Tuberc Respir Dis.
2015 Apr;78(2):125-127. 10.4046/trd.2015.78.2.125.
Agranulocytosis Induced by Ethambutol in a Patient with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. hms43@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2320605
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2015.78.2.125
Abstract
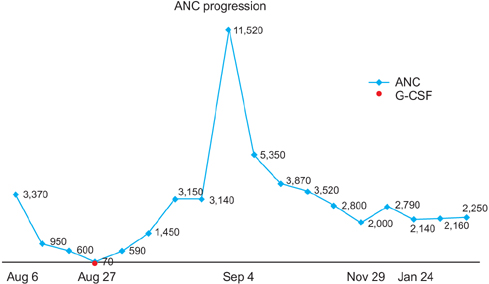
- We report a case of agranulocytosis caused by ethambutol in a 79-year-old man with pulmonary tuberculosis. He was referred for fever and skin rash developed on 21th day after antituberculosis drugs (isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide) intake. Complete blood count at the time of diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis was normal. On the seventh admission day, agranulocytosis was developed with absolute neutrophil count of 70/microL. We discontinued all antituberculosis drugs, and then treated with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Three days later, the number of white blood cell returned to normal. We administered isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol in order with an interval. However, fever and skin rash developed again when adding ethambutol, so we discontinued ethambutol. After these symptoms disappeared, we added rifampicin and ethambutol in order with an interval. However after administering ethambutol, neutropenia developed, so we discontinued ethambutol again. He was cured with isoniazid, rifampicin, and pyrazinamide for 9 months.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Umeki S. Adverse effects of antitubercular drugs and significance of measurement of the drug-stimulating lymphocyte transformation rate. Jpn J Med. 1989; 28:335–340.2. Shishido Y, Nagayama N, Masuda K, Baba M, Tamura A, Nagai H, et al. Agranulocytosis due to anti-tuberculosis drugs including isoniazid (INH) and rifampicin (RFP): a report of four cases and review of the literature. Kekkaku. 2003; 78:683–689.3. Citron KM. Ethambutol: a review with special reference to ocular toxicity. Tubercle. 1969; 50:Suppl. 32–36.4. Girling DJ. Adverse effects of antituberculosis drugs. Drugs. 1982; 23:56–74.5. Wong CF, Yew WW. Ethambutol-induced neutropenia and eosinophilia. Chest. 1994; 106:1638–1639.6. Tattersall PE. Agranulocytosis and anaemia associated with disseminated tuberculosis. Br Med J. 1957; 2:1351–1352.7. Jenkins PF, Williams TD, Campbell IA. Neutropenia with each standard antituberculosis drug in the same patient. Br Med J. 1980; 280:1069–1070.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bitemporal Hemianopsia in Ethambutol-Induced Optic Neuropathy
- A Case of Acute Kidney Injury in a Patient with Pulmonary Tuberculosis Receiving Ethambutol Therapy
- Development of Multidrug Resistance during Standardized Treatment in a Patient with Drug-Sensitive Tuberculosis
- Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis in elderly
- Lichenoid Drug Eruption due to Ethambutol