Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Aug;36(4):496-500. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.4.496.
Real-Time Visualization of Ultrasonography Guided Cubital Tunnel Injection: A Cadaveric Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Incheon 403-720, Korea. haz521@gmail.com
- KMID: 2266720
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.4.496
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
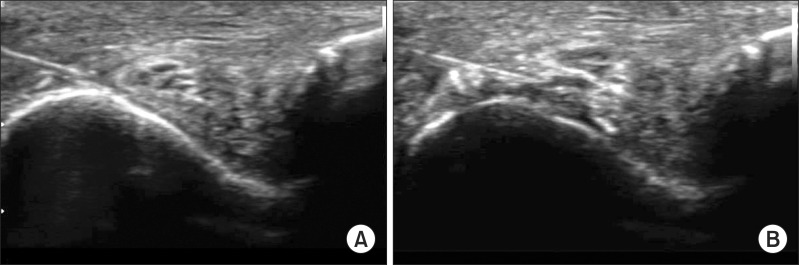
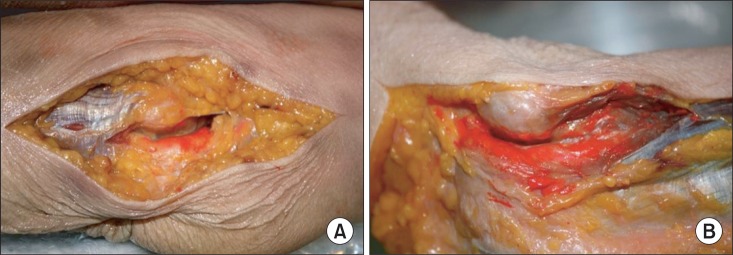
To describe an ultrasonography-guided technique for cubital tunnel injection. METHOD: The ulnar nerves from 12 elbows of 6 adult cadavers were scanned, and the cross-sectional areas of the ulnar nerves, cubital tunnel inlets and outlets were measured by using ultrasonography. All elbows were dissected after an ultrasonography-guided dye injection at the inlet of the cubital tunnel. The dissectors evaluated the spread of dye and the coloration of the nerve and remeasured the cross-sectional areas of the cubital tunnel inlets and outlets.
RESULTS
After a real-time visualization of an ultrasonography-guided injection, the ulnar nerves were seperated from the medial groove for the ulnar nerve. All the ulnar nerves of the cadavers were successfully colored with the dye, from the inlet to oulet of the cubital tunnel. The post-injection cross-sectional areas were significantly larger than the pre-injection cross-sectional areas. No significant differences were detected in the post-injection cross-sectional areas of the cubital tunnel outlet and the ulnar nerve as compared with the pre-injection areas.
CONCLUSION
Clinicians should consider real-time visualization of ultrasonography for guided injection around the ulnar nerve at the inlet of the cubital tunnel.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Implications of Real-Time Visualized Ultrasound-Guided Injection for the Treatment of Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow: A Pilot Study
Chang Kweon Choi, Hyun Seok Lee, Jae Yeoun Kwon, Won-Jae Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2015;39(2):176-182. doi: 10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.176.
Reference
-
1. Bayrak AO, Bayrak IK, Turker H, Elmali M, Nural MS. Ultrasonography in patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: comparison of cross-sectional area and swelling ratio with electrophysiological severity. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 41:661–666. PMID: 19941341.
Article2. Yoon JS, Hong SJ, Kim BJ, Kim SJ, Kim JM, Walker FO, Cartwright MS. Ulnar nerve and cubital tunnel ultrasound in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008; 89:887–889. PMID: 18452736.
Article3. Alblas CL, van Kasteel V, Jellema K. Injection with corticosteroids (ultrasound guided) in patients with an ulnar neuropathy at the elbow, feasibility study. Eur J Neurol. 2012; 16:1–4.
Article4. Rampen AJ, Wirtz PW, Tavy DL. Ultrasound-guided steroid injection to treat mild ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Muscle Nerve. 2011; 44:128–130. PMID: 21660983.
Article5. Smith J, Wisniewski SJ, Finnoff JT, Payne JM. Sonographically guided carpal tunnel injections: the ulnar approach. J Ultrasound Med. 2008; 27:1485–1490. PMID: 18809959.6. Hong CZ, Long HA, Kanakamedala RV, Chang YM, Yates L. Splinting and local steroid injection for the treatment of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: clinical and electrophysiological evaluation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1996; 77:573–577. PMID: 8831474.
Article7. Pechan J, Kredba J. Treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome by means of local administration of cortisonoids. II. Long-term follow-up. Acta Univ Carol Med (Praha). 1980; 26:135–140. PMID: 7315671.8. Pechan J, Kredba J. Treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome by means of local administration of corticosteroids. I. Short-term follow-up. Acta Univ Carol Med (Praha). 1980; 26:125–133. PMID: 7315670.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosed by Ultrasonography in Patient with Normal Electrodiagnostic Studies
- Clinical Implications of Real-Time Visualized Ultrasound-Guided Injection for the Treatment of Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow: A Pilot Study
- Ulnar neuropathy
- Cubital tunnel syndrome caused by an intraneural ganglion cyst treated with epineurectomy: a report of three cases
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Caused by Osteochondroma: A Case Report