Korean J Urol.
2008 Feb;49(2):107-112.
Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Nephrectomy for Inflammatory Renal Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, Cheonan, Korea. ysurol@schch.co.kr
- 2Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University College of Medicine, Masan, Korea.
Abstract
-
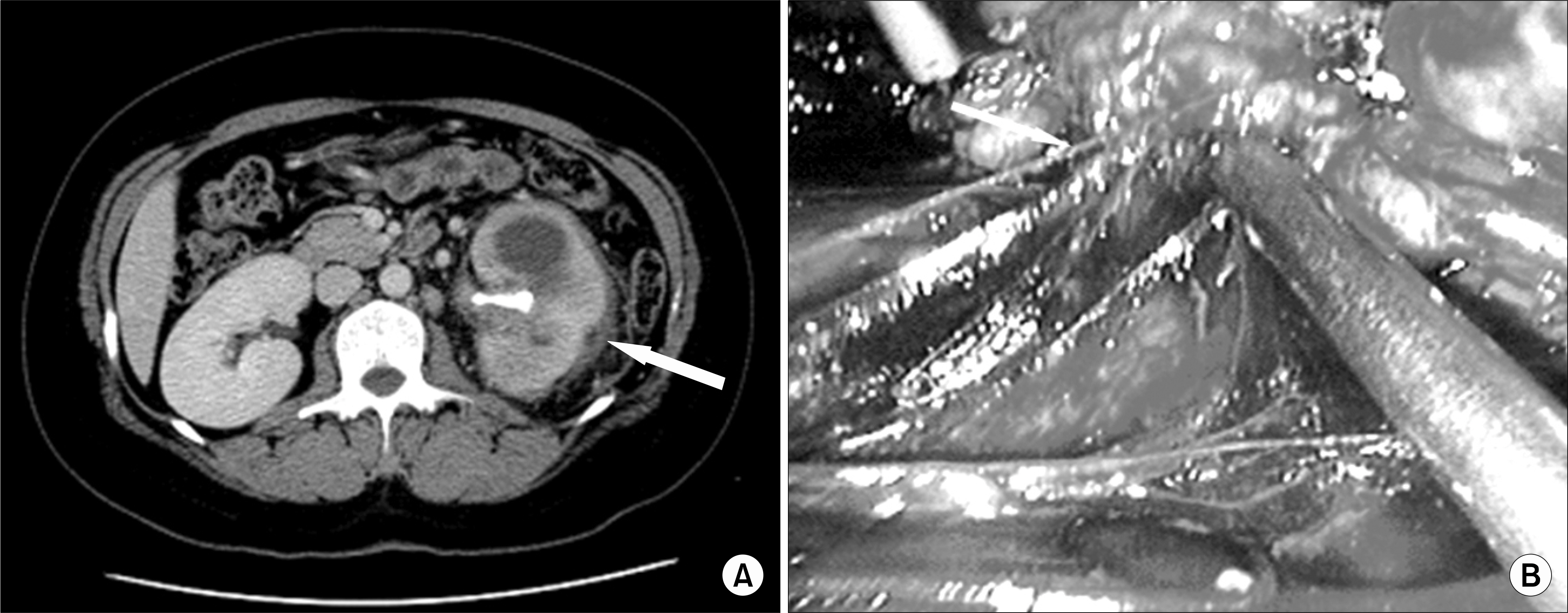
PURPOSE: Retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy for inflammatory renal conditions remains technically challenging, but can prevent intraperitoneal contamination by inflammatory or pathologic materials and decrease the risk of visceral injury or peritoneal morbidity. We evaluated retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy in terms of feasibility, safety, and efficacy in inflammatory renal disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
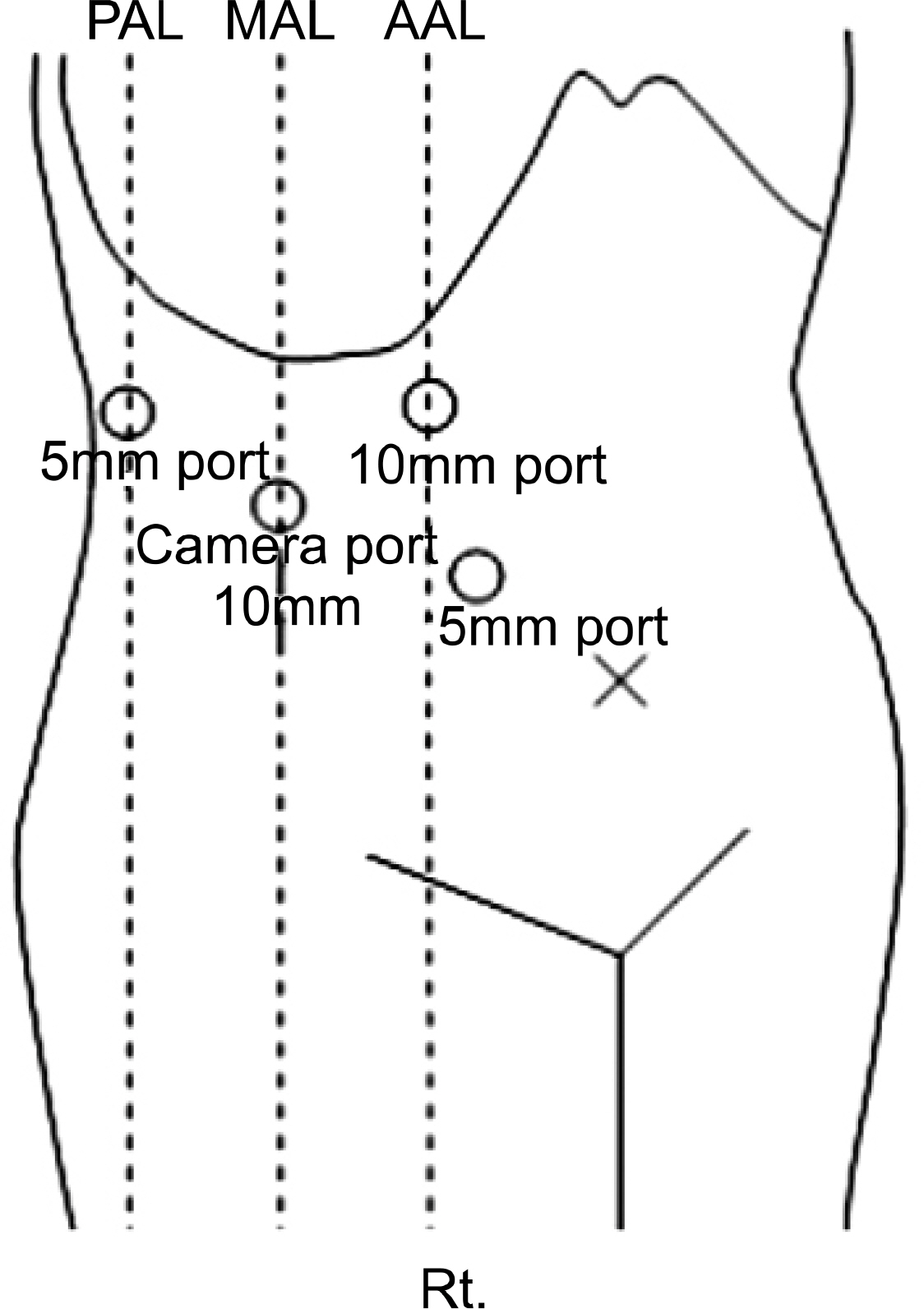
Between March 2003 and June 2006, retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy was performed in 39 patients with benign renal disease. Of the 39 patients, 18(group 1) had inflammatory renal diseases with perinephric stranding on CT, which was confirmed as an adhesion during surgery. The remaining 21 patients(group 2) had nonfunctioning kidneys without significant inflammation. Intraoperative and postoperative clinical parameters were analyzed and compared between the 2 groups.
RESULTS
Retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy was successful in all 39 patients without conversion to open surgery. Group 1 included tuberculous pyelonephritic kidney(n=11), xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (n=3), pyonephrosis(n=2) and renal abscess(n=2). Group 2 included chronic pyelonephritis(n=12), ureteropelvic junction obstruction(UPJ) stricture(n=6), and cystic disease(n=3). The mean operating time and the mean estimated blood loss were significantly different between the 2 groups(p<0.001). The mean time to oral intake and ambulation, and the mean duration of hospitalization were not different between the 2 groups. There were 1 major and 2 minor complications in group 1 and 2 minor complications in group 2.
CONCLUSIONS
Retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy is a feasible and safe treatment modality in inflammatory renal diseases as well as other benign renal diseases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jay TB, Louis RK. Laparoscopic surgery of the kidney. Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA, editors. editors.Campbell-Walsh urology. 9th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;2007. 1759-61.2. Gaur DD, Agarwal DK, Purohit KC. Retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy: initial case report. J Urol. 1993; 149:103–5.
Article3. Gupta NP, Agrawal AK, Sood S. Tubercular pyelonephritic nonfunctioning kidney-another relative contraindication for laparoscopic nephrectomy: a case report. Adv Surg Tech A. 1997; 7:131–4.4. Rassweiler J, Fornara P, Weber M, Janetschek G, Fahlenkamp D, Henkel T, et al. Laparoscopic nephrectomy: the experience of the laparoscopy working group of the German Urologic Association. J Urol. 1998; 160:18–21.
Article5. Bercowsky E, Shalhav AL, Portis A, Elbahnasy AM, Mc-Dougall EM, Clayman RV. Is the laparoscopic approach justified in patients with xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis? Urology. 1999; 54:437–42.
Article6. Shekarriz B, Meng MV, Lu HF, Yamada H, Duh QY, Stoller ML. Laparoscopic nephrectomy for inflammatory renal conditions. J Urol. 2001; 166:2091–4.
Article7. Chibber PJ, Shah HN, Jain P. Laparoscopic nephroureterectomy for tuberculous nonfunctioning kidneys compared with laparoscopic nephroureterectomy for other diseases. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2005; 15:308–11.
Article8. Vanderbrink BA, Ost MC, Rastinehad A, Anderson A, Badlani GH, Smith AD, et al. Laparoscopic versus open radical nephrectomy for xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: contemporary outcome analysis. J Endourol. 2007; 21:65–70.9. Hemal AK, Gupta NP, Kumar R. Comparison of retroperitoneoscopic nephrectomy with open surgery for tuberculous nonfunctioning kidneys. J Urol. 2000; 164:32–5.
Article10. Kim HH, Lee KS, Park KJ, Ahn HJ. Laparoscopic nephrectomy for nonfunctioning tuberculous kidney. J Endourol. 2000; 14:433–7.
Article11. Hemal AK, Gupta NP, Wadhwa SN, Goel A, Kumar R. Retroperitoneoscopic nephrectomy and nephroureterectomy for benign nonfunctioning kidneys: a single-center experience. Urology. 2001; 57:644–9.
Article12. Khaira HS, Shah RB, Wolf JS Jr. Laparoscopic and open surgical nephrectomy for xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. J Endourol. 2005; 19:813–7.
Article13. Zhang X, Zheng T, Ma X, Li HZ, Li LC, Wang SG, et al. Comparison of retroperitoneoscopic nephrectomy versus open approaches to nonfunctioning tuberculous kidney: a report of 44 cases. J Urol. 2005. 173:1586–9.14. Kim HH, Lee KS, Park K, Ahn H. Laparoscopic nephrectomy for tuberculous kidney. Korean J Urol. 2000; 41:554–9.15. Jay TB, Louis RK. Laparoscopic surgery of the kidney. Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA, editors. editors.Campbell-Walsh urology. 9th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;2007. 1762-9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Hand-assisted Laparoscopic Versus Retroperitoneo-scopic Radical Nephrectomy
- Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy using a Microwave Tissue Coagulator for Small Renal Tumor
- Initial Experience of Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Laparoscopic Surgery in Urology(I)
- Pneumothorax during Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Nephrectomy: A case report