Ann Dermatol.
2009 Aug;21(3):285-287. 10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.285.
Successful Treatment of Recalcitrant Primary Follicular Mucinosis with Indomethacin and Low-dose Intralesional Interferon Alpha
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine and Medical Research Institute, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. tyyoon@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine and Medical Research Institute, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2266292
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.285
Abstract
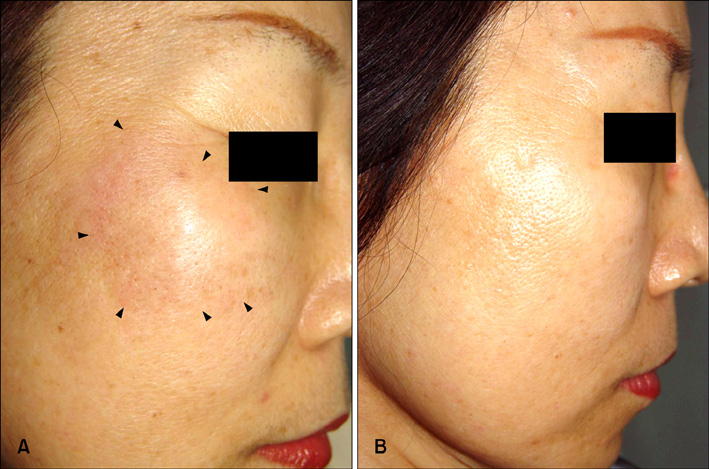
- Follicular mucinosis (FM) is an epithelial reaction pattern that is characterized by the accumulation of mucinous material in the epithelial hair follicle sheath and the sebaceous glands. Although various pharmacological agents have been employed in an attempt to treat FM, effective therapeutic options have remained elusive. We experienced a recalcitrant form of primary FM that we successfully treated with indomethacin and low-dose intralesional interferon alpha (IFN alpha), respectively. To the best of our knowledge, the primary type of FM that responded to indomethacin and low-dose IFN alpha, respectively, in a single case has not been reported in the English medical literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pinkus H. Alopecia mucinosa; inflammatory plaques with alopecia characterized by root-sheath mucinosis. AMA Arch Derm. 1957. 76:419–424.2. Jablonska S, Chorzelski T, Lancucki J. Mucinosis follicularis. Hautarzt. 1959. 10:27–33.3. Emmerson RW. Follicular mucinosis. A study of 47 patients. Br J Dermatol. 1969. 81:395–413.
Article4. Yotsumoto S, Uchimiya H, Kanzaki T. A case of follicular mucinosis treated successfully with minocycline. Br J Dermatol. 2000. 142:841–842.
Article5. Kodama H, Umemura S, Nohara N. Follicular mucinosis: response to indomethacin. J Dermatol. 1988. 15:72–75.
Article6. Kubba RK, Stewart TW. Follicular mucinosis responding to dapsone. Br J Dermatol. 1974. 91:217–220.
Article7. Meissner K, Weyer U, Kowalzick L, Altenhoff J. Successful treatment of primary progressive follicular mucinosis with interferons. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991. 24:848–850.
Article8. Hempstead RW, Ackerman AB. Follicular mucinosis. A reaction pattern in follicular epithelium. Am J Dermatopathol. 1985. 7:245–257.9. Reed RJ. The T-lymphocyte, the mucinous epithelial interstitium, and immunostimulation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1981. 3:207–214.
Article10. Takematsu H, Tagami H. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis. Studies on possible chemotactic factors involved in the formation of pustules. Br J Dermatol. 1986. 114:209–215.
Article11. Morley J, Beets JL, Bray MA, Paul W. Regulation of allergic responses by prostaglandins: a review. J R Soc Med. 1980. 73:443–447.
Article12. Martinez J, de Misa RF, Boixeda P, Arrazola JM, Ledo A. Long-term results of intralesional interferon alpha-2B in discoid lupus erythematosus. J Dermatol. 1993. 20:444–446.
Article13. Yoshida R, Murray HW, Nathan CF. Agonist and antagonist effects of interferon alpha and beta on activation of human macrophages. Two classes of interferon gamma receptors and blockade of the high-affinity sites by interferon alpha or beta. J Exp Med. 1988. 167:1171–1185.
Article14. Saito H, Hayakawa T, Yui Y, Shida T. Effect of human interferon on different functions of human neutrophils and eosinophils. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987. 82:133–140.
Article15. Aldebert D, Lamkhioued B, Desaint C, Gounni AS, Goldman M, Capron A, et al. Eosinophils express a functional receptor for interferon alpha: inhibitory role of interferon alpha on the release of mediators. Blood. 1996. 87:2354–2360.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intralesional Recombinant Alpha-2a Interferon for the Treatment of Patients With Verruca
- A Case of Lichen Spinulosus with an Histologic Finding of Follicular Mucinosis
- Combination Therapy with Intralesional Interferon α-2b and Pulsed Dye Laser for the Treatment of Periungual Warts
- A Case of Widespread Follicular Mucinosis Associated with Mycosis Fungoides
- A Case of Follicular Mucinosis