Ann Dermatol.
2009 Aug;21(3):330-333. 10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.330.
A Case of Concurrent Vitiligo and Psoriasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ykpark@ yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2266305
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.330
Abstract
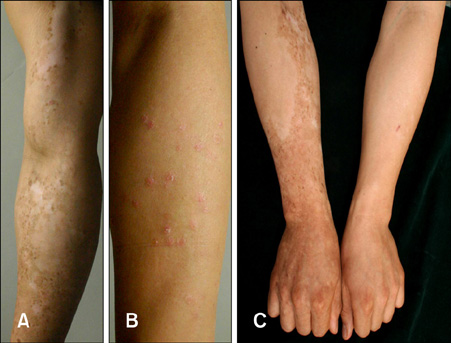
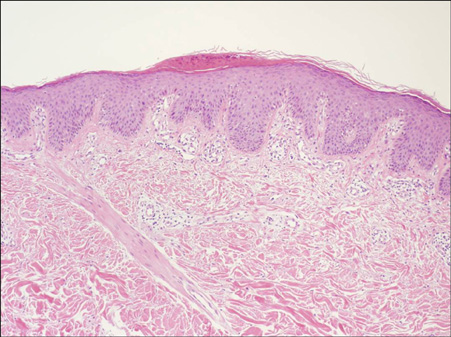
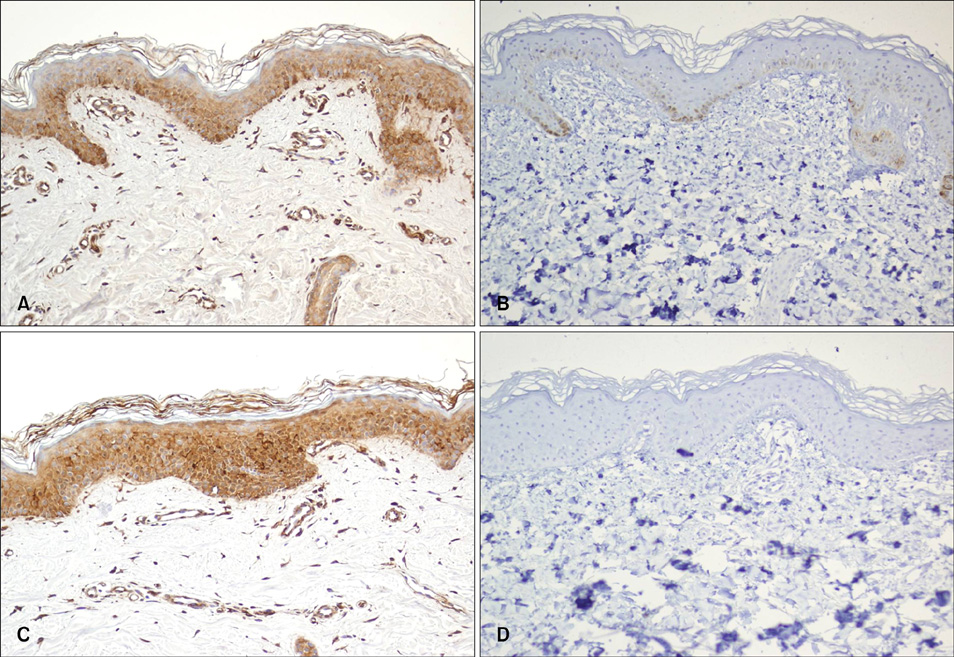
- Vitiligo and psoriasis are common dermatoses that occur in 1~3% and 0.5% of the general population, respectively. There have been several reports of the concurrence of these diseases in the English medical literature. Yet the pathogenesis of the association between these two dermatoses is still unknown. Psoriasis may occur coincidentally with vitiligo and it may be strictly confined to the vitiliginous patches or it may occur elsewhere. Despite the reports in the English literature, there has been only one case of vitiligo and psoriasis coexisting in the same patient and these diseases occurred in separate sites in the Korean dermatologic literature. A 30-year-old man recently presented with spreading vitiligo on the right forearm and a 3-month history of guttate psoriasis on the left forearm. He had a family history of psoriasis without any history of associated autoimmune disease. Herein, we report on a case of coexisting vitiligo and psoriasis in the same individual at different sites and we review the relevant literature.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Psoriasis, Vitiligo and Crohn's Disease Co-Existing in a Single Patient: A Variant Type of Multiple Autoimmune Syndrome?
Sul Hee Lee, Ye Seul Kim, Hyun Ju Kim, Young Lip Park
Ann Dermatol. 2017;29(6):782-785. doi: 10.5021/ad.2017.29.6.782.
Reference
-
1. Selenyi A. Vitiligo and psoriasis on the same side with syringomyelia. Borgyogy Venerol Sz. 1955. 9:94–96.2. Papadavid E, Yu RC, Munn S, Chu AC. Strict anatomical coexistence of vitiligo and psoriasis vulgaris--a Koebner phenomenon? Clin Exp Dermatol. 1996. 21:138–140.
Article3. Menter A, Boyd AS, Silverman AK. Guttate psoriasis and vitiligo: anatomic cohabitation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989. 20:698–700.
Article4. Lee HC, Lim SW, Suh MK, Choi JH, Kwon SW, Lee JW, et al. A case of psoriasis vulgaris associated with vitiligo. Korean J Dermatol. 2003. 41:1416–1418.5. Koransky JS, Roenigk HH Jr. Vitiligo and psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982. 7:183–189.
Article6. Kim YJ, Kang HY, Lee ES, Kim YC. A case of psoriasis strictly localized on a vitiligo lesion. Korean J Dermatol. 2006. 44:528–530.7. el-Mofty AM, el-Mofty M. Vitiligo. A symptom complex. Int J Dermatol. 1980. 19:237–244.8. Bor S, Feiwel M, Chanarin I. Vitiligo and its aetiological relationship to organ-specific autoimmune disease. Br J Dermatol. 1969. 81:83–88.
Article9. Percivalle S, Piccinno R, Caccialanza M. Concurrence of vitiligo and psoriasis: a simple coincidence? Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009. 34:90–91.
Article10. De Sica AB, Wakelin S. Psoriasis vulgaris confined to vitiligo patches and occurring contemporaneously in the same patient. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004. 29:434–435.
Article11. Sandhu K, Kaur I, Kumar B. Psoriasis and vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004. 51:149–150.
Article12. Dhar S, Malakar S. Colocalization of vitiligo and psoriasis in a 9-year-old boy. Pediatr Dermatol. 1998. 15:242–243.
Article13. Boyd AS, Neldner KH. The isomorphic response of Koebner. Int J Dermatol. 1990. 29:401–410.
Article14. Kovacs SO. Vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998. 38:647–666.
Article15. Jain R, Dogra S, Sandhu K, Handa S, Kumar B. Coexistence of vitiligo and pemphigus vulgaris in an indian patient. Pediatr Dermatol. 2003. 20:369–370.
Article16. Victor FC, Gottlieb AB, Menter A. Changing paradigms in dermatology: tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) blockade in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Dermatol. 2003. 21:392–397.
Article17. Prignano F, Pescitelli L, Ricceri F, Lotti T. The importance of genetical link in immuno-mediated dermatoses: psoriasis and vitiligo. Int J Dermatol. 2008. 47:1060–1062.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Psoriasis Strictly Localized on a Vitiligo Lesion
- An Unusual Case of Psoriasis Confined to Vitiligo Lesions
- A Case of Psoriasis vulgaris Associated with Vitiligo
- Progression of Pre-Existing Vitiligo during Secukinumab Treatment for Psoriasis
- Vitiligo in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Case Report