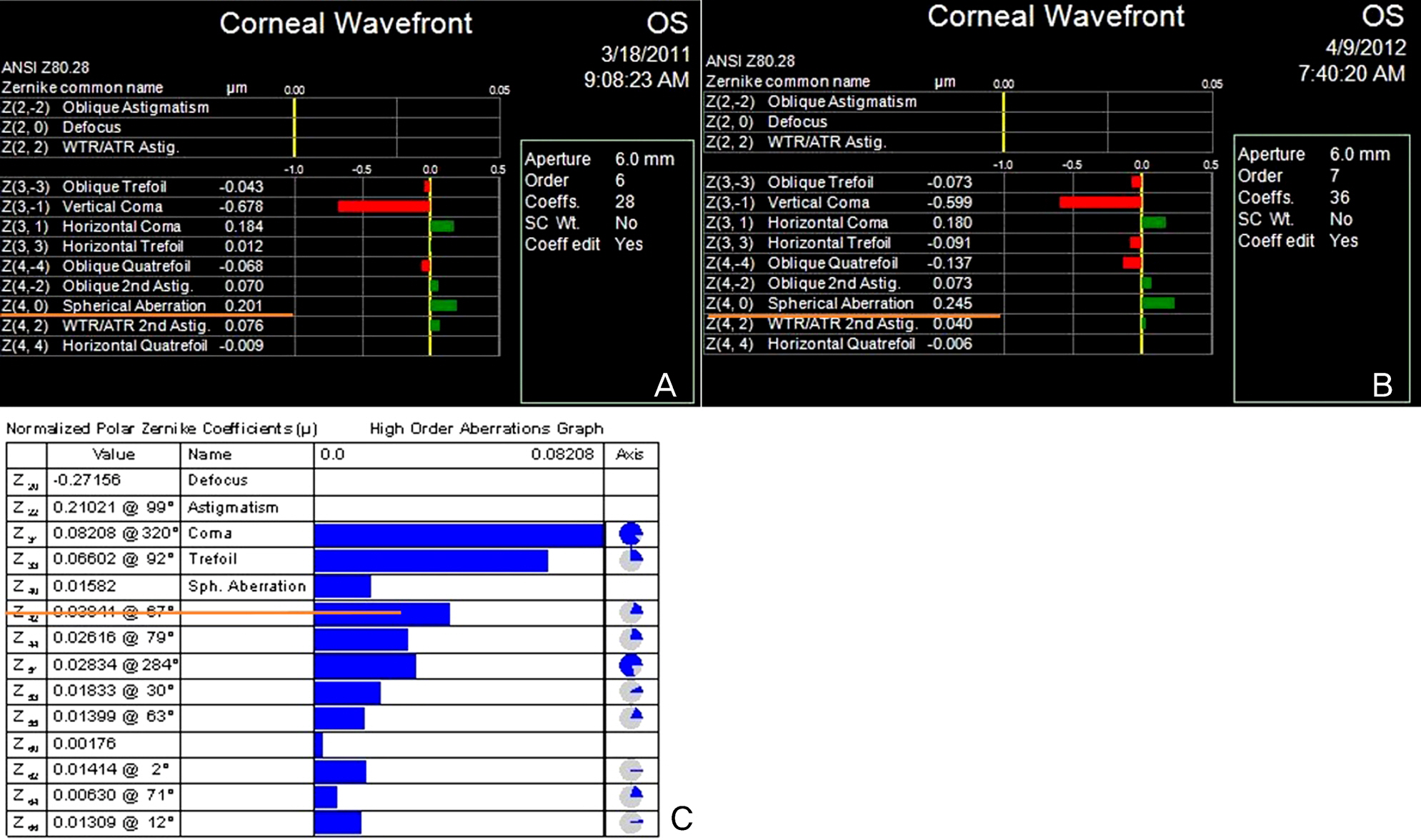
The medical records of patients who underwent phacoemulsification and IOL implantation in the posterior chamber by a surgeon (H.J.C) were reviewed (68 patients, 97 eyes). IOL was selected based on preoperative corneal spherical aberration measured by corneal topography (ATLAS 9000, Carl Zeiss). The target postoperative total ocular spherical aberration was set to zero (0) and one of the following lenses was chosen: Acrysof SA60AT (n = 25), Acrysof IQ (n = 36) or Tecnis(R) ZCB00 (n = 36). The Wavescan aberrometer and the corneal topography were obtained postoperatively. Absolute prediction errors of postoperative total ocular spherical aberration were analyzed.
RESULTS
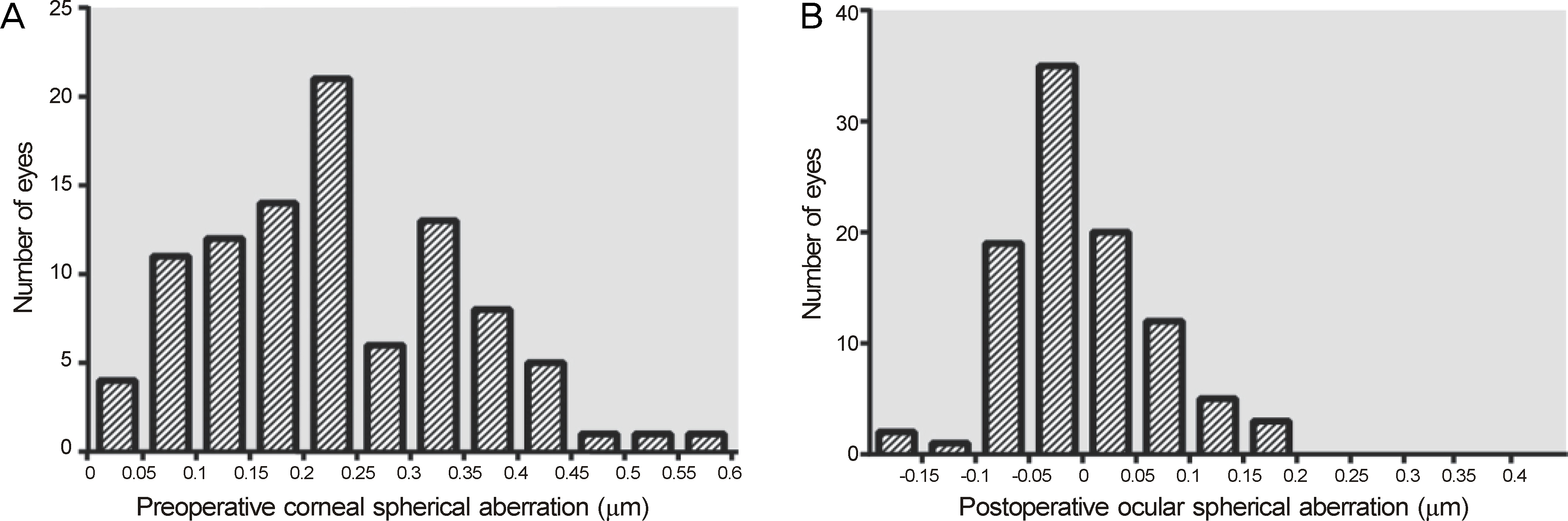
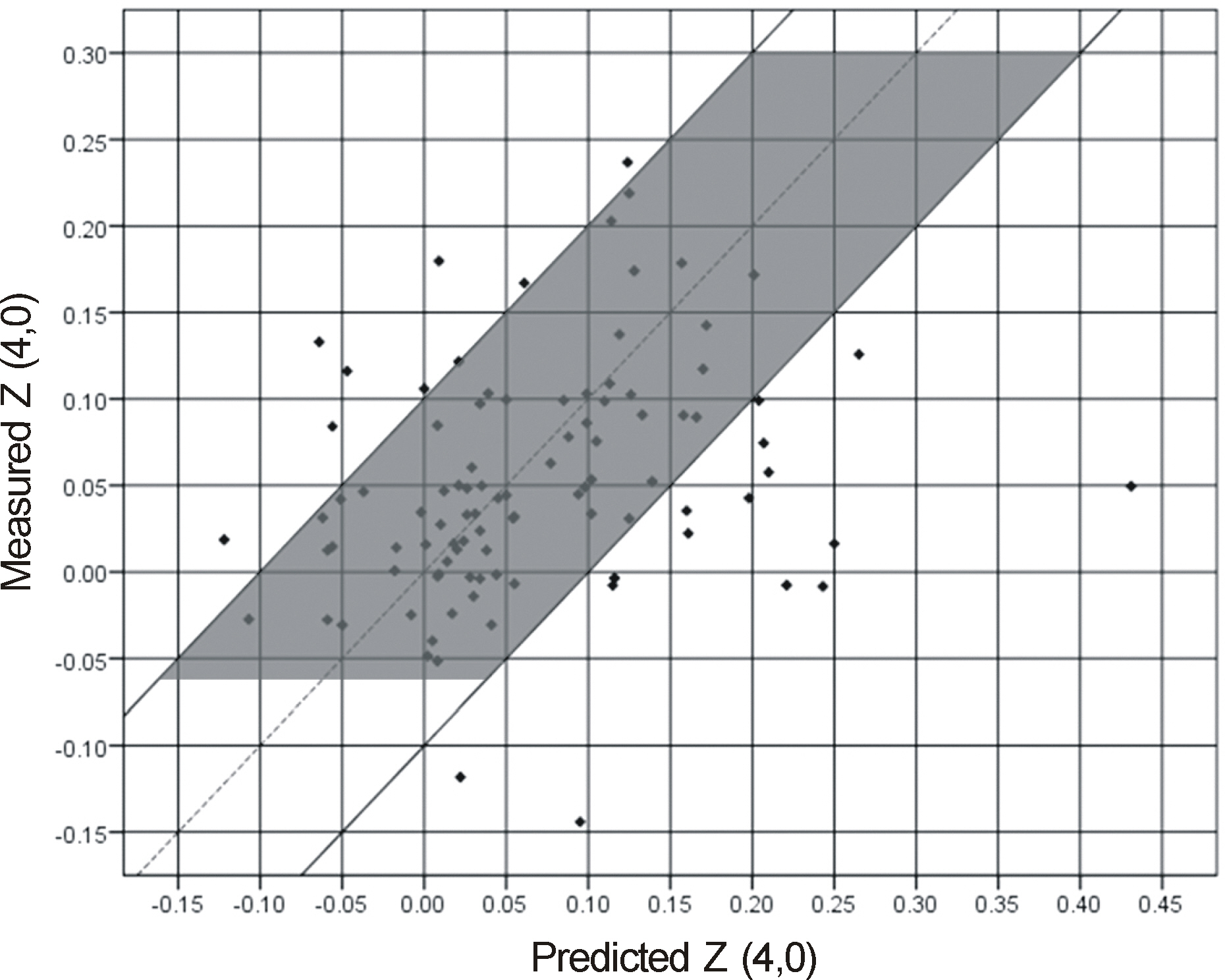
Preoperative corneal spherical aberration was 0.241 microm; total postoperative ocular spherical aberration was 0.0509 microm (Acrysof SA60AT: 0.0954 microm, Tecnis(R) ZCB00: 0.0374 microm, Acrysof IQ: 0.0335 microm). Postoperative corneal spherical aberration was 0.232 microm, which was not significantly different from the preoperative value (p = 0.199). Postoperative ocular spherical aberration was 0.051 microm; 0.095 microm (Acrysof SA60AT), 0.034 microm (Acrysof IQ), and 0.037 microm (ZCB00). The reducing amounts of spherical aberration were 0.185 microm (Acrysof IQ) and 0.311 microm (ZCB00). The overall absolute prediction error was 0.068 microm. The absolute prediction error of the Acrysof SA60AT group was 0.092 microm, Tecnis(R) ZCB00 group was 0.067 microm and Acrysof IQ group was 0.054 microm. There was no significant difference among the 3 groups (p = 0.089).
CONCLUSIONS
Aspheric IOLs can efficiently reduce total ocular spherical aberrations according to preoperative corneal spherical aberrations.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Desai P, Minassian DC, Reidy A. National cataract surgery survey 1997-8: a report of the results of the clinical outcomes. Br J Ophthalmol. 1999; 83:1336–40.
Article2. Steinberg EP, Tielsch JM, Schein OD, et al. National study of cata-ract surgery outcomes. Variation in 4-month postoperative out-comes as reflected in multiple outcome measures. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:1131–40. discussion 1140-1.3. Zhao J, Ellwein LB, Cui H, et al. Prevalence and outcomes of cata-ract surgery in rural China the China nine-province survey. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:2120–8.4. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS. Aspheric intraocular lens se-lection based on corneal wavefront. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25:12–20.
Article5. Ruttig NJ, Jancevski M, Shah SA. Evaluating wavefront analysis application in intraocular lens placement. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008; 19:309–13.
Article6. Solomon JD. Outcomes of corneal spherical aberration-guided cat-aract surgery measured by the OPD-scan. J Refract Surg. 2010; 26:863–9.
Article7. Harris WF. Optimal target refraction for implantation of monofocal intraocular lenses. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012; 90:e75–6. author reply e75.
Article8. de Vries NE, Webers CA, Montés-Micó R, et al. Visual outcomes after cataract surgery with implantation of a +3.00 D or +4.00 D as-pheric diffractive multifocal intraocular lens: Comparative study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1316–22.
Article9. Lane SS, Javitt JC, Nethery DA, Waycaster C. Improvements in patient-reported outcomes and visual acuity after bilateral im-plantation of multifocal intraocular lenses with +3.0 diopter addition: multicenter clinical trial. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1887–96.
Article10. Packer M, Chu YR, Waltz KL, et al. Evaluation of the aspheric tec-nis multifocal intraocular lens: one-year results from the first co-hort of the food and drug administration clinical trial. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 149:577–84.e1.
Article11. Amano S, Amano Y, Yamagami S, et al. Age-related changes in corneal and ocular higher-order wavefront aberrations. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:988–92.
Article12. Denoyer A, Denoyer L, Marotte D, et al. Intraindividual com-parative study of corneal and ocular wavefront aberrations after biaxial microincision versus coaxial small-incision cataract surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008; 92:1679–84.
Article13. Yeu E, Wang L, Koch DD. The effect of corneal wavefront aberrations on corneal pseudoaccommodation. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012; 153:972–81.e2.
Article14. Chantra S, Pachimkul P, Naripthaphan P. Wavefront and ocular spherical aberration after implantation of different types of asphe-ric intraocular lenses based on corneal spherical aberration. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011; 94(Suppl 2):S71–5.15. Denoyer A, Le Lez ML, Majzoub S, Pisella PJ. Quality of vision after cataract surgery after Tecnis Z9000 intraocular lens im-plantation: effect of contrast sensitivity and wavefront aberration improvements on the quality of daily vision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:210–6.16. Iseli HP, Jankov M, Bueeler M, et al. Corneal and total wavefront aberrations in phakic and pseudophakic eyes after implantation of monofocal foldable intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:762–71.
Article17. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS. Wavefront technology in cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004; 15:56–60.
Article18. Yu AY, Wang QM, Sun J, et al. Spherical aberration after im-plantation of an aspheric versus a spherical intraocular lens in high myopia. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2009; 37:558–65.
Article19. Rocha KM, Vabre L, Chateau N, Krueger RR. Expanding depth of focus by modifying higher-order aberrations induced by an adaptive optics visual simulator. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1885–92.
Article20. Hickenbotham A, Tiruveedhula P, Roorda A. Comparison of spher-ical aberration and small-pupil profiles in improving depth of focus for presbyopic corrections. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:2071–9.
Article21. Salvatore S, Lupo S, Nebbioso M, et al. New insight into visual function with aspherical intraocular lenses (IOLs): Tecnis ZCB00 and Acrysof SN60WF. Int Ophthalmol. 2011; 31:417–9.
Article22. Assaf A, Kotb A. Ocular aberrations and visual performance with an aspheric single-piece intraocular lens: contralateral comparative study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1536–42.
Article23. Kim YJ, Cheon MH, Ko DA, et al. Clinical outcome of in-the-bag single-piece aspheric intraocular lens implantation after micro-incision cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:595–601.
Article24. Lee K, Yoon MH, Seo KY, et al. Comparisons of clinical results af-ter implantation of three aspheric intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1213–8.
Article25. Guirao A, Redondo M, Artal P. Optical aberrations of the human cornea as a function of age. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2000; 17:1697–702.
Article26. Uchio E, Ohno S, Kusakawa T. Spherical aberration and glare dis-ability with intraocular lenses of different optical design. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1995; 21:690–6.
Article27. Yamaguchi T, Dogru M, Yamaguchi K, et al. Effect of spherical aberration on visual function under photopic and mesopic con-ditions after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:57–63.
Article28. Beiko GH. Personalized correction of spherical aberration in cata-ract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1455–60.
Article29. Wang L, Koch DD. Custom optimization of intraocular lens asphericity. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1713–20.
Article30. Awwad ST, Lehmann JD, McCulley JP, Bowman RW. A compar-ison of higher order aberrations in eyes implanted with AcrySof IQ SN60WF and AcrySof SN60AT intraocular lenses. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2007; 17:320–6.
Article31. Caporossi A, Martone G, Casprini F, Rapisarda L. Prospective randomized study of clinical performance of 3 aspheric and 2 spherical intraocular lenses in 250 eyes. J Refract Surg. 2007; 23:639–48.
Article32. Kasper T, Bühren J, Kohnen T. Visual performance of aspherical and spherical intraocular lenses: intraindividual comparison of vis-ual acuity, contrast sensitivity, and higher-order aberrations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:2022–9.
Article33. Mester U, Sauer T, Kaymak H. Decentration and tilt of a single-piece aspheric intraocular lens compared with the lens position in young phakic eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:485–90.
Article34. Lee JY, Lee SH, Chung SK. Decentration, tilt and anterior chamber depth: aspheric vs spheric acrylic intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:852–7.
Article35. Piers PA, Weeber HA, Artal P, Norrby S. Theoretical comparison of aberration-correcting customized and aspheric intraocular lenses. J Refract Surg. 2007; 23:374–84.
Article36. Guirao A, Tejedor J, Artal P. Corneal aberrations before and after small-incision cataract surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45:4312–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anterior and Posterior Corneal Spherical Aberration Measured With Pentacam in the Korean
- Comparative Study of Two Aspheric, Aberration-Free Intraocular Lenses in Cataract Surgery
- Comparison between Anterior Corneal Aberration and Ocular Aberration in Laser Refractive Surgery
- Wavefront Analysis of Successful Treatment of Monocular Triplopia After Cataract Extraction: Report of 2 Cases
- Estimation of Corneal Spherical Aberration from Topography