Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Jun;40(3):509-519. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.3.509.
Effect of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Sahmyook Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. btjrbj@gmail.com
- KMID: 2327614
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.3.509
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the effect of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy (rESWT) on hemiplegic shoulder pain (HSP) syndrome.
METHODS
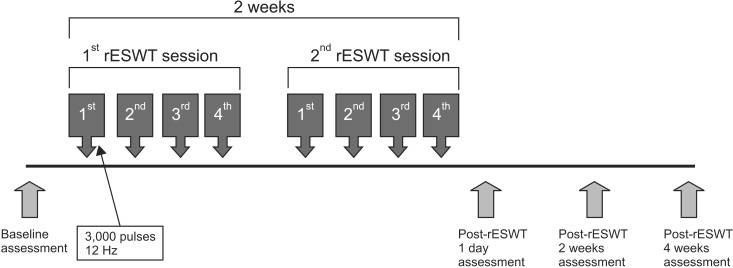
In this monocentric, randomized, patient-assessor blinded, placebo-controlled trial, patients with HSP were randomly divided into the rESWT (n=17) and control (n=17) groups. Treatment was administered four times a week for 2 weeks. The visual analogue scale (VAS) score and Constant-Murley score (CS) were assessed before and after treatment, and at 2 and 4 weeks. The Modified Ashworth Scale and Fugl-Meyer Assessment scores and range of motion of the shoulder were also assessed.
RESULTS
VAS scores improved post-intervention and at the 2-week and 4-week follow-up in the intervention group (p<0.05). Respective differences in VAS scores between baseline and post-intervention in the intervention and control groups were -1.69±1.90 and -0.45±0.79, respectively (p<0.05), between baseline and 2-week follow-up in the intervention and control groups were -1.60±1.74 and -0.34±0.70, respectively (p<0.05), and between baseline and 4-week follow-up in the intervention and control groups were -1.61±1.73 and -0.33±0.71, respectively (p<0.05). Baseline CS improved from 19.12±11.02 to 20.88±10.37 post-intervention and to 20.41±10.82 at the 2-week follow-up only in the intervention group (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
rESWT consisting of eight sessions could be one of the effective and safe modalities for pain management in people with HSP. Further studies are needed to generalize and support these results in patients with HSP and a variety conditions, and to understand the mechanism of rESWT for treating HSP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dromerick A, Reding M. Medical and neurological complications during inpatient stroke rehabilitation. Stroke. 1994; 25:358–361. PMID: 8303745.
Article2. Wanklyn P, Forster A, Young J. Hemiplegic shoulder pain (HSP): natural history and investigation of associated features. Disabil Rehabil. 1996; 18:497–501. PMID: 8902421.
Article3. Yoon TS, Kim DH, Park JW, Kwon BS, Ryu KH, Lee HJ, et al. Causes of the Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010; 34:158–162.4. Andres BM, Murrell GA. Treatment of tendinopathy: what works, what does not, and what is on the horizon. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:1539–1554. PMID: 18446422.
Article5. Sems A, Dimeff R, Iannotti JP. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in the treatment of chronic tendinopathies. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006; 14:195–204. PMID: 16585361.6. Ogden JA, Alvarez RG, Levitt R, Marlow M. Shock wave therapy (Orthotripsy) in musculoskeletal disorders. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (387):22–40. PMID: 11400888.
Article7. Sohn MK, Cho KH, Kim YJ, Hwang SL. Spasticity and electrophysiologic changes after extracorporeal shock wave therapy on gastrocnemius. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:599–604. PMID: 22506181.
Article8. Michener LA, Walsworth MK, Burnet EN. Effectiveness of rehabilitation for patients with subacromial impingement syndrome: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2004; 17:152–164. PMID: 15162102.
Article9. Gerdesmeyer L, Frey C, Vester J, Maier M, Weil L Jr, Weil L Sr, et al. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy is safe and effective in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant plantar fasciitis: results of a confirmatory randomized placebo-controlled multicenter study. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36:2100–2109. PMID: 18832341.10. Kim YW, Shin JC, Yoon JG, Kim YK, Lee SC. Usefulness of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the spasticity of the subscapularis in patients with stroke: a pilot study. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013; 126:4638–4643. PMID: 24342303.11. Galasso O, Amelio E, Riccelli DA, Gasparini G. Short-term outcomes of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic non-calcific tendinopathy of the supraspinatus: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012; 13:86. PMID: 22672772.
Article12. Seo HS, Sung YB, Lee JH, Park YH. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on pain and function in patients with rotator cuff tendinitis. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2012; 13:3132–3139.
Article13. Chen CY, Hu CC, Weng PW, Huang YM, Chiang CJ, Chen CH, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy improves short-term functional outcomes of shoulder adhesive capsulitis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014; 23:1843–1851. PMID: 25441567.
Article14. Notarnicola A, Moretti L, Tafuri S, Panella A, Filipponi M, Casalino A, et al. Shockwave therapy in the management of complex regional pain syndrome in medial femoral condyle of the knee. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010; 36:874–879. PMID: 20447749.
Article15. Moon SW, Kim JH, Jung MJ, Son S, Lee JH, Shin H, et al. The effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on lower limb spasticity in subacute stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013; 37:461–470. PMID: 24020026.
Article16. Bae H, Lee JM, Lee KH. The effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on spasticity in chronic stroke patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010; 34:663–669.17. Speed CA, Richards C, Nichols D, Burnet S, Wies JT, Humphreys H, et al. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for tendonitis of the rotator cuff: a double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:509–512. PMID: 12043769.18. Reips UD, Funke F. Interval-level measurement with visual analogue scales in Internet-based research: VAS Generator. Behav Res Methods. 2008; 40:699–704. PMID: 18697664.
Article19. Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; (214):160–164. PMID: 3791738.
Article20. Bohannon RW, Smith MB. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys Ther. 1987; 67:206–207. PMID: 3809245.
Article21. Gleitz M. Myofascial syndromes and trigger points. Heilbronn: Level10 Buchverlag;2011.22. Haake M, Deike B, Thon A, Schmitt J. Exact focusing of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for calcifying tendinopathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; (397):323–331. PMID: 11953624.
Article23. Knobloch K, Kuehn M, Vogt PM. Focused extracorporeal shockwave therapy in Dupuytren's disease: a hypothesis. Med Hypotheses. 2011; 76:635–637. PMID: 21277691.24. Huang CW, Wei CC, Liao VH. A low cost color-based bacterial biosensor for measuring arsenic in groundwater. Chemosphere. 2015; 141:44–49. PMID: 26092199.
Article25. Rompe JD, Hopf C, Kullmer K, witzsch U, Nafe B. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy of radiohumeral epicondylopathy: an alternative treatment concept. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1996; 134:63–66. PMID: 8650997.26. Rompe JD, Hope C, Kullmer K, Heine J, Burger R. Analgesic effect of extracorporeal shock-wave therapy on chronic tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:233–237. PMID: 8666632.
Article27. Kienle GS, Kiene H. The powerful placebo effect: fact or fiction? J Clin Epidemiol. 1997; 50:1311–1318. PMID: 9449934.
Article28. Hooper TD, Hibbert PD, Hannaford NA, Jackson N, Hindmarsh DM, Gordon DL, et al. Surgical site infection-a population-based study in Australian adults measuring the compliance with and correct timing of appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2015; 43:461–467. PMID: 26099757.
Article29. Vidal X, Morral A, Costa L, Tur M. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy (rESWT) in the treatment of spasticity in cerebral palsy: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. NeuroRehabilitation. 2011; 29:413–419. PMID: 22207070.
Article30. Kim KS, Seo JH, Song CG. Portable measurement system for the objective evaluation of the spasticity of hemiplegic patients based on the tonic stretch reflex threshold. Med Eng Phys. 2011; 33:62–69. PMID: 20932794.
Article31. Rizk TE, Christopher RP, Pinals RS, Salazar JE, Higgins C. Arthrographic studies in painful hemiplegic shoulders. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1984; 65:254–256. PMID: 6712451.32. Bohannon RW, Larkin PA, Smith MB, Horton MG. Shoulder pain in hemiplegia: statistical relationship with five variables. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1986; 67:514–516. PMID: 3741075.33. Hsu JE, Anakwenze OA, Warrender WJ, Abboud JA. Current review of adhesive capsulitis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20:502–514. PMID: 21167743.
Article34. Neviaser AS, Hannafin JA. Adhesive capsulitis: a review of current treatment. Am J Sports Med. 2010; 38:2346–2356. PMID: 20110457.35. Neviaser AS, Neviaser RJ. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011; 19:536–542. PMID: 21885699.
Article36. Kilian O, Pfeil U, Wenisch S, Heiss C, Kraus R, Schnettler R. Enhanced alpha 1(I) mRNA expression in frozen shoulder and dupuytren tissue. Eur J Med Res. 2007; 12:585–590. PMID: 18024269.37. Uhthoff HK, Boileau P. Primary frozen shoulder: global capsular stiffness versus localized contracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 456:79–84. PMID: 17179778.38. Manganotti P, Amelio E. Long-term effect of shock wave therapy on upper limb hypertonia in patients affected by stroke. Stroke. 2005; 36:1967–1971. PMID: 16109905.
Article39. Leone JA, Kukulka CG. Effects of tendon pressure on alpha motoneuron excitability in patients with stroke. Phys Ther. 1988; 68:475–480. PMID: 3353457.
Article40. Cohen SP, Mao J, Vu TN, Strassels SA, Gupta A, Erdek MA, et al. Does pain score in response to a standardized subcutaneous local anesthetic injection predict epidural steroid injection outcomes in patients with lumbosacral radiculopathy? A prospective correlational study. Pain Med. 2013; 14:327–335. PMID: 23294538.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Results of Radial and Focused Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Periscapular Myofascial Pain Syndrome
- Effect of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Patients With Fabella Syndrome
- The Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder
- Treatment of Nonunion of Tibia with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy: A Case Report
- Is Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Effective in the Treatment of Myofascial Pain Syndrome?