Korean J Pain.
2011 Mar;24(1):53-56. 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.1.53.
Relief of Postherpetic Neuralgia with Transforaminal Epidural Injection of Magnesium: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, Bucheon, Korea. anpjuno@gmail.com
- KMID: 2278098
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.1.53
Abstract
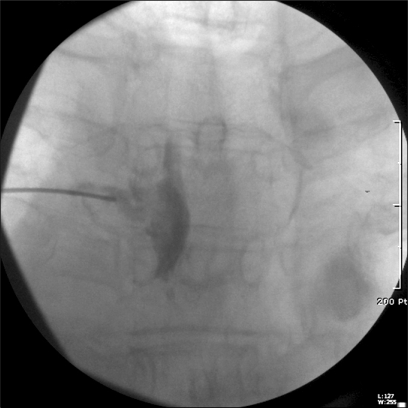
- Although postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a common chronic pain syndrome, the pathophysiology of this disorder is not well known and management is often very difficult. N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists are known to be effective in PHN, and magnesium, a physiological blocker of NMDA receptors, is widely used to treat various chronic pain disorders. Here, we present a case of the PHN refractory to conventional treatment, which was treated successfully with transforaminal epidural injection of magnesium sulphate at the affected dermatome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Medications in Treatment of Postherpetic Neuralgia
Sang Wook Shin
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(1):1-2. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Loeser JD. Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. Pain. 1986; 25:149–164. PMID: 2873549.
Article2. Kost RG, Straus SE. Postherpetic neuralgia--pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1996; 335:32–42. PMID: 8637540.
Article3. Eide PK, Jørum E, Stubhaug A, Bremnes J, Breivik H. Relief of post-herpetic neuralgia with the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor antagonist ketamine: a double-blind, cross-over comparison with morphine and placebo. Pain. 1994; 58:347–354. PMID: 7838584.
Article4. Arcioni R, Palmisani S, Tigano S, Santorsola C, Sauli V, Romanò S, et al. Combined intrathecal and epidural magnesium sulfate supplementation of spinal anesthesia to reduce post-operative analgesic requirements: a prospective, randomized, double- blind, controlled trial in patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007; 51:482–489. PMID: 17378788.
Article5. Eide PK, Stubhaug A, Stenehjem AE. Central dysesthesia pain after traumatic spinal cord injury is dependent on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation. Neurosurgery. 1995; 37:1080–1087. PMID: 8584148.
Article6. Crosby V, Wilcock A, Corcoran R. The safety and efficacy of a single dose (500 mg or 1 g) of intravenous magnesium sulfate in neuropathic pain poorly responsive to strong opioid analgesics in patients with cancer. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2000; 19:35–39. PMID: 10687324.
Article7. Brill S, Sedgwick PM, Hamann W, Di Vadi PP. Efficacy of intravenous magnesium in neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth. 2002; 89:711–714. PMID: 12393768.
Article8. Demirkaya S, Vural O, Dora B, Topçuoğlu MA. Efficacy of intravenous magnesium sulfate in the treatment of acute migraine attacks. Headache. 2001; 41:171–177. PMID: 11251702.
Article9. Collins S, Zuurmond WW, de Lange JJ, van Hilten BJ, Perez RS. Intravenous magnesium for complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (CRPS 1) patients: a pilot study. Pain Med. 2009; 10:930–940. PMID: 19496957.
Article10. Oppelt WW, MacIntyre I, Rall DP. Magnesium exchange between blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Am J Physiol. 1963; 205:959–962. PMID: 5877425.
Article11. Felsby S, Nielsen J, Arendt-Nielsen L, Jensen TS. NMDA receptor blockade in chronic neuropathic pain: a comparison of ketamine and magnesium chloride. Pain. 1996; 64:283–291. PMID: 8740606.
Article12. Ko SH, Lim HR, Kim DC, Han YJ, Choe H, Song HS. Magnesium sulfate does not reduce postoperative analgesic requirements. Anesthesiology. 2001; 95:640–646. PMID: 11575536.
Article13. Saeki H, Matsumoto M, Kaneko S, Tsuruta S, Cui YJ, Ohtake K, et al. Is intrathecal magnesium sulfate safe and protective against ischemic spinal cord injury in rabbits? Anesth Analg. 2004; 99:1805–1812. PMID: 15562076.
Article14. Chanimov M, Cohen ML, Grinspun Y, Herbert M, Reif R, Kaufman I, et al. Neurotoxicity after spinal anaesthesia induced by serial intrathecal injections of magnesium sulphate. An experimental study in a rat model. Anaesthesia. 1997; 52:223–228. PMID: 9124662.
Article15. Bilir A, Gulec S, Erkan A, Ozcelik A. Epidural magnesium reduces postoperative analgesic requirement. Br J Anaesth. 2007; 98:519–523. PMID: 17324976.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidural Neurolysis with Phenol in Postherpetic Neuragia
- The Trial of Continuous Intravenous Infusion of Magnesium in Patients with Postherpetic Neuralgia Refractory in Conventional Treatment: A report of 2 cases
- The Effects of Continuous Epidural Blockade in the Treatment of Postherpetic Neuralgia
- A Case of Diplopia after Epidural Catheterization for Postherpetic Neuralgia: A case report
- Newly Developed Urinary Retention and Motor Weakness of Lower Extremities in a Postherpetic Neuralgia Patient