Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2014 Jun;7(2):119-122.
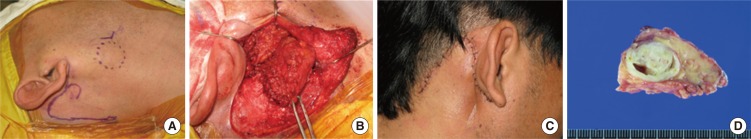
Partial Superficial Parotidectomy via Retroauricular Hairline Incision
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Asan Meidcal Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shchoi@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of retroauricular hair line incision (RAHI) in partial superficial parotidectomy by comparison with modified Blair incision or facelift incision.
METHODS
Medical records of 73 patients with benign parotid tumor who underwent partial superficial parotidectomy were retrospectively reviewed. Size and location of tumors, operative time, occurrence of facial nerve paralysis and Frey's syndrome, and cosmetic outcomes were compared among RAHI, facelift incision (FLI), modified Blair incision (MBI) groups.
RESULTS
RAHI group showed better cosmetic results than FLI group or MBI group compared with other type of incisions (P<0.001, P<0.001, respectively). Among the 3 groups, there were no significant differences of operative time and location of tumor (P=0.377), size of tumor (P>0.999), occurrence of temporary or permanent facial nerve paralysis (P=0.745) and Frey's syndrome (P=0.940).
CONCLUSION
Partial superficial parotidectomy can be done safely by RAHI in most cases of benign parotid tumor. Compared with MBI or FLI, RAHI has better cosmetic outcome with no increase of operative time or postoperative complications.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Donovan DT, Conley JJ. Capsular significance in parotid tumor surgery: reality and myths of lateral lobectomy. Laryngoscope. 1984; 3. 94(3):324–329. PMID: 6321863.2. Patey DH, Thackray AC. The treatment of parotid tumours in the light of a pathological study of parotidectomy material. Br J Surg. 1958; 3. 45(193):477–487. PMID: 13536351.
Article3. Witt RL, Rejto L. Pleomorphic adenoma: extracapsular dissection versus partial superficial parotidectomy with facial nerve dissection. Del Med J. 2009; 3. 81(3):119–125. PMID: 19507761.4. Roh JL. Extracapsular dissection of benign parotid tumors using a retroauricular hairline incision approach. Am J Surg. 2009; 5. 197(5):e53–e56. PMID: 19217603.
Article5. Roh JL, Kim HS, Park CI. Randomized clinical trial comparing partial parotidectomy versus superficial or total parotidectomy. Br J Surg. 2007; 9. 94(9):1081–1087. PMID: 17701949.
Article6. Fukushima M, Miyaguchi M, Kitahara T. Extracapsular dissection: minimally invasive surgery applied to patients with parotid pleomorphic adenoma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011; 6. 131(6):653–659. PMID: 21254958.
Article7. George KS, McGurk M. Extracapsular dissection: minimal resection for benign parotid tumours. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 9. 49(6):451–454. PMID: 21215499.8. Yamashita T, Tomoda K, Kumazawa T. The usefulness of partial parotidectomy for benign parotid gland tumors: a retrospective study of 306 cases. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1993; 500:113–116. PMID: 8452007.
Article9. Papadogeorgakis N, Skouteris CA, Mylonas AI, Angelopoulos AP. Superficial parotidectomy: technical modifications based on tumour characteristics. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2004; 12. 32(6):350–353. PMID: 15555516.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Partial Superficial Parotidectomy via Retroauricular Hairline Incision
- Retroauricular Hairline Incision and V-Shaped Incision for Parotidectomy
- Conservative Parotidectomy for Benign Parotid Tumors
- Partial Parotidectomy as a Conservative Procedure for the Parotid Tumor
- Surgical Outcome of Extracapsular Dissection of Benign Parotid Gland Tumor: A Comparative Study to Superficial Parotidectomy