Ann Surg Treat Res.
2016 Jul;91(1):23-28. 10.4174/astr.2016.91.1.23.
Positive immunostaining of Sal-like protein 4 is associated with poor patient survival outcome in the large and undifferentiated Korean hepatocellular carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. crane87@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2327413
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2016.91.1.23
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Previous studies have shown the role of Sal-like protein 4 (SALL4) as a biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and some studies have shown the relationship between SALL4 and prognosis. Given the debates in study groups differences in terms of etiologic causes between Western and Asian HCC and detection methods, we attempted to verify the features of SALL4 immunoreactivity and its clinical correlation in Korean HCC patients.
METHODS
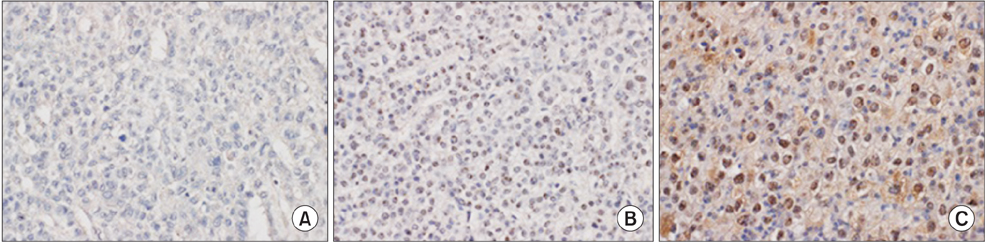
Immunohistochemical staining of SALL4 of tissue microarrays (TMAs) consisting of 213 surgically resected HCC patients' tissue were scored in a semiquantitative scoring system with immunoreactive score and the results analyzed with clinical outcome, in addition to general demographics and clinical characteristics.
RESULTS
SALL4 immunoreactivity was expressed in 50 cases. Relevance between SALL4 and α-FP correlated significantly (P = 0.002). Also, the SALL4-positive patients had considerably higher tumor grade (P < 0.001). The survival analysis showed negative correlation with SALL4 immunoreactivity in all HCC patient groups, but SALL4 immunoreactivity in T3 and T4 HCC correlated with poor prognosis.
CONCLUSION
Here, we found that positive immunostaining of SALL4 is correlated with poor patient survival outcome in large and undifferentiated Korean HCC. SALL4 expression showed close relationship with clinical outcomes of HCCs in Korean patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005; 55:74–108.2. Llovet JM, Bruix J. Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008; 48:1312–1327.3. Bruix J, Sherman M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022.4. Wurmbach E, Chen YB, Khitrov G, Zhang W, Roayaie S, Schwartz M, et al. Genome-wide molecular profiles of HCV-induced dysplasia and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2007; 45:938–947.5. Llovet JM, Chen Y, Wurmbach E, Roayaie S, Fiel MI, Schwartz M, et al. A molecular signature to discriminate dysplastic nodules from early hepatocellular carcinoma in HCV cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2006; 131:1758–1767.6. Villanueva A, Hoshida Y, Battiston C, Tovar V, Sia D, Alsinet C, et al. Combining clinical, pathology, and gene expression data to predict recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:1501–1512.e2.7. Yang J, Gao C, Chai L, Ma Y. A novel SALL4/OCT4 transcriptional feedback network for pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e10766.8. Rao S1, Zhen S, Roumiantsev S, McDonald LT, Yuan GC, Orkin SH. Differential roles of Sall4 isoforms in embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Mol Cell Biol. 2010; 30:5364–5380.9. Ma Y, Cui W, Yang J, Qu J, Di C, Amin HM, et al. SALL4, a novel oncogene, is constitutively expressed in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and induces AML in transgenic mice. Blood. 2006; 108:2726–2735.10. Kobayashi D, Kuribayshi K, Tanaka M, Watanabe N. SALL4 is essential for cancer cell proliferation and is overexpressed at early clinical stages in breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2011; 38:933–939.11. Fujimoto M, Sumiyoshi S, Yoshizawa A, Sonobe M, Kobayashi M, Moriyoshi K, et al. SALL4 immunohistochemistry in non-small-cell lung carcinomas. Histopathology. 2014; 64:309–311.12. Cao D, Li J, Guo CC, Allan RW, Humphrey PA. SALL4 is a novel diagnostic marker for testicular germ cell tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009; 33:1065–1077.13. Oikawa T, Kamiya A, Kakinuma S, Zeniya M, Nishinakamura R, Tajiri H, et al. Sall4 regulates cell fate decision in fetal hepatic stem/progenitor cells. Gastroenterology. 2009; 136:1000–1011.14. Yong KJ, Gao C, Lim JS, Yan B, Yang H, Dimitrov T, et al. Oncofetal gene SALL4 in aggressive hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:2266–2276.15. Liu TC, Vachharajani N, Chapman WC, Brunt EM. SALL4 immunoreactivity predicts prognosis in Western hepatocellular carcinoma patients but is a rare event: a study of 236 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014; 38:966–972.16. Han SX, Wang JL, Guo XJ, He CC, Ying X, Ma JL, et al. Serum SALL4 is a novel prognosis biomarker with tumor recurrence and poor survival of patients in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunol Res. 2014; 2014:262385.17. Oikawa T, Kamiya A, Zeniya M, Chikada H, Hyuck AD, Yamazaki Y, et al. Sal-like protein 4 (SALL4), a stem cell biomarker in liver cancers. Hepatology. 2013; 57:1469–1483.18. Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010; 127:2893–2917.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Collision Tumor of the Liver (Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Undifferentiated Sarcoma)
- C-reactive Protein Overexpression in the Background Liver of Hepatitis B Virus–Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is a Prognostic Biomarker
- Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Single Center Experience for Seventeen Years
- Expression Pattern of the Rb Protein and its Correlation with Prognosis in Primary Lung Cancer
- Undifferentiated Gallbladder Carcinoma with Osteoclast-like Giant Cells: A Case Report