Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2015 May;19(2):82-85. 10.14701/kjhbps.2015.19.2.82.
A rare case of gallbladder torsion along the axis of body: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kyungpook National University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea. ksg@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2243055
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/kjhbps.2015.19.2.82
Abstract
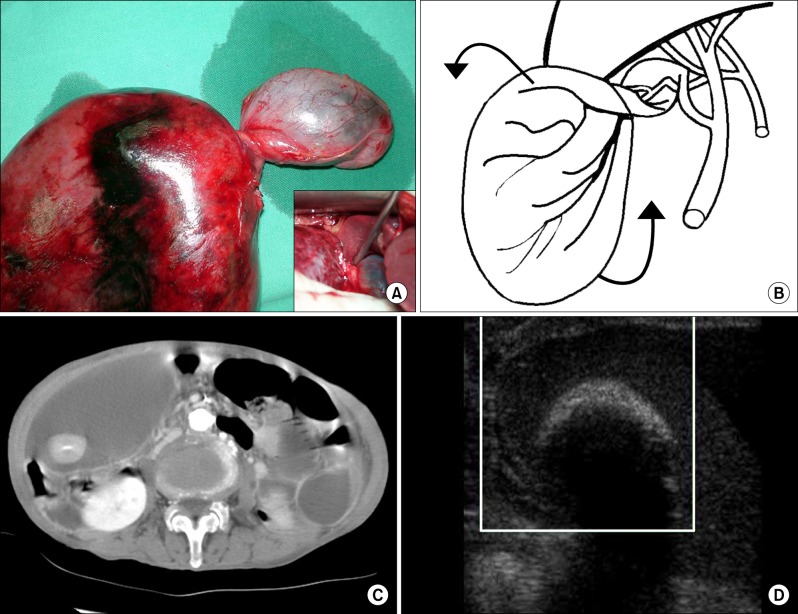
- Abnormal attachment of the gallbladder to the liver is the main cause for gallbladder torsion. However, the present study reports a rare case of gallbladder torsion in which a portion of fundus is rotated along the axis of body. So far, very few similar cases have been reported. An 87-year-old woman complaining right upper quadrant abdominal pain for 4 days was admitted. Her body temperature was 38.5degrees C with moderate dehydration. A large tender mass was palpated on the right abdomen extending to the right iliac fossa. Computed tomography of abdomen showed a large cavity with a diameter of 15 cm containing a big stone and a small normal looking gallbladder. Ultrasonographic scan showed a twisted portion of the gallbladder torsion. During emergency laparotomy, the middle portion of the gallbladder was found to be twisted counterclockwise with huge gangrenous gallbladder distal. The proximal body of the gallbladder was spared and attached firmly to the liver. Cholecystectomy was performed and the patient was discharged 2 weeks later without postoperative complications. Histological findings of specimen were consistent with operative findings. The current study reports on a rare case of gallbladder torsion by reviewing previous studies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Losken A, Wilson BW, Sherman R. Torsion of the gallbladder: a case report and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1997; 63:975–978. PMID: 9358785.2. McHenry CR, Byrne MP. Gallbladder volvulus in the elderly. An emergent surgical disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1986; 34:137–139. PMID: 3944403.3. Marano A, Yahchouchy-Chouillard E, Spinelli R, Iannelli A, Aura T, Fingerhut A. Gallbladder torsion: report of four cases and review of the literature. Asian J Surg. 2002; 25:175–178. PMID: 12376241.
Article4. Rossouw J. Torsion of the gallbladder-a case where the gallbladder was firmly attached to the liver. S Afr Med J. 1970; 44:47–48. PMID: 5411166.5. Schlinkert RT, Mucha P Jr, Farnell MB. Torsion of the gallbladder. Mayo Clin Proc. 1984; 59:490–492. PMID: 6738115.
Article6. Merriman TE, Houghton G, Ventura R. Torsion of the fundus of the gall-bladder. Aust N Z J Surg. 1993; 63:821–822. PMID: 8274129.
Article7. Jarman B, Price PD, Holden C. Acute gallbladder torsion: a review and case studies. Contemp Surg. 2003; 59:174–176.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Imaging Findings of Acute Torsion of the Gallbladder: Case Report
- Necrotizing Gallbladder Torsion Masking as Acalculous Cholecystitis: A Review of Two Cases Treated with Successful Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- Strangulation of the Floating Gallbladder by the Lesser Omentum
- Gallbladder Torsion: A Case Report and a Review of the Literature
- Acute Choleystitis due to Torsion of the Gallbladder