Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2013 Sep;18(3):148-151. 10.6065/apem.2013.18.3.148.
Insulin pump therapy in transient neonatal diabetes mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, CHA University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. pedyoo@cha.ac.kr
- 2Sungae Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2266367
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2013.18.3.148
Abstract
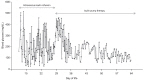
- Neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) is a rare disease requiring insulin treatment. Its treatment is primarily focused on maintaining adequate glycemic control and avoiding hypoglycemia. Although insulin pump therapy is frequently administered to adults and children, there is no consensus on the use of insulin pumps in NDM. A 10 day-old female infant was referred to us with intrauterine growth retardation and poor weight gain. Hyperglycemia was noted, and continuous intravenous insulin infusion was initiated. However, the patient's serum glucose levels fluctuated widely, and maintaining the intravenous route became difficult within the following weeks. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion with an insulin pump was introduced on the twenty-fifth day of life, and good glycemic control was achieved without any notable adverse effects including hypoglycemia. We suggest that the insulin pump is a safe and effective mode for treating NDM and its early adoption may shorten the length of hospital stays in patients with NDM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. von Mühlendahl KE, Herkenhoff H. Long-term course of neonatal diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:704–708. PMID: 7637748.
Article2. Polak M, Cave H. Neonatal diabetes mellitus: a disease linked to multiple mechanisms. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007; 2:12. PMID: 17349054.
Article3. Burns CM, Rutherford MA, Boardman JP, Cowan FM. Patterns of cerebral injury and neurodevelopmental outcomes after symptomatic neonatal hypoglycemia. Pediatrics. 2008; 122:65–74. PMID: 18595988.
Article4. Bharucha T, Brown J, McDonnell C, Gebert R, McDougall P, Cameron F, et al. Neonatal diabetes mellitus: Insulin pump as an alternative management strategy. J Paediatr Child Health. 2005; 41:522–526. PMID: 16150072.
Article5. Wintergerst KA, Hargadon S, Hsiang HY. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in neonatal diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes. 2004; 5:202–206. PMID: 15601363.
Article6. Temple IK, Mackay DJ, Docherty LE. Diabetes mellitus, 6q24-related transient neonatal. In : Pagon RA, Adam MP, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT, Stephens K, editors. GeneReviews™ [monograph on the Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle;2005. 10. updated 2012 Sep 27. cited 2013 Sep 10. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20301706.7. Gloyn AL, Pearson ER, Antcliff JF, Proks P, Bruining GJ, Slingerland AS, et al. Activating mutations in the gene encoding the ATP-sensitive potassium-channel subunit Kir6.2 and permanent neonatal diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1838–1849. PMID: 15115830.
Article8. Vaxillaire M, Populaire C, Busiah K, Cave H, Gloyn AL, Hattersley AT, et al. Kir6.2 mutations are a common cause of permanent neonatal diabetes in a large cohort of French patients. Diabetes. 2004; 53:2719–2722. PMID: 15448107.
Article9. Babenko AP, Polak M, Cave H, Busiah K, Czernichow P, Scharfmann R, et al. Activating mutations in the ABCC8 gene in neonatal diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:456–466. PMID: 16885549.
Article10. Temple IK, Shield JP. Transient neonatal diabetes, a disorder of imprinting. J Med Genet. 2002; 39:872–875. PMID: 12471198.
Article11. Docherty LE, Poole RL, Mattocks CJ, Lehmann A, Temple IK, Mackay DJ. Further refinement of the critical minimal genetic region for the imprinting disorder 6q24 transient neonatal diabetes. Diabetologia. 2010; 53:2347–2351. PMID: 20668833.
Article12. Sindelka G, Heinemann L, Berger M, Frenck W, Chantelau E. Effect of insulin concentration, subcutaneous fat thickness and skin temperature on subcutaneous insulin absorption in healthy subjects. Diabetologia. 1994; 37:377–380. PMID: 8063038.
Article13. Mecklenburg RS, Benson EA, Benson JW Jr, Blumenstein BA, Fredlund PN, Guinn TS, et al. Long-term metabolic control with insulin pump therapy: report of experience with 127 patients. N Engl J Med. 1985; 313:465–468. PMID: 4022079.
Article14. Shalitin S, Phillip M. The use of insulin pump therapy in the pediatric age group. Horm Res. 2008; 70:14–21. PMID: 18493145.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparision of Body Image between DM Patients who used Insulin Pump and didn't use Insulin Pump
- Comparision of Body Image between DM patients who used Insulin Pump and didn't use Insulin Pump
- Study of Genetic Imprinting on 3 Cases of Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Developed in Early Infantile Period
- Effective Use of Insulin Pump in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
- Transient Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus Managed with Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) and Continuous Glucose Monitoring