Korean J Urol.
2010 Apr;51(4):239-244.
Correlation between Claudins Expression and Prognostic Factors in Prostate Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. chp@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
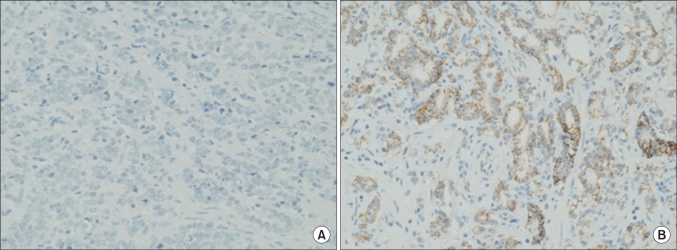
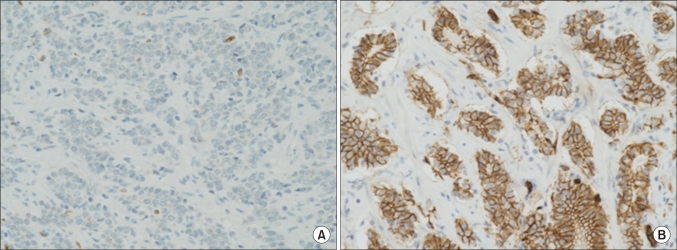
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the correlation between the expression of claudins and prognostic factors in patients with prostate cancer. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The subjects of this study were 48 patients who had undergone surgery for prostate cancer. The Gleason score (6 or lower, 7 or higher), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, T stage, biochemical recurrence, local recurrence, and distant metastasis were compared according to the expression of claudin-1 and claudin-5 in prostate cancer. RESULTS: In the group with a low expression of claudin-1, the Gleason score was 7 points or higher in 18 cases (82%) and 6 points or lower in 4 cases (18%). In the group with a high expression of claudin-1, the Gleason score was 7 points or higher in 13 cases (50%) and 6 points or lower in 13 cases (50%). Thus, the low-expression group had more cases with a Gleason score of 7 or higher (p=0.022). The group with a low expression of claudin-5 also had more cases with a Gleason score of 7 or higher (p=0.011). The mean PSA values in the groups with a low and high expression of claudin-1 were 9.6 ng/ml and 5.6 ng/ml, respectively (p=0.007). A low expression of claudin-5 was also associated with a high PSA value (p=0.002). There was no statistical difference in the expression of claudin-1 and claudin-5 by T stage, biochemical recurrence, local recurrence, or distant metastasis. CONCLUSIONS: The low expression of claudin-1, claudin-5 was associated with a Gleason score of 7 or higher and a high PSA value in prostate cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oliver SE, May MT, Gunnell D. International trends in prostate-cancer mortality in the "PSA ERA". Int J Cancer. 2001; 92:893–898. PMID: 11351313.
Article2. Väre P, Loikkanen I, Hirvikoski P, Vaarala MH, Soini Y. Low claudin expression is associated with high Gleason grade in prostate adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2008; 19:25–31. PMID: 18097572.
Article3. Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S. Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol. 1998; 141:1539–1550. PMID: 9647647.
Article4. Tsukita S, Furuse M. Claudin-based barrier in simple and stratified cellular sheets. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002; 14:531–536. PMID: 12231346.
Article5. Sawada N, Murata M, Kikuchi K, Osanai M, Tobioka H, Kojima T, et al. Tight junctions and human diseases. Med Electron Microsc. 2003; 36:147–156. PMID: 14505058.
Article6. Matsuda M, Kubo A, Furuse M, Tsukita S. A peculiar internalization of claudins, tight junction-specific adhesion molecules, during the intercellular movement of epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2004; 117:1247–1257. PMID: 14996944.
Article7. Jiang WG, Puntis MC, Hallett MB. Molecular and cellular basis of cancer invasion and metastasis: implications for treatment. Br J Surg. 1994; 81:1576–1590. PMID: 7827878.
Article8. Turksen K, Troy TC. Barriers built on claudins. J Cell Sci. 2004; 117:2435–2447. PMID: 15159449.
Article9. Miwa N, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Niikawa N, Nakamura Y, Furukawa Y. Involvement of claudin-1 in the bata-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway and its frequent upregulation in human colorectal cancers. Oncol Res. 2001; 12:469–476. PMID: 11939410.10. Tsukahara M, Nagai H, Kamiakito T, Kawata H, Takayashiki N, Saito K, et al. Distinct expression patterns of claudin-1 and claudin-4 in intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Pathol Int. 2005; 55:63–69. PMID: 15693851.
Article11. Kominsky SL, Argani P, Korz D, Evron E, Raman V, Garrett E, et al. Loss of the tight junction protein claudin-7 correlates with histological grade in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncogene. 2003; 22:2021–2033. PMID: 12673207.
Article12. Tokes AM, Kulka J, Paku S, Szik A, Páska C, Novák PK, et al. Claudin-1, -3 and -4 proteins and mRNA expression in benign and malignant breast lesions: a research study. Breast Cancer Res. 2005; 7:R296–R305. PMID: 15743508.
Article13. Hough CD, Sherman-Baust CA, Pizer ES, Montz FJ, Im DD, Rosenshein NB, et al. Large-scale serial analysis of gene expression reveals genes differentially expressed in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:6281–6287. PMID: 11103784.14. Long H, Crean CD, Lee WH, Cummings OW, Gabig TG. Expression of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin receptors claudin-3 and claudin-4 in prostate cancer epithelium. Cancer Res. 2001; 61:7878–7881. PMID: 11691807.15. Gumbiner BM. Cell adhesion: the molecular basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell. 1996; 84:345–357. PMID: 8608588.
Article16. Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Nava P, Jaramillo BE. Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2003; 81:1–44. PMID: 12475568.17. Hornsby CD, Cohen C, Amin MB, Picken MM, Lawson D, Yin-Goen Q, et al. Claudin-7 immunohistochemistry in renal tumors: a candidate marker for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma identified by gene expression profiling. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007; 131:1541–1546. PMID: 17922590.
Article18. Nichols LS, Ashfaq R, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA. Claudin 4 protein expression in primary and metastatic pancreatic cancer: support for use as a therapeutic target. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004; 121:226–230. PMID: 14983936.19. Lee SM, Lee JH, Kim BG, Kim YS, Park YG, Chi KC, et al. Correlation of decreased expressions of claudin 4 and E-cadherin proteins and the clinicopathologic factors of stomach cancer. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007; 73:221–226.20. Tokés AM, Kulka J, Paku S, Máthé M, Páska C, Lódi C, et al. The expression of five different claudins in invasive breast carcinomas: comparison of pT1pN1 and pT1pN0 tumors. Pathol Res Pract. 2005; 201:537–544. PMID: 16259105.21. Soler AP, Miller RD, Laughlin KV, Carp NZ, Klurfeld DM, Mullin JM. Increased tight junctional permeability is associated with the development of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis. 1999; 20:1425–1431. PMID: 10426787.
Article22. Choi HJ, Jung JH, Yoo J, Kang SJ, Lee KY. Expression of claudin-1 and -4 in benign lesions and invasive ductal carcinomas of the breast. Korean J Pathol. 2007; 41:232–237.23. Sheehan GM, Kallakury BV, Sheehan CE, Fisher HA, Kaufman RP Jr, Ross JS. Loss of claudins-1 and -7 and expression of claudins-3 and -4 correlate with prognostic variables in prostatic adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2007; 38:564–569. PMID: 17306334.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Invited Commentary: Role of Estrogen Receptor-alpha in Regulating Claudin-6 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells
- Correlation between Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 Expression and Prognostic Factors in Patients with Prostate Cancer
- Claudin-1, -2, -4, and -5: comparison of expression levels and distribution in equine tissues
- Prognostic Value of TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2 Expression and Ki-67 Labelling Index in Prostate Cancer
- Correlation of AR, EGFR, and HER2 Expression Levels in Prostate Cancer: Immunohistochemical Analysis and Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization