J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Sep;65(3):229-233.
Direct Puncture Embolization of Scalp Arteriovenous Malformation in a Patient with Severe Hemophilia A: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Kyung Hee University, Graduate School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. euijkim@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Kyung Hee University, Graduate School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
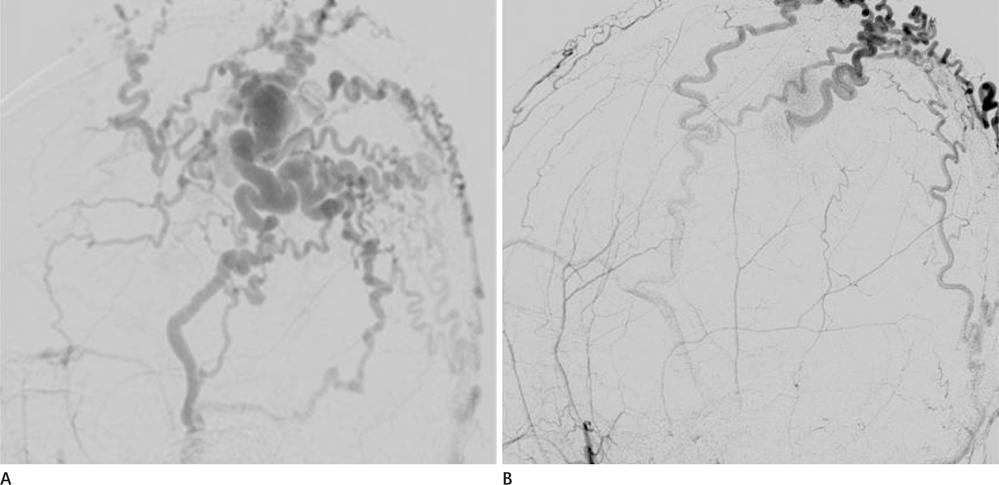
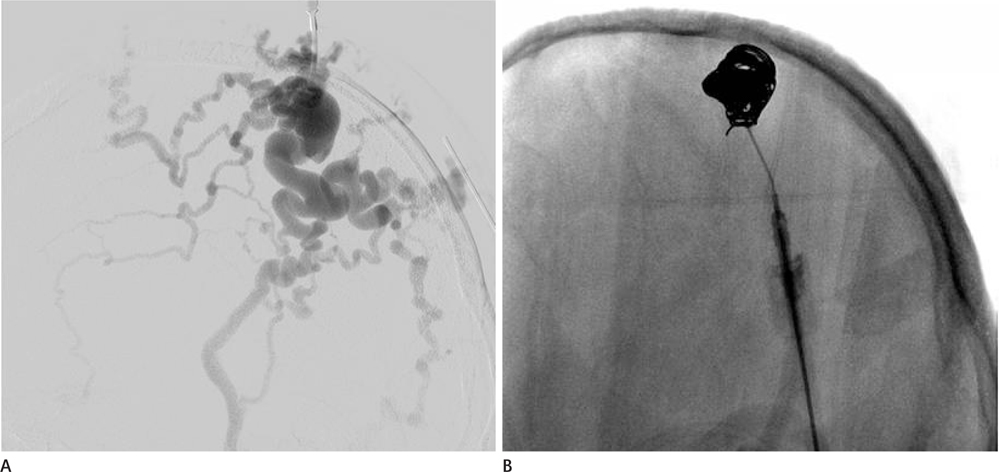
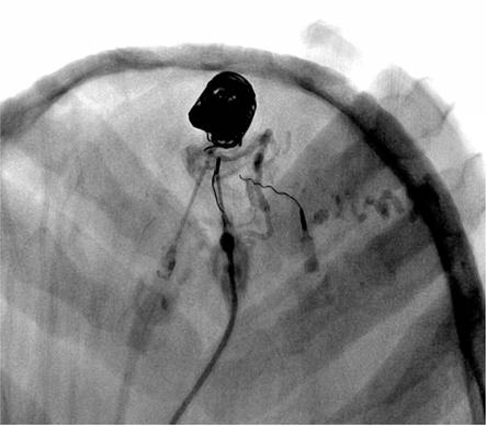
- We present a case of scalp arteriovenous malformation (AVM) in a patient with severe hemophilia A. The 22-year-old man presented with a pulsatile right parietal scalp mass. Digital subtraction angiography revealed an AVM in the right parietal scalp, supplied by superficial temporal and occipital arteries that drained into multiple venous structures. We successfully performed direct puncture embolization followed by surgical resection of the scalp AVM in conjunction with supplemental infusion of coagulation factor VIII before, during and after the embolization and the operation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fisher-Jeffes ND, Domingo Z, Madden M, de Villiers JC. Arteriovenous malformations of the scalp. Neurosurgery. 1995; 36:656–660. discussion 660.2. Bowen DJ. Haemophilia A and haemophilia B: molecular insights. Mol Pathol. 2002; 55:1–18.3. Nagasaka S, Fukushima T, Goto K, Ohjimi H, Iwabuchi S, Maehara F. Treatment of scalp arteriovenous malformation. Neurosurgery. 1996; 38:671–677. discussion 677.4. Jeong HS, Choi JY, Lee HJ, Kim TW, Kim MB, So YK, et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Extracranial Arteriovenous Malformations in the Head and Neck Region. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2005; 48:1136–1142.5. Han MH, Seong SO, Kim HD, Chang KH, Yeon KM, Han MC. Craniofacial arteriovenous malformation: preoperative embolization with direct puncture and injection of n-butyl cyanoacrylate. Radiology. 1999; 211:661–666.6. Jeong HS, Baek CH, Son YI, Kim TW, Lee BB, Byun HS. Treatment for extracranial arteriovenous malformations of the head and neck. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006; 126:295–300.7. Widlus DM, Murray RR, White RI Jr, Osterman FA Jr, Schreiber ER, Satre RW, et al. Congenital arteriovenous malformations: tailored embolotherapy. Radiology. 1988; 169:511–516.8. Ryu CW, Whang SM, Suh DC, Kim SM, Jang YJ, Kim HJ, et al. Percutaneous direct puncture glue embolization of high-flow craniofacial arteriovenous lesions: a new circular ring compression device with a beveled edge. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:528–530.9. Benndorf G, Kim DM, Menneking H, Klein M. Endovascular management of a mandibular arteriovenous malformation in a patient with severe hemophilia a. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:614–617.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Posttraumatic Pseudoaneurysm in Scalp Treated by Direct Puncture Embolization Using N-Butyl-2-Cyanoacrylate: a Case Report
- A Case of Acquired Multiple Arteriovenous Malformations on the Scalp in the Patient of Liver Cirrhosis
- A Case of Multiple Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformation Treated with Coil Embolization
- Arteriovenous Fistula at Scalp: Rapid Progression After Embolization of Contralateral Facial Arteriovenous Malformation
- Congenital Renal Arteriovenous Malformation in Pregnancy