Current Status of Diabetes Management in Korea Using National Health Insurance Database
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pochon CHA University.
- 2Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Eulji University.
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University.
- 5Department of Endocrinology, Gachon University of Science and Medicine, Gil Medical Center.
- 6Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Pusan Paik Hospital, Inje College of Medicine.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine.
- 9Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine.
- 10Department of Biostatistics, College of Medicine, Korea University.
- 11Department of Internal Medicine, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University.
- 12Department of Research, Health Insurance Review Agency.
- 13Task Force Team for Basic Statistical Study of Diabetes Mellitus of Korean Diabetes Association.
- KMID: 2222524
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.4.362
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: The prevalence of diabetes is steadily increasing in Korea. The increase in number of people with diabetes would ultimately result in premature death, poor quality of life, and increasing economic burden. However, in our country, researches regarding on the quality of diabetes management are lacking. This study was conducted in 2005 using National Health Insurance Database to know the current status of diabetes management in Korea.
METHODS
We have randomly selected 3,902 subjects out of 2,503,754 subjects who had claims with diagnosis of diabetes between January 2003 to December 2003 by using two staged cluster sampling method. Field survey with review of medical records and telephone survey was conducted with standardized record forms developed by Korean Diabetes Association; Task Force Team For Basic Statistical Study of Korean Diabetes Mellitus.
RESULTS
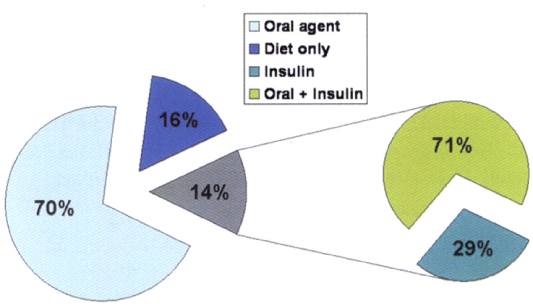
The age of diabetic subjects was 58.1 +/- 12.6 years and the duration of diabetes was 6.2 +/- 5.5 years. Hypertension was present in 54% of diabetic subjects. Among those with hypertension, 59% were controlled with blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg, but only 19% were controlled with blood pressure below 130/80 mmHg. Hyperlipidemia was present in 29% of diabetic subjects. Only 38% of those with hyperlipidemia were controlled with LDL-cholesterol below 100 mg/dL. For glycemic control, only 40% of diabetic subjects achieved the goal of HbA1c less than 7%, which was suggested by ADA.
CONCLUSION
We found that only 20~40% of diabetic subjects in Korea achieved the management goal for glucose, blood pressure, and lipids. It seems urgent to develop a quality management program for diabetes subjects in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Bowl-Based Meal Plan versus Food Exchange-Based Meal Plan for Dietary Intake Control in Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Hee-Jung Ahn, Boo-Kyung Koo, Ji-Yeon Jung, Hwi-Ryun Kwon, Hyun-Jin Kim, Kang-Seo Park, Kyung-Ah Han, Kyung-Wan Min
Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(2):155-163. doi: 10.4093/kdj.2009.33.2.155.The Effectiveness of Multidisciplinary Team-Based Education in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Jong Ho Kim, Yun Jeong Nam, Won Jin Kim, Kyung Ah Lee, A Ran Baek, Jung Nam Park, Jin Mi Kim, Seo Young Oh, Eun Heui Kim, Min Jin Lee, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Sang Soo Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2018;19(2):119-133. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2018.19.2.119.Influences of Patient Activation on Diabetes Self-Care Activities and Diabetes-Specific Distress
Sookyung Choi, Su Hyun Kim
Korean J Adult Nurs. 2020;32(1):10-20. doi: 10.7475/kjan.2020.32.1.10.Physician-Directed Diabetes Education without a Medication Change and Associated Patient Outcomes
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hae-Kyung Yang, Eun Young Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In Young Choi, Hyeon Woo Yim, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(3):187-194. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.187.
Reference
-
2. Park Y, Lee H, Koh CS, Min H, Yoo K, Kim Y, Shin Y. Prevalence of diabetes and IGT in Yonchon County, South Korea. Diabetes Care. 1995. 18:545–548.3. Kim SM, Lee JS, Lee J, Na JK, Han JH, Yoon DK, Baik SH, Choi DS, Choi KM. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:226–231.6. Amos AF, McCarty DJ, Zimmet P. The rising global burden of diabetes and its complications: estimates and projections to the year 2010. Diabet Med. 1997. 14:Suppl 5. S1–S85.8. http://www.nso.go.kr/. 2006. assessed on November 24.9. National Diabetes Surveillance System: National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. 2006. assessed on November 24. http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/statistics/.11. Rhee SY, Kim YS, Oh SJ, Choi WH, Park JE, Jeong WJ. Diabcare Asia 2001-Korea: Country Report on Outcome Data and Analysis. Korean J Intern Med. 2005. 20:48–54.14. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA. Association of glycemia and macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000. 321:405–412.15. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: UKPDS38. BMJ. 1998. 317:703–713.16. Gaede P, Vedel P, Lasen N. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:383–393.17. Chuang LM, Tsai ST, Huang BY, Tai TY. Diabcare_Asia 1998 Study Group. The status of diabetes control in Asia-a cross-sectional survey of 24,317 patients with diabetes mellitus in 1998. Diabet Med. 2002. 19:978–985.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiologic Characteristics of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Current Status of Diabetic Patients Using Korean Health Insurance Database
- Epidemiology and Current Status of Diabetes in Korea
- Data Analytic Process of a Nationwide Population-Based Study Using National Health Information Database Established by National Health Insurance Service
- Status of Diabetic Neuropathy in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort Analysis (2006 to 2015) (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:115-9)
- Management of Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Current Status and Suggestions