Ann Rehabil Med.
2011 Jun;35(3):344-353. 10.5535/arm.2011.35.3.344.
The Effect and Complication of Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection with Serial Casting for the Treatment of Spastic Equinus Foot
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 138-736, Korea. iysung@amc.seoul.kr
- 2CHA Bundang Medicine Center, CHA University, Seongnam 463-712, Korea.
- KMID: 2266853
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.3.344
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
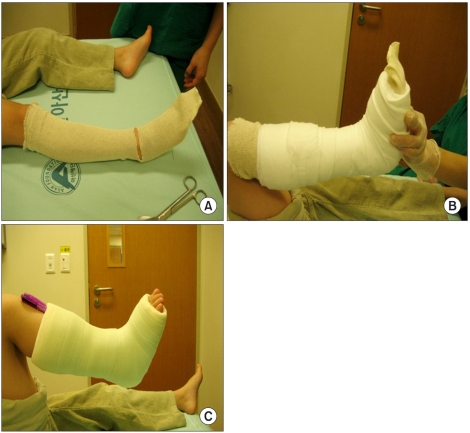
To identify the effect of serial casting combined with Botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) injection on spastic equinus foot. METHOD: Twenty-nine children with cerebral palsy who had equinus foot were recruited from the outpatient clinic of Rehabilitation Medicine. The children were divided into 2 groups, one of which received serial casting after BTX-A injection, and the other which only received BTX-A injection. Serial casting started 3 weeks after the BTX-A injection, and was changed weekly for 3 times. Spasticity of the ankle joint was evaluated using the modified Ashworth scale (MAS), and the modified Tardieu scale (MTS). Gait pattern was measured using the physician's rating scale (PRS).
RESULTS
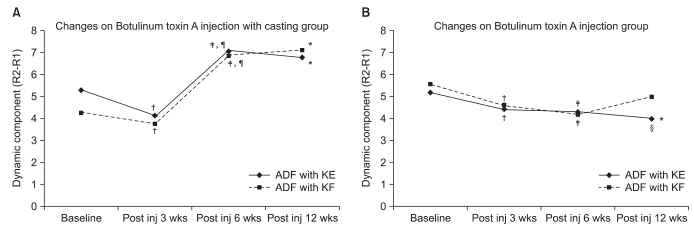
The degree of ankle dorsiflexion and the MAS improved significantly until 12 weeks following the BTX-A injection in the serial casting group (p<0.001), while the BTX-A injection-only group improved until 6 weeks following injection (p<0.05). The combined group showed a significantly greater increase in the degree of dorsiflexion compared to the BTX-A injection-only group at post-injection weeks 6 and 12 (p<0.05). Three children (11.5%) suffered from foot ulcers as a complication caused by the serial casting.
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrated that the effect of BTX-A injection with serial casting was superior and lasted longer than the effect of BTX-A injection only in patients with spastic equinus foot. We therefore recommend BTX-A injection with serial casting for the treatment of equinus foot. However, physicians must also consider the possible complications associated with serial casting.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Short-Term Effect of Botulinum Toxin A Injection on Spastic Equinovarus Foot in Cerebral Palsy Patients: A Study Using the Foot Pressure Measurement System
Su Min Son, In Sik Park, Jin Sun Yoo
Ann Rehabil Med. 2015;39(1):1-9. doi: 10.5535/arm.2015.39.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, Jacobsson B, Damiano D. Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005; 47:571–576. PMID: 16108461.
Article2. Bax MC. Terminology and classification of cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1964; 6:295–297. PMID: 14155190.
Article3. Goldstein EM. Spasticity management: an overview. J Child Neurol. 2001; 16:16–23. PMID: 11225951.
Article4. Huang W, Foster JA, Rogachefsky AS. Pharmacology of botulinum toxin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000; 43:249–259. PMID: 10906647.
Article5. Gajdosik RL. Passive extensibility of skeletal muscle: review of the literature with clinical implications. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2001; 16:87–101.
Article6. Cosgrove AP, Corry IS, Graham HK. Botulinum toxin in the management of the lower limb in cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1994; 36:386–396. PMID: 8168657.
Article7. Corry IS, Cosgrove AP, Duffy CM, McNeill S, Taylor TC, Graham HK. Botulinum toxin A compared with stretching casts in the treatment of spastic equinus: a randomised prospective trial. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998; 18:304–311. PMID: 9600553.
Article8. Flett PJ, Stern LM, Waddy H, Connell TM, Seeger JD, Gibson SK. Botulinum toxin A versus fixed cast stretching for dynamic calf tightness in cerebral palsy. J Paediatr Child Health. 1999; 35:71–77. PMID: 10234640.
Article9. Houltram J, Noble I, Boyd RN, Corry I, Flett P, Graham HK. Botulinum toxin type A in the management of equinus in children with cerebral palsy: an evidence-based economic evaluation. Eur J Neurol. 2001; 8(Suppl 5):194–202. PMID: 11851748.
Article10. Booth MY, Yates CC, Edgar TS, Bandy WD. Serial casting vs combined intervention with botulinum toxin A and serial casting in the treatment of spastic equinus in children. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2003; 15:216–220. PMID: 17057457.
Article11. Kay RM, Rethlefsen SA, Fern-Buneo A, Wren TA, Skaggs DL. Botulinum toxin as an adjunct to serial casting treatment in children with cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86-A:2377–2384. PMID: 15523006.
Article12. Koman LA, Mooney JF 3rd, Smith BP, Goodman A, Mulvaney T. Management of spasticity in cerebral palsy with botulinum-A toxin: report of a preliminary, randomized, double-blind trial. J Pediatr Orthop. 1994; 14:299–303. PMID: 8006158.
Article13. Kelly B, MacKay-Lyons MJ, Berryman S, Hyndman J, Wood E. Assessment protocol for serial casting after botulinum toxin a injections to treat equinus gait. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2008; 20:233–241. PMID: 18703960.
Article14. Desloovere K, Molenaers G, Jonkers I, De Cat J, De Borre L, Nijs J, Eyssen M, Pauwels P, De Cock P. A randomized study of combined botulinum toxin type A and casting in the ambulant child with cerebral palsy using objective outcome measures. Eur J Neurol. 2001; 8(Suppl 5):75–87. PMID: 11851736.
Article15. Glanzman AM, Kim H, Swaminathan K, Beck T. Efficacy of botulinum toxin A, serial casting, and combined treatment for spastic equinus: a retrospective analysis. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2004; 46:807–811. PMID: 15581153.
Article16. Bottos M, Benedetti MG, Salucci P, Gasparroni V, Giannini S. Botulinum toxin with and without casting in ambulant children with spastic diplegia: a clinical and functional assessment. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2003; 45:758–762. PMID: 14580131.
Article17. Newman CJ, Kennedy A, Walsh M, O'Brien T, Lynch B, Hensey O. A pilot study of delayed versus immediate serial casting after botulinum toxin injection for partially reducible spastic equinus. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007; 27:882–885. PMID: 18209608.
Article18. Tardieu G, Tardieu C, Colbeau-Justin P, Lespargot A. Muscle hypoextensibility in children with cerebral palsy: II. Therapeutic implications. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1982; 63:103–107. PMID: 7073451.19. Fosang AL, Galea MP, McCoy AT, Reddihough DS, Story I. Measures of muscle and joint performance in the lower limb of children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2003; 45:664–670. PMID: 14515937.
Article20. Koman LA, Brashear A, Rosenfeld S, Chambers H, Russman B, Rang M, Root L, Ferrari E, Garcia de Yebenes Prous J, Smith BP, et al. Botulinum toxin type a neuromuscular blockade in the treatment of equinus foot deformity in cerebral palsy: a multicenter, open-label clinical trial. Pediatrics. 2001; 108:1062–1071. PMID: 11694682.
Article21. Park ES, Rha DW, Yoo JK, Kim SM, Chang WH, Song SH. Short-term effects of combined serial casting and botulinum toxin injection for spastic equinus in ambulatory children with cerebral palsy. Yonsei Med J. 2010; 51:579–584. PMID: 20499426.
Article22. Mackey AH, Walt SE, Lobb G, Stott NS. Intraobserver reliability of the modified Tardieu scale in the upper limb of children with hemiplegia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2004; 46:267–272. PMID: 15077704.
Article23. Boyd RN, Pliatsios V, Starr R, Wolfe R, Graham HK. Biomechanical transformation of the gastroc-soleus muscle with botulinum toxin A in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000; 42:32–41. PMID: 10665973.
Article24. Rhim SY, Kim MJ, Han SH. The effects of dilution volume of botulinum toxin A on the spasticity of children with cerebral palsy. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2008; 32:294–299.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Short-Term Effects of Combined Serial Casting and Botulinum Toxin Injection for Spastic Equinus in Ambulatory Children with Cerebral Palsy
- Short-Term Effect of Botulinum Toxin A Injection on Spastic Equinovarus Foot in Cerebral Palsy Patients: A Study Using the Foot Pressure Measurement System
- Application of Botulinum Toxin Injection in Plastic Surgery
- Botulinum Toxin A Treatment for the Improvement of Hand Function in Spastic Hemiplegia
- Effects of Botulinum Toxin A Treatment in Cerebral Palsy