Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Apr;40(2):190-196. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.190.
Assessment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Patients With Parkinson Disease: Use of Ultrasonography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. khojing@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2309916
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.190
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
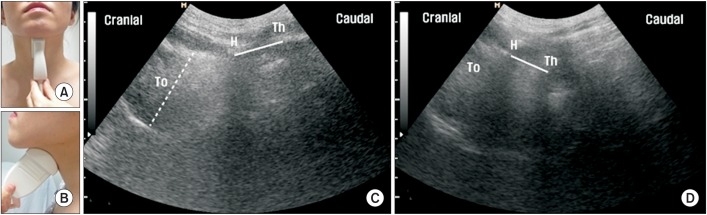
To compare tongue thickness, the shortest hyoid-thyroid approximation (distance between the hyoid bone and thyroid cartilage), and the time interval between the initiation of tongue movement and the time of the shortest hyoid-thyroid approximation, by using ultrasonography in healthy controls and patients with Parkinson disease (PD).
METHODS
Healthy controls and PD patients with dysphagia were compared. Ultrasonography was performed 3 times for the evaluation of tongue thickness, the shortest hyoid-thyroid approximation, and the time between the initiation of tongue movement and the shortest hyoid-thyroid approximation.
RESULTS
A total of 24 healthy controls and 24 PD patients with dysphagia were enrolled. No significant differences were demonstrated between the two groups for the shortest hyoid-thyroid approximation (controls, 1.19±0.34 cm; PD patients, 1.37±0.5 cm; p=0.15) and tongue thickness (controls, 4.42±0.46 cm; PD patients, 4.27±0.51 cm; p=0.3). In contrast, the time to the shortest hyoid-thyroid approximation was significantly different between the two groups (controls, 1.53±0.87 ms; PD patients, 2.4±1.4 ms, p=0.048).
CONCLUSION
Ultrasonography can be useful in evaluating dysphagia in patients with PD by direct visualization and measurement of the hyoid bone. Moreover, ultrasonography might contribute to a greater understanding of the pathophysiology of dysphagia in PD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jankovic J. Parkinson's disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008; 79:368–376. PMID: 18344392.
Article2. Storch A, Schneider CB, Wolz M, Sturwald Y, Nebe A, Odin P, et al. Nonmotor fluctuations in Parkinson disease: severity and correlation with motor complications. Neurology. 2013; 80:800–809. PMID: 23365054.
Article3. Nicaretta DH, Rosso AL, Mattos JP, Maliska C, Costa MM. Dysphagia and sialorrhea: the relationship to Parkinson's disease. Arq Gastroenterol. 2013; 50:42–49. PMID: 23657306.4. Kalf JG, de Swart BJ, Bloem BR, Munneke M. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012; 18:311–315. PMID: 22137459.
Article5. Cereda E, Cilia R, Klersy C, Canesi M, Zecchinelli AL, Mariani CB, et al. Swallowing disturbances in Parkinson's disease: a multivariate analysis of contributing factors. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014; 20:1382–1387. PMID: 25456827.
Article6. Baijens LW, Speyer R, Passos VL, Pilz W, Roodenburg N, Clave P. Swallowing in Parkinson patients versus healthy controls: reliability of measurements in videofluoroscopy. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2011; 2011:380682. PMID: 21977026.
Article7. Monte FS, da Silva-Junior FP, Braga-Neto P, Nobre e Souza MA, de Bruin VM. Swallowing abnormalities and dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2005; 20:457–462. PMID: 15625689.
Article8. Troche MS, Okun MS, Rosenbek JC, Musson N, Fernandez HH, Rodriguez R, et al. Aspiration and swallowing in Parkinson disease and rehabilitation with EMST: a randomized trial. Neurology. 2010; 75:1912–1919. PMID: 21098406.
Article9. Logemann JA. Role of the modified barium swallow in management of patients with dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997; 116:335–338. PMID: 9121786.
Article10. Kuhl V, Eicke BM, Dieterich M, Urban PP. Sonographic analysis of laryngeal elevation during swallowing. J Neurol. 2003; 250:333–337. PMID: 12638025.
Article11. Macrae PR, Doeltgen SH, Jones RD, Huckabee ML. Intra- and inter-rater reliability for analysis of hyoid displacement measured with sonography. J Clin Ultrasound. 2012; 40:74–78. PMID: 21953135.
Article12. Kim JH, Kim MS. Lateral pharyngeal wall motion analysis using ultrasonography in stroke patients with dysphagia. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012; 38:2058–2064. PMID: 23062372.
Article13. Yabunaka K, Sanada H, Sanada S, Konishi H, Hashimoto T, Yatake H, et al. Sonographic assessment of hyoid bone movement during swallowing: a study of normal adults with advancing age. Radiol Phys Technol. 2011; 4:73–77. PMID: 20945118.
Article14. Huang YL, Hsieh SF, Chang YC, Chen HC, Wang TG. Ultrasonographic evaluation of hyoid-larynx approximation in dysphagic stroke patients. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009; 35:1103–1108. PMID: 19427098.
Article15. Hsiao MY, Chang YC, Chen WS, Chang HY, Wang TG. Application of ultrasonography in assessing oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012; 38:1522–1528. PMID: 22698507.
Article16. Volonte MA, Porta M, Comi G. Clinical assessment of dysphagia in early phases of Parkinson's disease. Neurol Sci. 2002; 23(Suppl 2):S121–S122. PMID: 12548373.17. Goetz CG, Poewe W, Rascol O, Sampaio C, Stebbins GT, Counsell C, et al. Movement Disorder Society Task Force report on the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale: status and recommendations. Mov Disord. 2004; 19:1020–1028. PMID: 15372591.18. Morgan A, Ward E, Murdoch B, Bilbie K. Acute characteristics of pediatric dysphagia subsequent to traumatic brain injury: videofluoroscopic assessment. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 2002; 17:220–241. PMID: 12086576.19. Nagaya M, Kachi T, Yamada T, Igata A. Videofluorographic study of swallowing in Parkinson's disease. Dysphagia. 1998; 13:95–100. PMID: 9513304.
Article20. Shawker TH, Sonies B, Hall TE, Baum BF. Ultrasound analysis of tongue, hyoid, and larynx activity during swallowing. Invest Radiol. 1984; 19:82–86. PMID: 6398320.
Article21. Fanucci A, Cerro P, Ietto F, Brancaleone C, Berardi F. Physiology of oral swallowing studied by ultrasonography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1994; 23:221–225. PMID: 7835528.
Article22. Mu L, Sobotka S, Chen J, Su H, Sanders I, Adler CH, et al. Altered pharyngeal muscles in Parkinson disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2012; 71:520–530. PMID: 22588389.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dysphagia in the patients with Parkinson's Disease
- Oropharyngeal Cancer and Dysphagia
- Oro-Pharyngeal Dysphagia in Parkinson's Disease and Related Movement Disorders
- Swallowing Training for Patients with Impaired Cardiopulmonary Function
- Clinical Characteristics and Evaluation of Dysphagia in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease