Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis.
2011 Dec;18(2):154-162.
Analysis of Palivizumab Prophylaxis in Patients with Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infection Caused by Respiratory Syncytial Virus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. kimhs@dumc.or.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to identify the clinical characteristics of lower respiratory tract infection due to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in young children and to provide information for an effective guideline for palivizumab administration in Korea.
METHODS
We reviewed medical charts of 167 patients under 3 years of age who were hospitalized in Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital for lower respiratory tract infection between January 2007 and February 2011. Diagnosis of the virus was made based on the multiplex real time polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
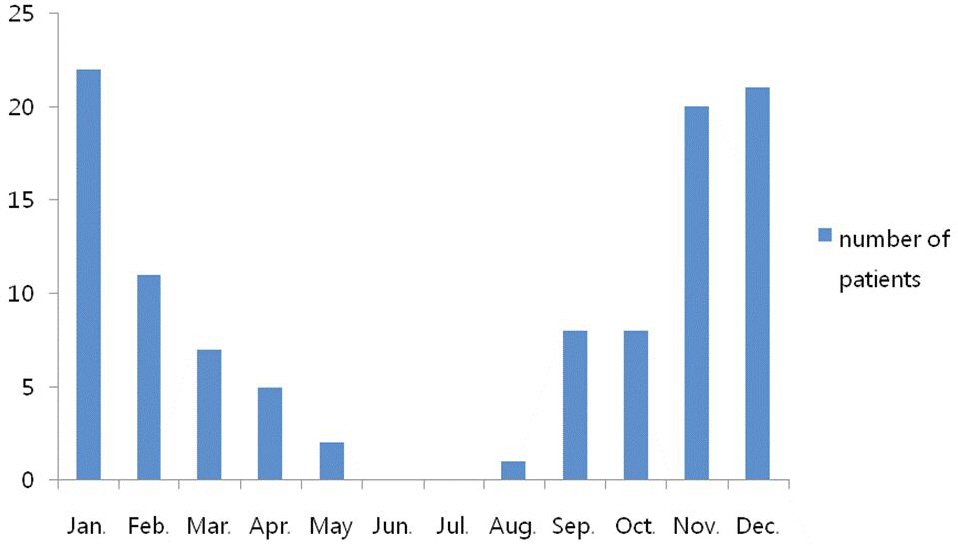
There were 113 patients who were infected by respiratory syncytial virus. 90 patients were term infants and 23 patients were preterm infants. No difference was shown between term and preterm infants except the days of admission which was 9.0+/-6.0 days and 12.6+/-21.0 days respectively. In the preterm group their mean age at the time of admission was 5.21+/-4.9 months and the mean gestational age was 33.1+/-4.3 weeks, and the mean birth weight was 2,152+/-950 g. Only 4 patients were born under 28 weeks gestational age and were candidates for palivizumab administration.
CONCLUSION
Most of the patients with severe RSV lower respiratory tract infection were term or near term infants who were not candidates for palivizumab prophylaxis. A nationwide study is needed to make a new risk stratified guideline for RSV prophylaxis for our country.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Park JS. Acute viral lower respiratory tract infections in children. Korean Journal of Pediatrics. 2009; 52:269–76.
Article2). Jung BS, Cho B, Kim HH, Lee JS. A clinical study of respiratory tract infection. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis (Korea). 1996; 6:60–3.3). Elliot AJ, Fleming DM. Viral infections and acute otitis media in young children. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 47:146–7.
Article4). Williams JV. The clinical presentation and outcomes of children infected with newly identified respiratory tract viruses. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2005; 19:569–84.
Article5). Ogra PL. Respiratory syncytial virus: the virus, the disease and the immune response. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2004; 5:119–26.
Article6). Stensballe LG, Devasundaram JK, Simoes EA. Respiratory syncytial virus epidemics: the ups and downs of a seasonal virus. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 21–32.
Article7). Hahn WH, Chang JY, Bae CW. Birth statistics and mortality rates for neonatal intensive care units in Korea during 2007: collective results from 57 hospitals. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2009; 16:36–46.8). Glezen WP, Taber LH, Frank AL, Kasel JA. Risk of primary infection and reinfection with respiratory syncytial virus. Am J Dis Child. 1986; 140:543–6.
Article9). Garenne M, Ronsmans C, Campbell H. The magnitude of mortality from acute respiratory infections in children under 5 years in developing countries. World Health Stat Q. 1992; 45:180–91.10). The IMpact-RSV Study Group. Palivizumab, a humanized respiratory syncytial virus monoclonal antibody, reduces hospitalization from respiratory syncytial virus infection in high-risk infants. Pediatrics. 1998; 102:531–7.11). Prais D, Schonfeld T, Amir J. Admission to the intensive care unit for respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis: a national survey before palivizumab use. Pediatrics. 2003; 112:548–52.
Article12). Reeve CA, Whitehall JS, Buettner PG, Norton R, Reeve DM, Francis F. Cost-effectiveness of respiratory syncytial virus prophylaxis with palivizumab. J Paediatr Child Health. 2006; 42:253–8.
Article13). Fariñ a D, Rodrí guez SP, Bauer G, Novali L, Bouzas L, Gon-z lez H, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus prophylaxis: á cost-effective analysis in Argentina. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002; 21:287–91.14). Nuijten MJ, Wittenberg W. Cost effectiveness of palivizumab in Spain: an analysis using observational data. Eur J Health Econ. 2010; 11:105–15.
Article15). Resch B, Gusenleitner W, Nuijten MJ, Lebmeier M, Wittenberg W. Cost-effectiveness of palivizumab against respiratory syncytial viral infection in high-risk children in Austria. Clin Ther. 2008; 30:749–60.
Article16). Lanctot KL, Masoud ST, Paes BA, Tarride JE, Chiu A, Hui C, et al. The cost-effectiveness of palivizumab for respiratory syncytial virus prophylaxis in premature infants with a gestational age of 32–35 weeks: a Canadian-based analysis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008; 24:3223–37.17). Denny FW, Clyde WA Jr. Acute lower respiratory tract infections in nonhospitalized children. J Pediatr. 1986; 108:635–46.
Article18). Hall CB. Respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1917–28.
Article19). Law BJ, Langley JM, Allen U, Paes B, Lee DS, Mitchell I, et al. The pediatric investigators collaborative network on infections in Canada study of predictors of hospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus infection for infants born at 33 through 35 completed weeks of gestation. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004; 23:806–14.
Article20). Law BJ, Carbonell-Estrany X, Simoes EA. An update on respiratory syncytial virus epidemiology: a developed country perspective. Respir Med. 2002; 96:1–7.
Article21). Tatochenko V, Uchaikin V, Gorelov A, Gudkov K, Campbell A, Schulz G, et al. Epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus in children 2 years of age hospitalized with≤ lower respiratory tract infections in the Russian Federation: a prospective, multicenter study. Clin Epidemiol. 2010; 2:221–7.22). Mori M, Kawashima H, Nakamura H, Nakagawa M, Kusuda S, Saji T, et al. Nationwide survey of severe respiratory syncytial virus infection in children who do not meet indications for palivizumab in Japan. J Infect Chemother. 2011; 17:254–63.
Article23). Fitzgerald DA. Preventing RSV bronchiolitis in vulnerable infants: the role of palivizumab. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2009; 10:143–7.
Article24). The PREVENT Study Group. Reduction of respiratory syncytial virus hospitalization among premature infants and infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia using respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin prophylaxis. Pediatrics. 1997; 99:93–9.25). Romero JR. Palivizumab prophylaxis of respiratory syncytial virus disease from 1998 to 2002: results from four years of palivizumab usage. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003; 22:46–54.
Article26). American academy of pediatrics committee on infectious diseases and committee of fetus and newborn. Prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infections: indications for the use of palivizumab and update on the use of RSV-IGIV. Pediatrics. 1998; 102:1211–6.27). Resch B, Paes B. Are late preterm infants as susceptible to RSV infection as full term infants? Early Hum Dev. 2011; 87:47–9.
Article28). Lanari M, Silvestri M, Rossi GA. Palivizumab prophylaxis in ‘late preterm' newborns. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010; 23:53–5.
Article29). Figueras Aloy J, Quero J, Domenech E, Lopez Herrera MC, Izquierdo I, Losada A, et al. Recommendations for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection. An Pediatr (Barc). 2005; 63:357–62.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infection of Respiratory Syncytial Virus
- Outcomes of Palivizumab Prophylaxis for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Preterm Children with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia at a Single Hospital in Korea from 2005 to 2009
- Respiratory syncytial virus prevention in children with congenital heart disease: who and how?
- Recovery of respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, influenza virus , and parainfluenza virus from nasopharyngeal aspirates from children with acute respiratory tract infections
- Clinical and epidemiologic features of respiratory sybcytial virus infection