Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Dec;37(6):913-918. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.913.
Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Injury After Brachial Plexus Block: Two Case Reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea. hsshin@nongae.gsnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2266574
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.913
Abstract
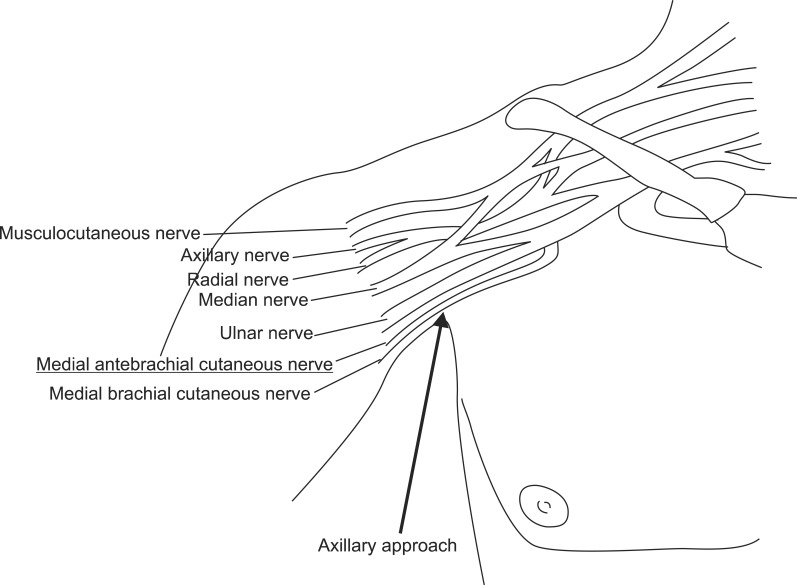
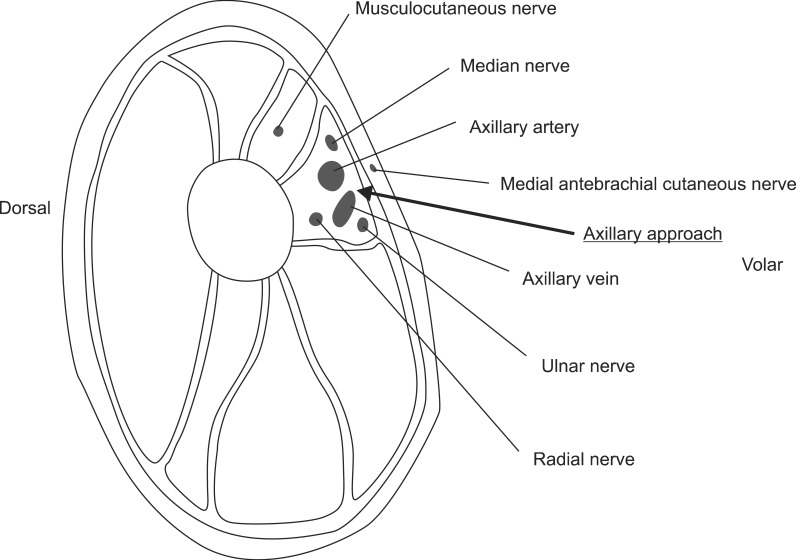
- Medial antebrachial cutaneous (MABC) nerve injury associated with iatrogenic causes has been rarely reported. Local anesthesia may be implicated in the etiology of such injury, but has not been reported. Two patients with numbness and painful paresthesia over the medial aspect of the unilateral forearm were referred for electrodiagnostic study, which revealed MABC nerve lesion in each case. The highly selective nature of the MABC nerve injuries strongly suggested that they were the result of direct nerve injury by an injection needle during previous brachial plexus block procedures. Electrodiagnostic studies can be helpful in evaluating cases of sensory disturbance after local anesthesia. To our knowledge, these are the first documented cases of isolated MABC nerve injury following ultrasound-guided axillary brachial plexus block.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Ultrasound-Guided Axillary Brachial Plexus Block, Performed by Orthopedic Surgeons
Cheol-U Kim, Chul-Hyung Lee, Ja-Yeong Yoon, Seung-Koo Rhee
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2018;53(6):513-521. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.6.513.Determination of an Ideal Stimulation Site of the Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Using Ultrasound and Investigation of the Efficiency
Chang Hoon Oh, Nam Su Park, Jae Min Kim, Min Wook Kim
Ann Rehabil Med. 2014;38(6):836-842. doi: 10.5535/arm.2014.38.6.836.Ultrasound-guided Continuous Axillary Brachial Plexus Block Using a Nerve Stimulating Catheter: EpiStim® Catheter
Sang Sik Choi, Mi Kyoung Lee, Jung Eun Kim, Se Hee Kim, Gwi Eun Yeo
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(4):287-289. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.4.287.
Reference
-
1. Richards RR, Regan WD. Medial epicondylitis caused by injury to the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve: a case report. Can J Surg. 1989; 32:366–367. 369PMID: 2766143.2. Asheghan M, Khatibi A, Holisaz MT. Paresthesia and forearm pain after phlebotomy due to medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve injury. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2011; 6:5. PMID: 21896172.
Article3. Yildiz N, Ardic F. A rare cause of forearm pain: anterior branch of the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve injury: a case report. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2008; 3:10. PMID: 18426569.
Article4. Horlocker TT, Kufner RP, Bishop AT, Maxson PM, Schroeder DR. The risk of persistent paresthesia is not increased with repeated axillary block. Anesth Analg. 1999; 88:382–387. PMID: 9972761.
Article5. Thallaj A, Marhofer P, Kettner SC, Al-Majed M, Al-Ahaideb A, Moriggl B. High-resolution ultrasound accurately identifies the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve at the midarm level: a clinical anatomic study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2011; 36:499–501. PMID: 21857274.6. Sandhu K, Dash HH. Anaesthesia related neurological complications. Indian J Anaesth. 2004; 48:439–445.7. Hebl JR, Horlocker TT, Sorenson EJ, Schroeder DR. Regional anesthesia does not increase the risk of postoperative neuropathy in patients undergoing ulnar nerve transposition. Anesth Analg. 2001; 93:1606–1611. PMID: 11726453.
Article8. Makitie J, Teravainen H. Peripheral nerve injury and recovery after temporary ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 1977; 37:55–63. PMID: 842295.
Article9. Fanelli G, Casati A, Garancini P, Torri G. Study Group on Regional Anesthesia. Nerve stimulator and multiple injection technique for upper and lower limb blockade: failure rate, patient acceptance, and neurologic complications. Anesth Analg. 1999; 88:847–852. PMID: 10195536.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Phrenic nerve palsy following coracoid infraclavicular brachial plexus block
- Brachial Plexus Injury Following Axillary Brachial Plexus Block Using a Transarterial Approach: A case report
- Axillary Brachial Plexus Block with Peripheral Nerve Stimulator
- Anatomical Distribution of Branches of the Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve during Cubital Tunnel Surgery
- Uncommon configuration of intercostobrachial nerves, lateral roots, and absent medial cutaneous nerve of arm in a cadaveric study