Ann Rehabil Med.
2011 Dec;35(6):772-780. 10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.772.
Usefulness of the Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia (SARA) in Ataxic Stroke Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center and School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leej@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and National University Health System, Singapore.
- KMID: 2266802
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.772
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To examine the usefulness of the Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia (SARA) in ataxic stroke patients. METHOD: This was a retrospective study of 54 patients following their first ataxic stroke. The data used in the analysis comprised ambulation status on admission and scores on the SARA, the Korean version of the Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI) and the Berg Balance Scale (BBS). The subjects were divided into four groups by gait status and into five groups by level of dependency in activities of daily living (ADLs) based on their K-MBI scores. Data were subjected to a ROC curve analysis to obtain cutoff values on the SARA for individual gait status and levels of activity dependency. The correlations between the SARA, K-MBI and BBS scores were also computed.
RESULTS
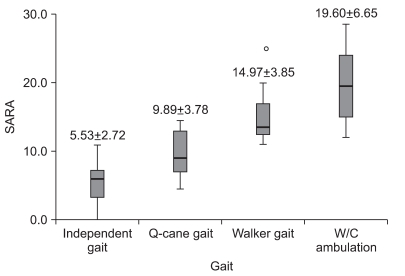
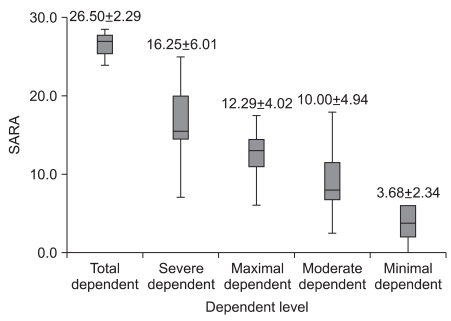
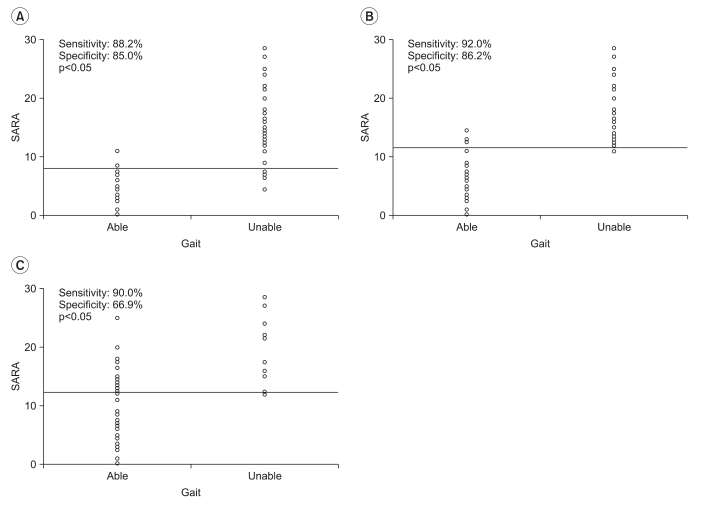
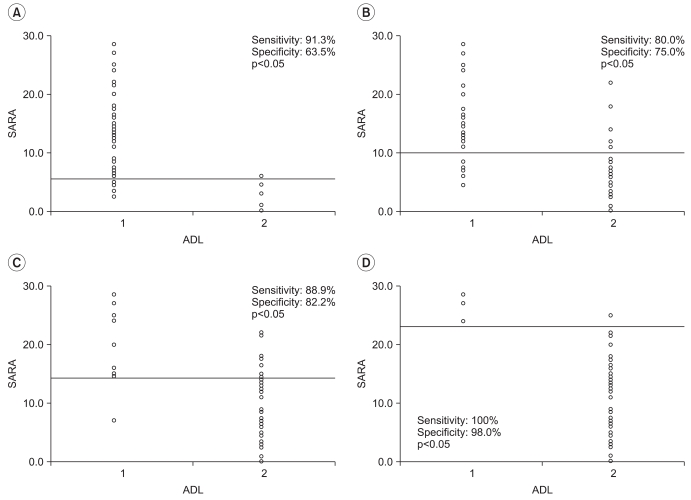
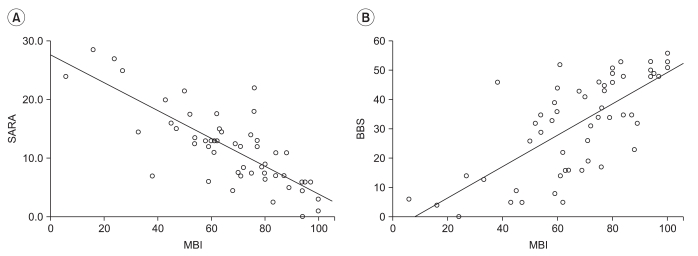
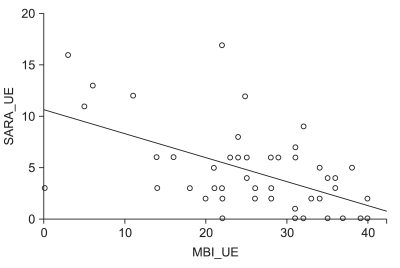
There was significant correlation between the SARA and the K-MBI scores (p<0.001), and this correlation (r=-0.792) was higher than that found between the BBS and the K-MBI scores (r=0.710). The SARA scores of upper extremity ataxia categories were significantly related to the K-MBI scores of upper extremity related function (p<0.001). The SARA scores were also significantly correlated negatively with ambulation status (p<0.001) and positively with ADL dependency (p<0.001). In the ROC analysis, patients with less than 5.5 points on the SARA had minimal dependency in ADL, while those with more than 23 points showed total dependency.
CONCLUSION
SARA corresponds well with gait status and ADL dependency in ataxic stroke patients and is considered to be a useful functional measure in that patient group.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Korean Version of the Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia in Ataxic Stroke Patients
Bo-Ram Kim, Jin-Youn Lee, Min Jeong Kim, Heeyoune Jung, Jongmin Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2014;38(6):742-751. doi: 10.5535/arm.2014.38.6.742.Evaluation of Ataxia in Mild Ischemic Stroke Patients Using the Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia (SARA)
Sung Won Choi, Nami Han, Sang Hoon Jung, Hyun Dong Kim, Mi Ja Eom, Hyun Woo Bae
Ann Rehabil Med. 2018;42(3):375-383. doi: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.3.375.Ultrasound Imaging of the Trunk Muscles in Acute Stroke Patients and Relations With Balance Scales
Yunho Kim, Jeeyoung Kim, Heesung Nam, Hyun Dong Kim, Mi Ja Eom, Sang Hoon Jung, Nami Han
Ann Rehabil Med. 2020;44(4):273-283. doi: 10.5535/arm.19125.
Reference
-
1. Hwang SH. Stroke and ataxia. Korean J Stroke. 1999; 1:139–145.2. Blum L, Korner-Bitensky N. Usefulness of the Berg Balance Scale in stroke rehabilitation: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2008; 88:559–566. PMID: 18292215.
Article3. Trouillas P, Takayanagi T, Hallett M, Currier RD, Subramony SH, Wessel K, Bryer A, Diener HC, Massaquoi S, Gomez CM, et al. The Ataxia Neuropharmacology Committee of the World Federation of Neurology. International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale for pharmacological assessment of the cerebellar syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 1997; 145:205–211. PMID: 9094050.
Article4. Schmitz-Hübsch T, du Montcel ST, Baliko L, Berciano J, Boesch S, Depondt C, Giunti P, Globas C, Infante J, Kang JS, et al. Scale for the assessment and rating of ataxia: development of a new clinical scale. Neurology. 2006; 66:1717–1720. PMID: 16769946.
Article5. Kim HS, Lee KW, Sung DH, Hwang JH, Kim TU. Posturographic characteristics of lesion site in stroke patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2000; 24:363–369.6. Jung HY, Park BK, Shin HS, Kang YK, Pyun SB, Paik NJ, Kim SH, Kim TH, Han TR. Development of the Korean Version of Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI): multicenter study for subjects with stroke. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2007; 31:283–297.7. Jung HY, Kim TH, Park JH. Relationship between Berg Balance Scale and functional independence measure in stroke patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005; 29:167–170.8. Berg K, Wood-Dauphinee S, Williams JI, Gayton D. Measuring balance in the elderly: preliminary development of an instrument. Physiother Can. 1989; 41:304–311.9. Dettmann MA, Linder MT, Sepic SB. Relationships among walking performance, postural stability, and functional assessments of the hemiplegic patient. Am J Phys Med. 1987; 66:77–90. PMID: 3578493.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Korean Version of the Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia in Ataxic Stroke Patients
- Evaluation of Ataxia in Mild Ischemic Stroke Patients Using the Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia (SARA)
- Role of Cortico-ponto-cerebellar Tract from Supplementary Motor Area in Ataxic Hemiparesis of Supratentorial Stroke Patients
- Clinical Profile and Localization of Ataxic Hemiparesis as a Lacunar Syndrome
- Ultrasound Imaging of the Trunk Muscles in Acute Stroke Patients and Relations With Balance Scales