Ann Dermatol.
2009 Aug;21(3):291-293. 10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.291.
Cyclosporine Treatment in a Patient with Concurrent Autoimmune Urticaria and Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yymmpark6301@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2266294
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.291
Abstract
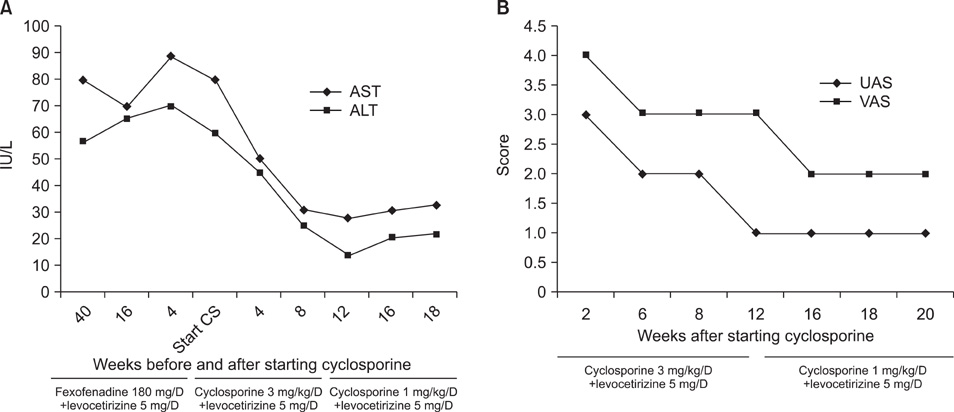
- Patients with autoimmune urticaria show a higher rate of seropositivity for other autoantibodies and often have a history of autoimmune conditions. They also tend to have more severe symptoms and to have a poor response to conventional antihistamine treatment. Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic inflammatory disorder in which progressive liver injury is thought to be the result of a T-cell-mediated immunologic attack against liver cells in genetically predisposed individuals. While the association between autoimmune urticaria and other autoimmune disorders such as thyroid disease is well known, there has been no reported case of autoimmune urticaria concomitant with autoimmune hepatitis. We report a case of autoimmune urticaria concurrent with autoimmune hepatitis, which was successfully treated with cyclosporine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Grattan CE. Autoimmune urticaria. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2004. 24:163–181. v
Article2. Krawitt EL. Autoimmune hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:54–66.
Article3. Leznoff A, Josse RG, Denburg J, Dolovich J. Association of chronic urticaria and angioedema with thyroid autoimmunity. Arch Dermatol. 1983. 119:636–640.
Article4. Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, Bianchi L, Burroughs AK, Cancado EL, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1999. 31:929–938.
Article5. Grattan CE, O'Donnell BF, Francis DM, Niimi N, Barlow RJ, Seed PT, et al. Randomized double-blind study of cyclosporin in chronic 'idiopathic' urticaria. Br J Dermatol. 2000. 143:365–372.
Article6. Lee JY, Park CW, Lee CH. Evaluation of autoimmunity in patients with chronic urticaria. Korean J Dermatol. 2000. 38:221–226.7. Cebeci F, Tanrikut A, Topcu E, Onsun N, Kurtulmus N, Uras AR. Association between chronic urticaria and thyroid autoimmunity. Eur J Dermatol. 2006. 16:402–405.8. Hide M, Francis DM, Grattan CE, Hakimi J, Kochan JP, Greaves MW. Autoantibodies against the high-affinity IgE receptor as a cause of histamine release in chronic urticaria. N Engl J Med. 1993. 328:1599–1604.
Article9. Sabroe RA, Seed PT, Francis DM, Barr RM, Black AK, Greaves MW. Chronic idiopathic urticaria: comparison of the clinical features of patients with and without anti-FcepsilonRI or anti-IgE autoantibodies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999. 40:443–450.
Article10. Sabroe RA, Grattan CE, Francis DM, Barr RM, Kobza Black A, Greaves MW. The autologous serum skin test: a screening test for autoantibodies in chronic idiopathic urticaria. Br J Dermatol. 1999. 140:446–452.
Article11. Malekzadeh R, Nasseri-Moghaddam S, Kaviani MJ, Taheri H, Kamalian N, Sotoudeh M. Cyclosporin A is a promising alternative to corticosteroids in autoimmune hepatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2001. 46:1321–1327.12. Kim BS, Cho HH, Ko HC, Kim SJ, Oh CK, Kwon KS, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of low-dose cyclosporine in chronic idiopathic urticaria. Korean J Dermatol. 2007. 45:680–686.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Autoimmune Hepatitis
- A case of autoimmune hepatitis accompanied by systemic lupus erythematosus
- A Case of Overlap Syndromebetween Autoimmune Hepatitis and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
- The major diagnostic role of autoantibodies in the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis, a disease of all ages
- Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis