Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2014 Jun;17(2):112-115.
Duodenal Perforation: Unusual Complication of Gastrostomy Tube Replacement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Surgery, Pusan National University Children's Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatric Surgery, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. spkhy2@snu.ac.kr
Abstract
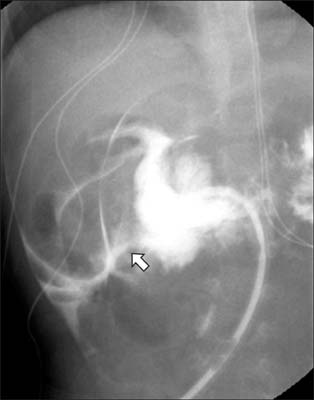
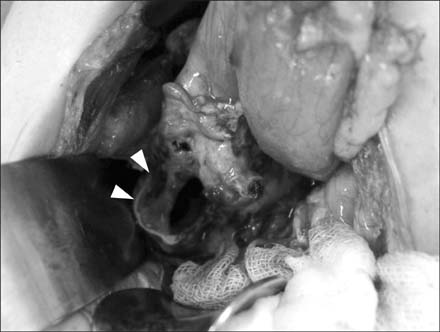
- Feeding gastrostomy is widely used for children with feeding impairment. The replacement of gastrostomy tube is known as an easy and safe procedure. However, various complications associated with replacement of gastrostomy tube were reported, including fistula disruption and colo-cutaneous fistula. For replacement of gastrostomy tube in small children with small stomach, special cautions are needed. Here, we report a rare case of duodenal perforation as an acute complication after the replacement of gastrostomy tube for a 33-month-old girl.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fascetti-Leon F, Gamba P, Dall'Oglio L, Pane A, dé Angelis GL, Bizzarri B, et al. Complications of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children: results of an Italian multicenter observational study. Dig Liver Dis. 2012; 44:655–659.
Article2. Nishiwaki S, Araki H, Fang JC, Hayashi M, Takada J, Iwashita M, et al. Retrospective analyses of complications associated with transcutaneous replacement of percutaneous gastrostomy and jejunostomy feeding devices. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:784–791.
Article3. Showalter CD, Kerrey B, Spellman-Kennebeck S, Timm N. Gastrostomy tube replacement in a pediatric ED: frequency of complications and impact of confirmatory imaging. Am J Emerg Med. 2012; 30:1501–1506.
Article4. Imamura H, Konagaya T, Hashimoto T, Kasugai K. Acute pancreatitis and cholangitis: a complication caused by a migrated gastrostomy tube. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:5285–5287.
Article5. Taheri MR, Singh H, Duerksen DR. Peritonitis after gastrostomy tube replacement: a case series and review of literature. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2011; 35:56–60.6. Moriwaki Y, Arata S, Tahara Y, Toyoda H, Kosuge T, Suzuki N. Duodenal perforation due to compression necrosis by the tip of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube. Nutrition. 2011; 27:979–981.
Article7. Schrag SP, Sharma R, Jaik NP, Seamon MJ, Lukaszczyk JJ, Martin ND, et al. Complications related to percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes. A comprehensive clinical review. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2007; 16:407–418.8. Bustorff-Silva J, Perez CA, Fonkalsrud EW, Hoh C, Raybould HE. Gastric emptying after fundoplication is dependent on changes in gastric volume and compliance. J Pediatr Surg. 1999; 34:1232–1235.
Article9. Dar AQ, Shah ZA. Anesthesia and sedation in pediatric gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures: a review. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 2:257–262.
Article10. Lee MC. Sedation for pediatric endoscopy. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2014; 17:6–12.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Severe Gastric Ulcer Bleeding after Exchange for Replacement Balloon Gastrostomy Tube in Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
- Duodenal Decubitus Ulcer Caused by Percutaneous Endoscopic Transgastric Jejunostomy Tube
- Percutaneous Radiologic Gastrostomy: A 12-Year Series
- Two Cases of Early Onset Acute Buried Bumper Syndrome after Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
- Massive Gastric Bleeding Occuring after the Replacement of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube