Korean J Urol.
2012 Mar;53(3):209-213.
Giant Multilocular Cystadenoma of the Prostate: A Rare Cause of Huge Cystic Pelvic Mass
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Istanbul University Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Istanbul, Turkey.
- 2Department of Urology, Istanbul University Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Istanbul, Turkey. bulonal@yahoo.com
- 3Department of Pathology, Istanbul University Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Istanbul, Turkey.
Abstract
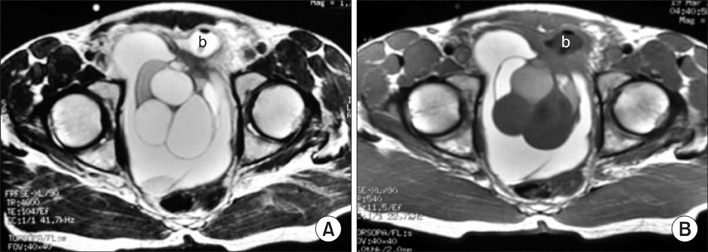
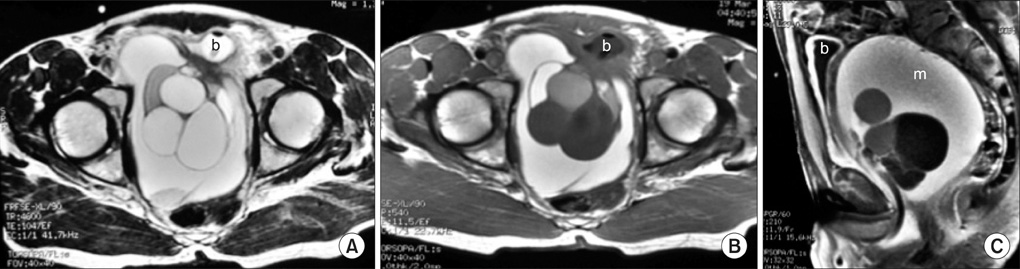
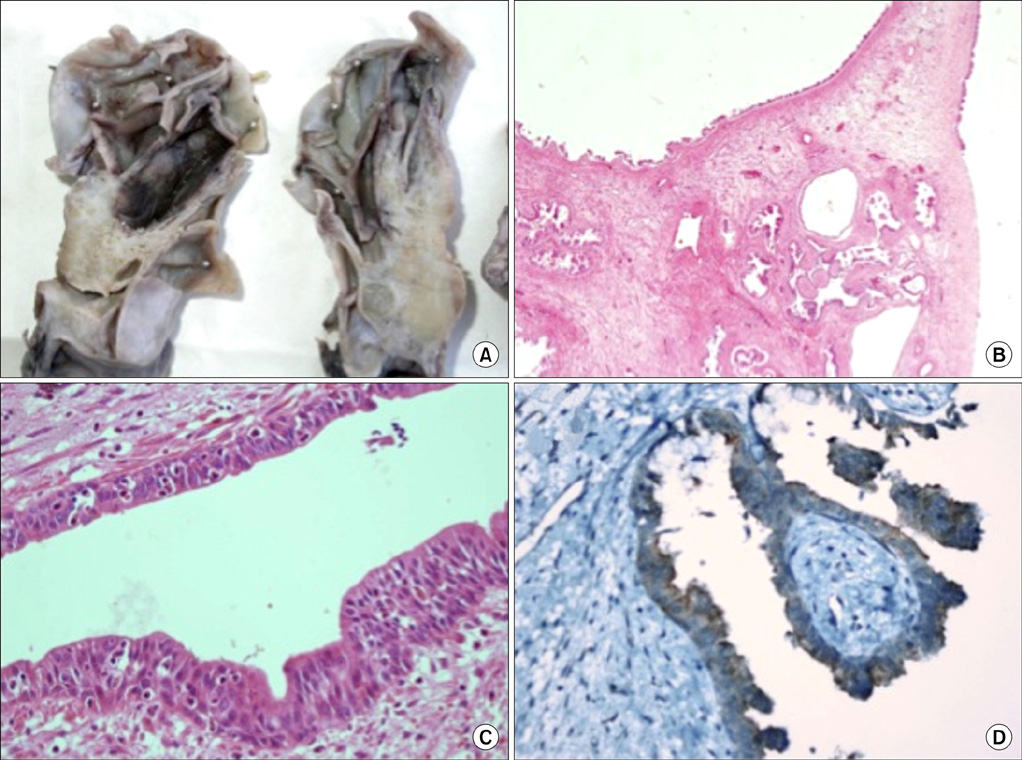
- Giant multilocular prostatic cystadenoma is a rare benign tumor that evolves from the prostate gland. Obstructive voiding symptoms occur in all reported cases. These lesions do not invade adjacent structures. Preoperative radiologic evaluation can define the benign nature of the lesion. Here we report a case of large cystic lesions identified by magnetic resonance imaging and sonographic findings that caused an extensive mass effect in the pelvis. When retrovesical, huge cystic lesions fill the pelvis completely in young men, with high levels of serum prostate-specific antigen, giant multilocular prostatic cystadenoma should be considered as a differential diagnosis. To our knowledge, this is the youngest case of prostatic cystadenoma reported in the literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Watanabe J, Konishi T, Takeuchi H, Tomoyoshi T. A case of giant prostatic cystadenoma. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1990. 36:1077–1079.2. Maluf HM, King ME, DeLuca FR, Navarro J, Talerman A, Young RH. Giant multilocular prostatic cystadenoma: a distinctive lesion of the retroperitoneum in men. A report of two cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991. 15:131–135.3. Lim DJ, Hayden RT, Murad T, Nemcek AA Jr, Dalton DP. Multilocular prostatic cystadenoma presenting as a large complex pelvic cystic mass. J Urol. 1993. 149:856–859.4. Levy DA, Gogate PA, Hampel N. Giant multilocular prostatic cystadenoma: a rare clinical entity and review of the literature. J Urol. 1993. 150:1920–1922.5. Kirsch AJ, Newhouse J, Hibshoosh H, O'Toole K, Ritter J, Benson MC. Giant multilocular cystadenoma of the prostate. Urology. 1996. 48:303–305.6. Seong BM, Cheon J, Lee JG, Kim JJ, Chae YS. A case of multilocular prostatic cystadenoma. J Korean Med Sci. 1998. 13:554–558.7. Matsumoto K, Egawa S, Iwabuchi K, Baba S. Prostatic cystadenoma presenting as a large multilocular mass. Int J Urol. 2002. 9:410–412.8. Rusch D, Moinzadeh A, Hamawy K, Larsen C. Giant multilocular cystadenoma of the prostate. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 179:1477–1479.9. Allen EA, Brinker DA, Coppola D, Diaz JI, Epstein JI. Multilocular prostatic cystadenoma with high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Urology. 2003. 61:644.10. Datta MW, Hosenpud J, Osipov V, Young RH. Giant multilocular cystadenoma of the prostate responsive to GnRH antagonists. Urology. 2003. 61:225.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Giant Multilocular Cystadenoma of the Prostate: A Case Report
- Erratum: Giant Multilocular Cystadenoma of the Prostate: A Rare Cause of Huge Cystic Pelvic Mass
- Retrovesical Multilocular Prostatic Cystadenoma Mimicking a Pelvic Cavity Tumor
- A case of multilocular prostatic cystadenoma
- Radiology findings of abdominal cystic lymphangioma