Ann Rehabil Med.
2011 Dec;35(6):816-825. 10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.816.
Motor Unit Number Estimation and Motor Unit Action Potential Analysis in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 301-172, Korea. h5034@cnuh.co.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 301-172, Korea.
- KMID: 2266807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.816
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the clinical significance of motor unit number estimation (MUNE) and quantitative analysis of motor unit action potential (MUAP) in carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) according to electrophysiologic severity, ultrasonographic measurement and clinical symptoms. METHOD: We evaluated 78 wrists of 45 patients, who had been diagnosed with CTS and 42 wrists of 21 healthy controls. Median nerve conduction studies, amplitude and duration of MUAP, and the MUNE of the abductor pollicis brevis were measured. The cross sectional area (CSA) of the median nerve at the pisiform and distal radioulnar joint level was determined by high resolution ultrasonography. Clinical symptom of CTS was assessed using the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire (BCTQ).
RESULTS
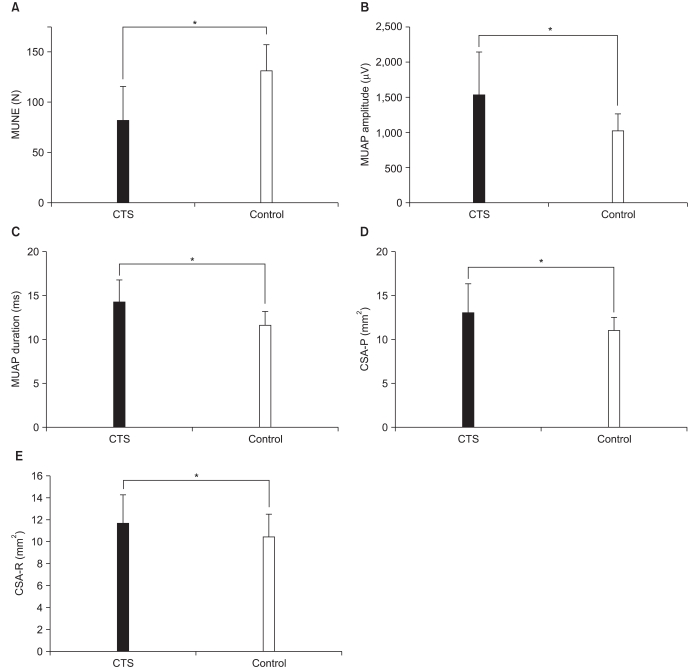
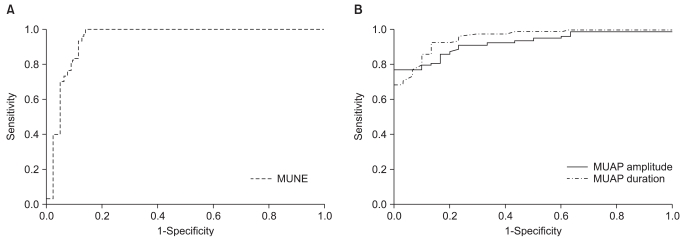
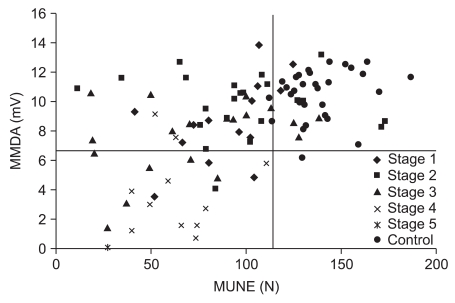
The MUNE, the amplitude and the duration of MUAP of the CTS group were significantly different from those found in the control group. The area under the ROC curve was 0.944 for MUNE, 0.923 for MUAP amplitude and 0.953 for MUAP duration. MUNE had a negative correlation with electrophysiologic stage of CTS, amplitude and duration of MUAP, CSA at pisiform level, and the score of BCTQ. The amplitude and duration of MUAP had a positive correlation with the score of BCTQ. The electrophysiologic stage was correlated with amplitude but not with the duration of MUAP.
CONCLUSION
MUNE, amplitude and duration of MUAP are useful tests for diagnosis of CTS. In addition, the MUNE serves as a good indicator of CTS severity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Motor-Unit Number Estimation Is Sensitive in Detecting Motor Nerve Involvement in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Orhan Yilmaz, Gulin Sunter, Celal Salcini, Pınar Kahraman Koytak, Tulin Tanridag, Onder Us, Kayihan Uluc
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(2):166-171. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.2.166.
Reference
-
1. Di Guglielmo G, Torrieri F, Repaci M, Uncini A. Conduction block and segmental velocities in carpal tunnel syndrome. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1997; 105:321–327. PMID: 9284240.
Article2. Stevens JC. AAEM minimonograph #26: the electrodiagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. Muscle Nerve. 1997; 20:1477–1148. PMID: 9390659.3. Daube JR. Estimating the number of motor units in a muscle. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1995; 12:585–594. PMID: 8600173.
Article4. Brown WF. Thenar motor unit estimates in the carpal tunnel syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973; 36:194–198. PMID: 4708453.5. McComas AJ, Fawcett PR, Campbell MJ, Sica RE. Electrophysiological estimation of the number of motor units within a human muscle. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971; 34:121–131. PMID: 5571599.
Article6. Koç F, Yerdelen D, Sarica Y, Sertdemir Y. Motor unit number estimation in cases with carpal tunnel syndrome. Int J Neurosci. 2006; 116:1263–1270. PMID: 17000528.7. Bayrak IK, Bayrak AO, Tilki HE, Nural MS, Sunter T. Ultrasonography in carpal tunnel syndrome: comparison with electrophysiological stage and motor unit number estimate. Muscle Nerve. 2007; 35:344–348. PMID: 17143879.
Article8. Pino LJ, Stashuk DW, Boe SG, Doherty TJ. Probabilistic muscle characterization using QEMG: application to neuropathic muscle. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 41:18–31. PMID: 19768760.
Article9. Stålberg E, Nandedkar SD, Sanders DB, Falck B. Quantitative motor unit potential analysis. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1996; 13:401–422. PMID: 8897206.
Article10. Cuturic M, Palliyath S. Motor unit number estimate (MUNE) testing in male patients with mild to moderate carpal tunnel syndrome. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 2000; 40:67–72. PMID: 10746180.11. Werner RA, Albers JW. Relation between needle electromyography and nerve conduction studies in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995; 76:246–249. PMID: 7717817.
Article12. Dumitru D. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 2002. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus Inc;p. 1058–1070.13. Padua L, LoMonaco M, Gregori B, Valente EM, Padua R, Tonali P. Neurophysiological classification and sensitivity in 500 carpal tunnel syndrome hands. Acta Neurol Scand. 1997; 96:211–217. PMID: 9325471.
Article14. Stalberg E, Falck B, Sonoo M, Stalberg S, Astrom M. Multi-MUP EMG analysis - a two year experience in daily clinical work. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995; 97:145–154. PMID: 7607102.15. Levine DW, Simmons BP, Koirs MJ, Daltroy LH, Hohl GG, Fossel AH, Katz JN. A self-administered questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symptoms and functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993; 75:1585–1592. PMID: 8245050.
Article16. Bromberg MB. Motor unit estimation: reproducibility of the spike-triggered averaging technique in normal and ALS subjects. Muscle Nerve. 1993; 16:466–471. PMID: 8515754.
Article17. Doherty TJ, Brown WF. The estimated numbers and relative sizes of thenar motor units as selected by multiple point stimulation in young and older adults. Muscle Nerve. 1993; 16:355–366. PMID: 8455648.
Article18. Yune YS, Sohn MK, Kim BO. Motor unit number estimation of the thenar muscles. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1997; 21:1184–1193.19. Boe SG, Stashuk DW, Doherty TJ. Motor unit number estimates and quantitative motor unit analysis in healthy subjects and patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle nerve. 2007; 36:62–70. PMID: 17455264.
Article20. Olney RK, Yuen EC, Engstrom JW. Statistical motor unit number estimation: reproducibility and sources of error in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle nerve. 2000; 23:193–197. PMID: 10639610.
Article21. Bayrak AO, Tilki HE, Coşkun M. Sympathetic skin response and axon count in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007; 24:70–75. PMID: 17277581.
Article22. Cho SK, Park YK, Lee SC, Moon JH, Min KH, Park YB. Utility of quantitative electromyography in the evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Korean EMG Electrodiagn Med. 2007; 9:36–42.23. Miller RG. AAEM minimonograph #28: injury to peripheral motor nerves. Muscle Nerve. 1987; 10:698–710. PMID: 3317034.24. Sohn MK, Yune YS. Changes of electromyographic signals following peripheral nerve injury. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1997; 21:547–552.25. Buchberger W. Radiologic imaging of the carpal tunnel. Eur J Radiol. 1997; 25:112–117. PMID: 9283839.
Article26. Visser LH, Smidt MH, Lee ML. High-resolution sonography versus EMG in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Neurol Neurochir Psychiatry. 2008; 79:63–67.
Article27. Kaymak B, Ozçakar L, Cetin A, Candan Cetin M, Akinci A, Hasçelik Z. A comparison of the benefits of sonography and electrophysiologic measurements as predictors of symptom severity and functional status in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008; 89:743–748. PMID: 18374007.
Article28. Kele H, Verheggen R, Bittermann HJ, Reimers CD. The potential value of ultrasonography in the evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurology. 2003; 61:389–391. PMID: 12913205.
Article29. Park DS, Nam HS, Lee SE, Kim DH, Lee JG, Jeong HO. The usefulness of various electrodiagnostic parameters in mild carpal tunnel syndrome. J Korean Assoc EMG-Electrodiagn Med. 2008; 10:135–143.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Motor Unit Number Estimation of Normal Thenar Muscle
- Motor Unit Number Estimation of the Thenar Muscles
- Motor Unit Numbers Estimation in Abductor Pollicis Brevis Muscle of Normal Adult
- Motor Unit Number Estimation in Thenar Muscles of the Hemiplegic Patients
- Motor-Unit Number Estimation Is Sensitive in Detecting Motor Nerve Involvement in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome