J Clin Neurol.
2013 Jan;9(1):57-60. 10.3988/jcn.2013.9.1.57.
Two Cases of X-Linked Myotubular Myopathy with Novel MTM1 Mutations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tsko@amc.seoul.kr
- 3Medical Genetics Center, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2287572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2013.9.1.57
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Myotubular myopathy (MTM) is a congenital myopathy characterized by centrally placed nuclei in muscle fibers. Mutations in the myotubularin 1 gene (MTM1) have been identified in the most of the patients with the X-linked recessive form.
CASE REPORT
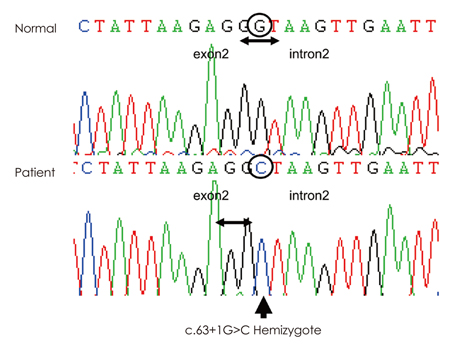
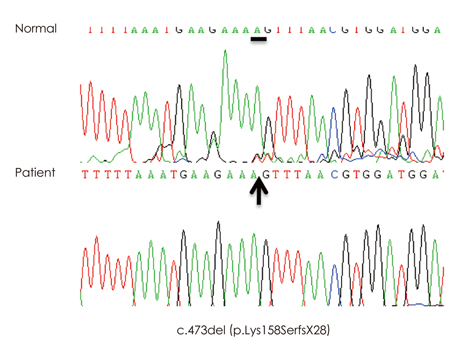
This report describes two male infants with X-linked MTM (XLMTM). Both patients presented with generalized hypotonia and respiratory difficulties since birth. We did not perform a muscle biopsy in either patient, but their conditions were diagnosed by genetic testing of MTM1. One splicing mutation, c.63+1G>C, and a frame-shift mutation, c.473delA (p. Lys158SerfxX28), were identified. Neither mutation has been reported previously.
CONCLUSIONS
Genetic testing for MTM1 is helpful for the differential diagnosis of floppy male infants. We suggest that advanced molecular genetic testing may permit a correct diagnosis while avoiding invasive procedures.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Prasad AN, Prasad C. The floppy infant: contribution of genetic and metabolic disorders. Brain Dev. 2003. 25:457–476.
Article2. Spiro AJ, Shy GM, Gonatas NK. Myotubular myopathy. Persistence of fetal muscle in an adolescent boy. Arch Neurol. 1966. 14:1–14.3. Laporte J, Biancalana V, Tanner SM, Kress W, Schneider V, Wallgren-Pettersson C, et al. MTM1 mutations in X-linked myotubular myopathy. Hum Mutat. 2000. 15:393–409.
Article4. Jungbluth H, Wallgren-Pettersson C, Laporte J. Centronuclear (myotubular) myopathy. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2008. 3:26.
Article5. Bijarnia S, Puri RD, Jain M, Kler N, Roy S, Urtizberea JA, et al. Mutation studies in X-linked myotubular myopathy in three Indian families. Indian J Pediatr. 2010. 77:431–433.
Article6. Hortobágyi T, Szabó H, Kovács KS, Bódi I, Bereg E, Katona M, et al. X-linked myotubular myopathy: report of a case with novel mutation. J Child Neurol. 2007. 22:447–451.
Article7. Pierson CR, Tomczak K, Agrawal P, Moghadaszadeh B, Beggs AH. X-linked myotubular and centronuclear myopathies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005. 64:555–564.
Article8. De Angelis MS, Palmucci L, Leone M, Doriguzzi C. Centronuclear myopathy: clinical, morphological and genetic characters. A review of 288 cases. J Neurol Sci. 1991. 103:2–9.
Article9. Joseph M, Pai GS, Holden KR, Herman G. X-linked myotubular myopathy: clinical observations in ten additional cases. Am J Med Genet. 1995. 59:168–173.
Article10. Herman GE, Finegold M, Zhao W, de Gouyon B, Metzenberg A. Medical complications in long-term survivors with X-linked myotubular myopathy. J Pediatr. 1999. 134:206–214.
Article11. Laporte J, Guiraud-Chaumeil C, Tanner SM, Blondeau F, Hu LJ, Vicaire S, et al. Genomic organization of the MTM1 gene implicated in X-linked myotubular myopathy. Eur J Hum Genet. 1998. 6:325–330.
Article12. Laporte J, Hu LJ, Kretz C, Mandel JL, Kioschis P, Coy JF, et al. A gene mutated in X-linked myotubular myopathy defines a new putative tyrosine phosphatase family conserved in yeast. Nat Genet. 1996. 13:175–182.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- X-linked Myotubular Myopathy in a Family with Two Infant Siblings: A Case with MTM1 Mutation
- X-linked recessive myotubular myopathy with MTM1 mutations
- Familial Myotubular Myopathy Occurred in a Sibling
- Myotubular myopathy: A case report
- Clinical Characteristics and Neurologic Outcomes of X-Linked Myotubular Myopathy