Tuberc Respir Dis.
2015 Oct;78(4):385-389. 10.4046/trd.2015.78.4.385.
Single Nodular Pulmonary Amyloidosis: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. starbag1@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2320712
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2015.78.4.385
Abstract
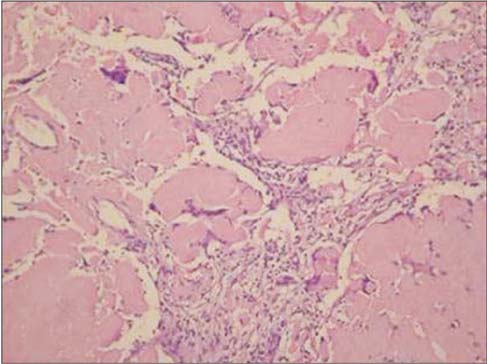
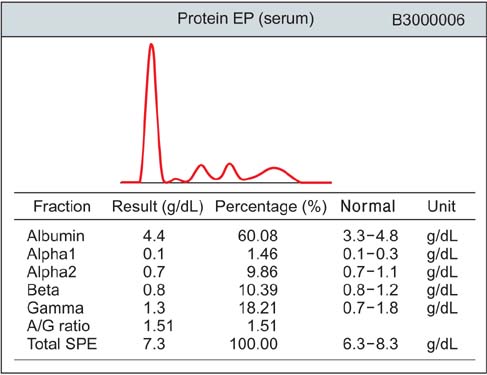
- Amyloidosis is defined as the presence of extra-cellular deposits of an insoluble fibrillar protein, amyloid. The pulmonary involvement of amyloidosis is usually classified as tracheobronchial, parenchymal nodular, or diffuse alveolar septal. A single nodular lesion can mimic various conditions, including malignancy, pulmonary tuberculosis, and fungal infection. To date, only one case of nodular pulmonary amyloidosis has been reported in Korea, a case involving multiple nodular lesions. Here, we report and discuss the case of a patient having single nodular amyloidosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sipe JD, Benson MD, Buxbaum JN, Ikeda S, Merlini G, Saraiva MJ, et al. Amyloid fibril protein nomenclature: 2012 recommendations from the Nomenclature Committee of the International Society of Amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2012; 19:167–170.2. Utz JP, Swensen SJ, Gertz MA. Pulmonary amyloidosis. The Mayo Clinic experience from 1980 to 1993. Ann Intern Med. 1996; 124:407–413.3. Shin B, Ko J, Lee SS, Lim KS, Han JH, Chung MP, et al. A case of pulmonary amyloidosis mimicking lymphangitic lung carcinomatosis. Korean J Med. 2014; 86:339–342.4. Glenner GG. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis: the beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980; 302:1283–1292.5. Rajkumar SV, Gertz MA, Kyle RA. Primary systemic amyloidosis with delayed progression to multiple myeloma. Cancer. 1998; 82:1501–1505.6. Madan S, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Buadi F, Hayman SR, Zeldenrust SR, et al. Clinical features and treatment response of light chain (AL) amyloidosis diagnosed in patients with previous diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010; 85:232–238.7. Hui AN, Koss MN, Hochholzer L, Wehunt WD. Amyloidosis presenting in the lower respiratory tract. Clinicopathologic, radiologic, immunohistochemical, and histochemical studies on 48 cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986; 110:212–218.8. Kung J, Zhuang H, Yu JQ, Duarte PS, Alavi A. Intense fluorodeoxyglucose activity in pulmonary amyloid lesions on positron emission tomography. Clin Nucl Med. 2003; 28:975–976.9. Kim CH, Kim S, Kwon OJ, Han SK, Lee JS, Kim KY. Pulmonary diffuse alveolar septal amyloidosis: diagnosed by transbronchial lung biopsy. Korean J Intern Med. 1990; 5:63–68.10. Park HS, Kim HJ, Kho YM, Seo JY, Chung MP, Kwon OJ, et al. A case of pulmonary diffuse alveolar amyloidosis localized in the lung. Korean J Med. 1998; 55:956–959.11. Kwon SW, Kim YK, Jung KH, Kim DS, Jeon WK, Suh YL. A case of tracheo-bronchial amyloidosis. Korean J Med. 1993; 45:690–695.12. Kwak YG, Kim HJ, Lee CH, Kim SY, Cho JH, Kwak SM, et al. A case of primary localized tracheobronchial amyloidosis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2002; 52:174–178.13. Jung SK, Oh J, Roh YW, Kong HS, Park KY, Park JW, et al. A case of primary diffuse nodular pulmonary amyloidosis localized in the lung. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2000; 49:365–371.14. Gottenberg JE, Merle-Vincent F, Bentaberry F, Allanore Y, Berenbaum F, Fautrel B, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy in fifteen patients with AA amyloidosis secondary to inflammatory arthritides: a followup report of tolerability and efficacy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48:2019–2024.15. Palladini G, Perfetti V, Obici L, Caccialanza R, Semino A, Adami F, et al. Association of melphalan and high-dose dexamethasone is effective and well tolerated in patients with AL (primary) amyloidosis who are ineligible for stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2004; 103:2936–2938.