Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Feb;39(1):32-38. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.1.32.
Determination of Injection Site in Flexor Digitorum Longus for Effective and Safe Botulinum Toxin Injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, St. Paul's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. park9262@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2273016
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.1.32
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To determine the optimal injection site in the flexor digitorum longus (FDL) muscle for effective botulinum toxin injection.
METHODS
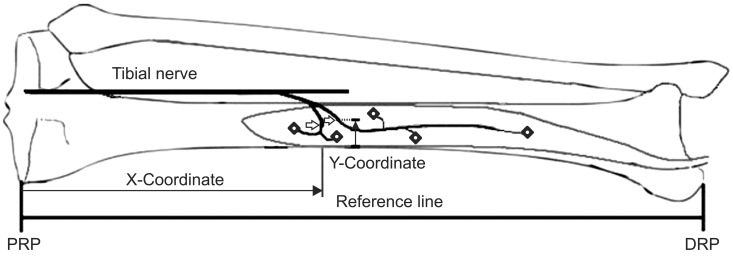
Fourteen specimens from eight adult Korean cadavers were used in this study. The most proximal medial point of the tibia plateau was defined as the proximal reference point; the most distal tip of the medial malleolus was defined as the distal reference point. The distance of a line connecting the proximal and distal reference points was defined as the reference length. The X-coordinate was the distance from the proximal reference point to the intramuscular motor endpoint (IME), or motor entry point (MEP) on the reference line, and the Y-coordinate was the distance from the nearest point from MEP on the medial border of the tibia to the MEP. IME and MEP distances from the proximal reference point were evaluated using the raw value and the X-coordinate to reference length ratio was determined as a percentage.
RESULTS
The majority of IMEs were located within 30%-60% of the reference length from the proximal reference point. The majority of the MEPs were located within 40%-60% of the reference length from the proximal reference point.
CONCLUSION
We recommend the anatomical site for a botulinum toxin injection in the FDL to be within a region 30%-60% of the reference length from the proximal reference point.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Assessment : the clinical usefulness of botulinum toxin-A in treating neurologic disorders. Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 1990; 40:1332–1336. PMID: 2202925.2. Rousseaux M, Compere S, Launay MJ, Kozlowski O. Variability and predictability of functional efficacy of botulinum toxin injection in leg spastic muscles. J Neurol Sci. 2005; 232:51–57. PMID: 15850582.
Article3. Bakheit AM. The pharmacological management of post-stroke muscle spasticity. Drugs Aging. 2012; 29:941–947. PMID: 23138834.
Article4. Lim EC, Ong BK, Seet RC. Botulinum toxin-A injections for spastic toe clawing. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2006; 12:43–47. PMID: 16198612.
Article5. Thibaut A, Chatelle C, Ziegler E, Bruno MA, Laureys S, Gosseries O. Spasticity after stroke: physiology, assessment and treatment. Brain Inj. 2013; 27:1093–1105. PMID: 23885710.
Article6. Suputtitada A. Local botulinum toxin type A injections in the treatment of spastic toes. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 81:770–775. PMID: 12362118.
Article7. Hesse S, Brandi-Hesse B, Bardeleben A, Werner C, Funk M. Botulinum toxin A treatment of adult upper and lower limb spasticity. Drugs Aging. 2001; 18:255–262. PMID: 11341473.
Article8. Burbaud P, Wiart L, Dubos JL, Gaujard E, Debelleix X, Joseph PA, et al. A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial of botulinum toxin in the treatment of spastic foot in hemiparetic patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1996; 61:265–269. PMID: 8795597.
Article9. Yelnik AP, Bonan IV. Post stroke hemiplegia: lower limb benefit from botulinum toxin (review). Ann Readapt Med Phys. 2003; 46:281–285. PMID: 12928130.10. Childers MK. Targeting the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscles. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 83(10 Suppl):S38–S44. PMID: 15448576.
Article11. Hwang K, Jin S, Hwang SH, Lee KM, Han SH. Location of nerve entry points of flexor digitorum profundus. Surg Radiol Anat. 2007; 29:617–621. PMID: 17805470.
Article12. Lepage D, Parratte B, Tatu L, Vuiller F, Monnier G. Extra-and intramuscular nerve supply of the muscles of the anterior antebrachial compartment: applications for selective neurotomy and for botulinum toxin injection. Surg Radiol Anat. 2005; 27:420–430. PMID: 16308665.13. Parratte B, Tatu L, Vuillier F, Diop M, Monnier G. Intramuscular distribution of nerves in the human triceps surae muscle: anatomical bases for treatment of spastic drop foot with botulinum toxin. Surg Radiol Anat. 2002; 24:91–96. PMID: 12197026.
Article14. Kim HS, Hwang JH, Lee PK, Kwon JY, Oh-Park MY, Kim JM, et al. Localization of the motor nerve branches and motor points of the triceps surae muscles in Korean cadavers. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 81:765–769. PMID: 12362117.15. An XC, Lee JH, Im S, Lee MS, Hwang K, Kim HW, et al. Anatomic localization of motor entry points and intramuscular nerve endings in the hamstring muscles. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010; 32:529–537. PMID: 20063163.
Article16. Van Campenhout A, Hubens G, Fagard K, Molenaers G. Localization of motor nerve branches of the human psoas muscle. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 42:202–207. PMID: 20544927.
Article17. Lee JH, Lee BN, An X, Chung RH, Han SH. Location of the motor entry point and intramuscular motor point of the tibialis posterior muscle: for effective motor point block. Clin Anat. 2011; 24:91–96. PMID: 21154644.
Article18. Gracies JM, Lugassy M, Weisz DJ, Vecchio M, Flanagan S, Simpson DM. Botulinum toxin dilution and endplate targeting in spasticity: a double-blind controlled study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009; 90:9–16. PMID: 19154823.
Article19. O'Brien CF. Injection techniques for botulinum toxin using electromyography and electrical stimulation. Muscle Nerve Suppl. 1997; 6:S176–S180. PMID: 9826989.20. Crystal R, Malone AA, Eastwood DM. Motor points for neuromuscular blockade of the adductor muscle group. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 437:196–200. PMID: 16056049.
Article21. Shaari CM, Sanders I. Quantifying how location and dose of botulinum toxin injections affect muscle paralysis. Muscle Nerve. 1993; 16:964–969. PMID: 8355728.
Article22. Childers MK, Kornegay JN, Aoki R, Otaviani L, Bogan DJ, Petroski G. Evaluating motor end-plate-targeted injections of botulinum toxin type A in a canine model. Muscle Nerve. 1998; 21:653–655. PMID: 9572248.
Article23. Aquilonius SM, Askmark H, Gillberg PG, Nandedkar S, Olsson Y, Stalberg E. Topographical localization of motor endplates in cryosections of whole human muscles. Muscle Nerve. 1984; 7:287–293. PMID: 6203034.
Article24. Christensen E. Topography of terminal motor innervation in striated muscles from stillborn infants. Am J Phys Med. 1959; 38:65–78. PMID: 13637190.
Article25. Mu L, Sanders I. Human tongue neuroanatomy: nerve supply and motor endplates. Clin Anat. 2010; 23:777–791. PMID: 20607833.
Article26. Won SY, Rha DW, Kim HS, Jung SH, Park ES, Hu KS, et al. Intramuscular nerve distribution pattern of the adductor longus and gracilis muscles demonstrated with Sihler staining: guidance for botulinum toxin injection. Muscle Nerve. 2012; 46:80–85. PMID: 22644785.
Article27. Ye JF, Lee JH, An XC, Lin CH, Yue B, Han SH. Anatomic localization of motor entry points and accurate regions for botulinum toxin injection in the flexor digitorum superficialis. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011; 33:601–607. PMID: 21258930.
Article28. Lee JH, Lee BN, Han SH, An XC, Chung RH. The effective zone of botulinum toxin A injections in the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011; 33:185–190. PMID: 20886338.
Article29. Lee JH, Han SH, Ye JF, Lee BN, An X, Kwon SO. Effective zone of botulinum toxin a injections in hallux claw toe syndrome: an anatomical study. Muscle Nerve. 2012; 45:217–221. PMID: 22246877.
Article30. Im S, Han SH, Choi JH, Lee JH, Ko YJ, Lee JI, et al. Anatomic localization of motor points for the neuromuscular blockade of hand intrinsic muscles involved in thumb-in-palm. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2008; 87:703–709. PMID: 18617859.
Article31. Van Campenhout A, Molenaers G. Localization of the motor endplate zone in human skeletal muscles of the lower limb: anatomical guidelines for injection with botulinum toxin. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011; 53:108–119. PMID: 20964675.
Article32. Oddy MJ, Brown C, Mistry R, Eastwood DM. Botulinum toxin injection site localization for the tibialis posterior muscle. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2006; 15:414–417. PMID: 17001247.
Article33. Woodley SJ, Mercer SR. Hamstring muscles: architecture and innervation. Cells Tissues Organs. 2005; 179:125–141. PMID: 15947463.
Article34. Shaari CM, George E, Wu BL, Biller HF, Sanders I. Quantifying the spread of botulinum toxin through muscle fascia. Laryngoscope. 1991; 101:960–964. PMID: 1886444.
Article35. Ma J, Smith BP, Smith TL, Walker FO, Rosencrance EV, Koman LA. Juvenile and adult rat neuromuscular junctions: density, distribution, and morphology. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 26:804–809. PMID: 12451605.
Article36. Amirali A, Mu L, Gracies JM, Simpson DM. Anatomical localization of motor endplate bands in the human biceps brachii. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2007; 9:306–312. PMID: 18090684.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Selective Fascicle Injection of Botulinum Toxin at the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis and Flexor Digitorum Profundus in Patient with Focal Dystonia Affecting Fingers
- The Complications of Botulinum Toxin Type A Chemodenervation in Strabismus
- The Complications Developed after Repeated Botulinum Toxin Injection
- Botulinum Toxin Injection Treatment for Facial Spasm
- Neurophysiological Changes after Botulinum Toxin A Injection in Normal Adults