Imaging Sci Dent.
2013 Dec;43(4):303-308. 10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.303.
Multiple calcifying hyperplastic dental follicles: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, Baskent University Faculty of Dentistry, Ankara, Turkey.
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Suleyman Demirel University Faculty of Dentistry, Isparta, Turkey.
- 3Department of Oral Pathology, Gazi University Faculty of Dentistry, Ankara, Turkey.
- 4Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, Suleyman Demirel University Faculty of Dentistry, Isparta, Turkey. dtesin@hotmail.com
- 5Atlas Dent Dental Health Center, Aydin, Turkey.
- KMID: 2229620
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.303
Abstract
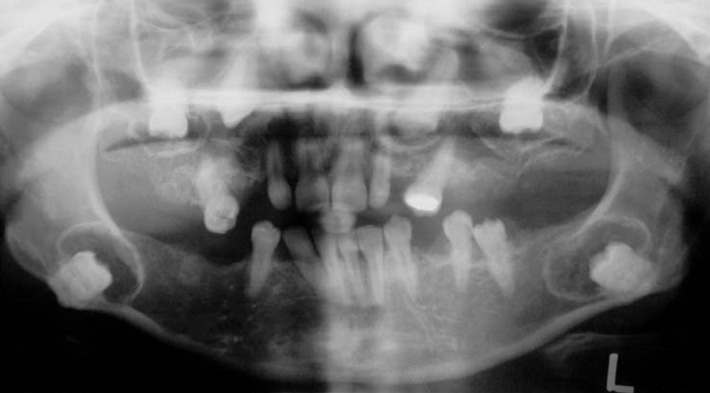
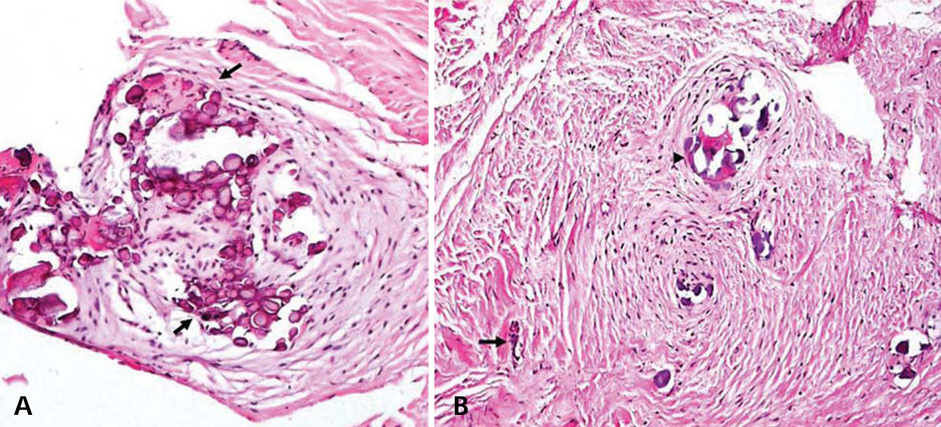
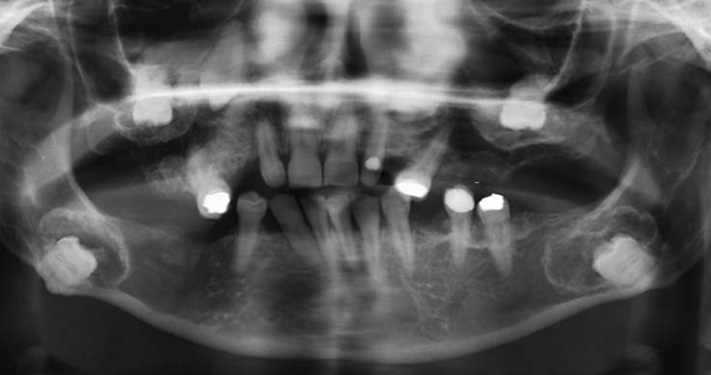
- This report describes a 31-year-old female patient with six impacted teeth. The crowns of the impacted teeth were surrounded with cyst-like lesions with a mixed internal structure and well-defined cortical borders. Microscopic examination of the specimen obtained from the follicle of the left mandibular third molar tooth revealed loose to moderately dense collagenous connective tissue with abundant calcified material and sparse epithelial islands. A diagnosis of multiple calcifying hyperplastic dental follicles was made.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gardner DG, Radden B. Multiple calcifying hyperplastic dental follicles. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995; 79:603–606.
Article2. Sandler HJ, Nersasian RR, Cataldo E, Pochebit S, Dayal Y. Multiple dental follicles with odontogenic fibroma-like changes (WHO type). Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988; 66:78–84.
Article3. Gomez RS, Silva EC, Silva-Filho EC, Castro WH. Multiple calcifying hyperplastic dental follicles. J Oral Pathol Med. 1998; 27:333–334.
Article4. Lukinmaa PL, Hietanen J, Anttinen J, Ahonen P. Contiguous enlarged dental follicles with histologic features resembling the WHO type of odontogenic fibroma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1990; 70:313–317.
Article5. Cho YA, Yoon HJ, Hong SP, Lee JI, Hong SD. Multiple calcifying hyperplastic dental follicles: comparison with hyperplastic dental follicles. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011; 40:243–249.
Article6. Magliocca KR, Bhattacharyya I, Wolfrom RB, Cohen DM. Multiple impacted teeth and associated pericoronal tissue abnormality in tuberous sclerosis complex. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 70:2581–2584.
Article7. Wood NK, Goaz PW, Lehnert JF. Mixed radiolucent-radiopaque lesions associated with teeth. In : Wood NK, Goaz PW, editors. Differential diagnosis of oral and maxillofacial lesions. 5th ed. St Louis, MO: Mosby;1997. p. 415–432.8. Wood NK, Kuc IM. Pericoronal radiolucencies. In : Wood NK, Goaz PW, editors. Differential diagnosis of oral and maxillofacial lesions. 5th ed. St Louis, MO: Mosby;1997. p. 279–295.9. Sun CX, Ririe C, Henkin JM. Hyperplastic dental follicle-review of literature and report of two cases in one family. Chin J Dent Res. 2010; 13:71–75.10. Baykul T, Saglam AA, Aydin U, Basak K. Incidence of cystic changes in radiographically normal impacted lower third molar follicles. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005; 99:542–545.
Article11. Buchner A. The central (intraosseous) calcifying odontogenic cyst: an analysis of 215 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991; 49:330–339.
Article12. Handschel JG, Depprich RA, Zimmermann AC, Braunstein S, Kübler NR. Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor of the mandible: review of the literature and report of a rare case. Head Face Med. 2005; 1:3.
Article13. Philipsen HP, Reichart PA. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumour: biological profile based on 181 cases from the literature. Oral Oncol. 2000; 36:17–26.
Article14. White SC, Phaorah M. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Mosby;2008.15. Li TJ, Yu SF. Clinicopathologic spectrum of the so-called calcifying odontogenic cysts: a study of 21 intraosseous cases with reconsideration of the terminology and classification. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003; 27:372–384.16. Sedghizadeh PP, Wong D, Shuler CF, Linz V, Kalmar JR, Allen CM. Multifocal calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 104:e30–e34.
Article17. Bartake AR, Punnya VA, Sudeendra P, Rekha K. Two adenomatoid odontogenic tumours of the maxilla: a case report. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 47:638–640.
Article18. Dare A, Yamaguchi A, Yoshiki S, Okano T. Limitation of panoramic radiography in diagnosing adenomatoid odontogenic tumors. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1994; 77:662–668.
Article19. Odell EW, Morgan PR. Biopsy pathology of the oral tissues. London: Chapman & Hall Medical;1998.20. Wise GE. Cellular and molecular basis of tooth eruption. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2009; 12:67–73.
Article21. Kim SG, Kim MH, Chae CH, Jung YK, Choi JY. Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinases in hyperplastic dental follicles results in abnormal tooth eruption. BMB Rep. 2008; 41:322–327.
Article22. Mohan RP, Suma GN, Vashishth S, Goel S. Cleidocranial dysplasia: clinico-radiological illustration of a rare case. J Oral Sci. 2010; 52:161–166.
Article23. Bradley JF, Orlowski WA. Multiple osteomas, impacted teeth and odontomas - a case report of Gardner's Syndrome. J N J Dent Assoc. 1977; 48:32–33.24. Suri L, Gagari E, Vastardis H. Delayed tooth eruption: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. A literature review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004; 126:432–445.
Article25. Cutando A, Gil JA, López J. Oral health management implications in patients with tuberous sclerosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000; 90:430–435.
Article