Korean J Urol.
2011 Jan;52(1):64-67.
Concomitant Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery for Ureterolithotomy and Contralateral Renal Cyst Marsupialization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Eulji Hospital, Eulji University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. swleepark@gmail.com
Abstract
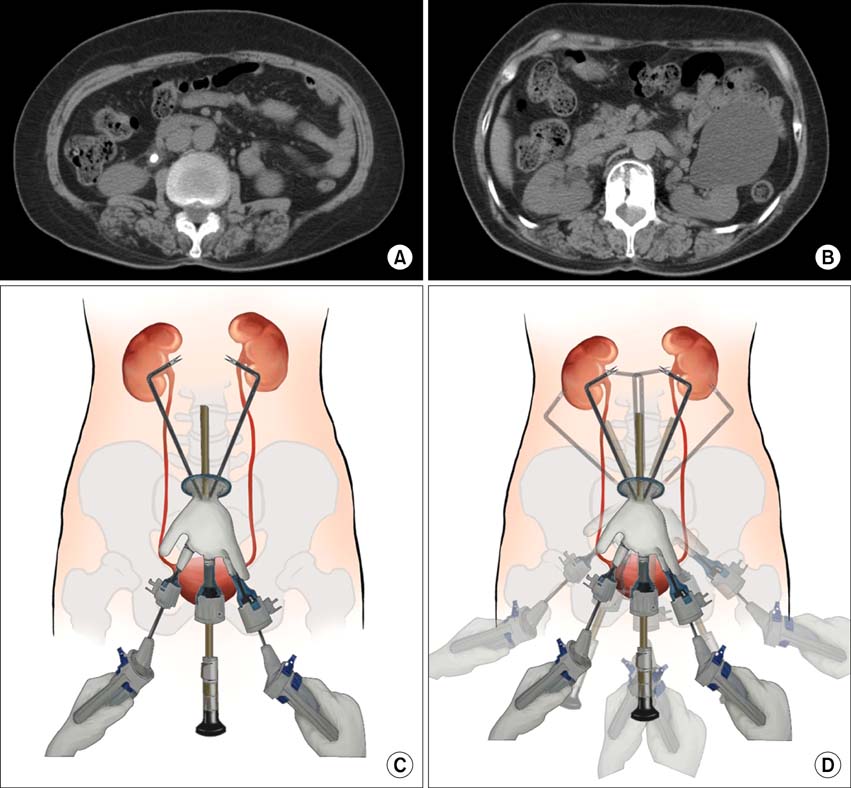
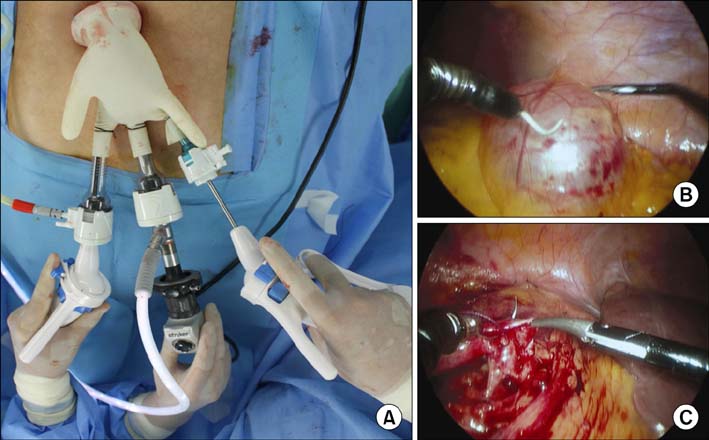
- A 63-year-old woman presented with acute right-flank pain and left-flank pain. Computed tomography identified a right ureter stone and a left renal cyst. The patient underwent concomitant laparoendoscopic single-site surgery (LESS) for ureterolithotomy and renal cyst marsupialization with the use of an Alexis(R) wound retractor, which was inserted through the umbilical incision. Flexible laparoscopic instruments and conventional rigid instruments were used during LESS following a procedure similar to that used with conventional laparoscopic surgery without additional transcutaneous ports. LESS may be more efficient at treating bilateral diseases than is conventional laparoscopic surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kaouk JH, Haber GP, Goel RK, Desai MM, Aron M, Rackley RR, et al. Single-port laparoscopic surgery in urology: initial experience. Urology. 2008. 71:3–6.2. Box G, Averch T, Cadeddu J, Cherullo E, Clayman R, Desai M, et al. Nomenclature of natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) and laparoendoscopic single-site surgery (LESS) procedures in urology. J Endourol. 2008. 22:2575–2581.3. Lee SY, Kim YT, Park HY, Lee TY, Park SY. Initial experience with laparoendoscopic single-site surgery by use of a homemade transumbilical port in urology. Korean J Urol. 2010. 51:613–618.4. Jeong CW, Park YH, Shin CS, Kim HH. Synchronous bilateral laparoendoscopic single-site adrenalectomy. J Endourol. 2010. 24:1301–1305.5. Micali S, Isgrò G, De Stefani S, Pini G, Sighinolfi MC, Bianchi G. Retroperitoneal laparoendoscopic single-site surgery: preliminary experience in kidney and ureteral indications. Eur Urol. 2010. Epub ahead of print.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery for Benign Urologic Disease with a Homemade Single Port Device: Design and Tips for Beginners
- Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery (LESS) for Excision of a Seminal Vesicle Cyst Associated with Ipsilateral Renal Agenesis
- Concomitant Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery for Vesicolithotomy and Finger-Assisted Single-Port Transvesical Enucleation of the Prostate
- Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgeries: A Single-Center Experience of 171 Consecutive Cases
- Simultaneous Robot-Assisted Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Partial Nephrectomy and Standard Radical Prostatectomy