J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Nov;54(11):1731-1736. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.11.1731.
Long-Term Changes in Foveal Microstructure after Macular Hole Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kim's Eye Hospital, Konyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kjh7997@daum.net
- KMID: 2217921
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.11.1731
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate long-term outcome of foveal tissue elongation after macular hole (MH) surgery.
METHODS
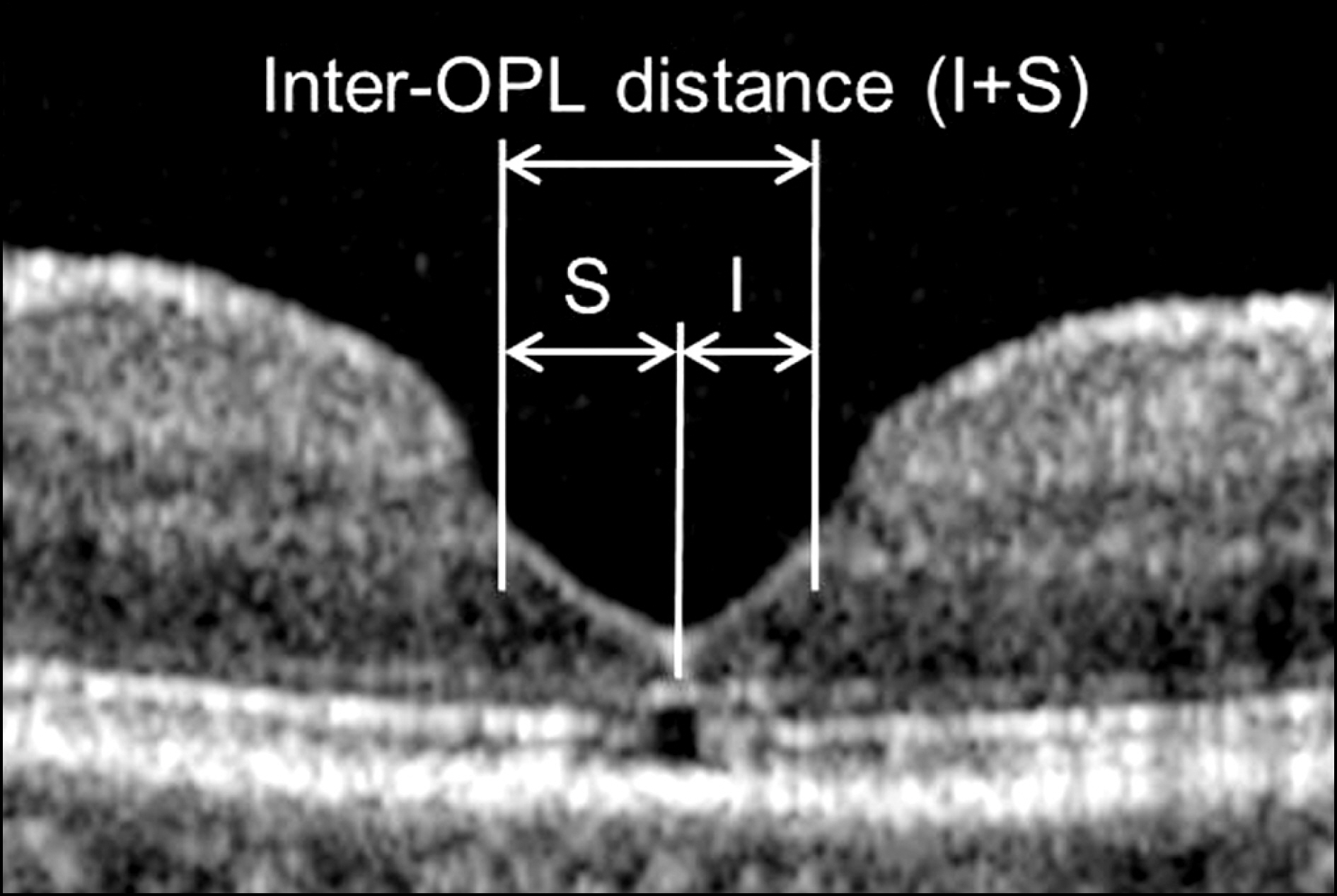
This retrospective, observational case series was performed on patients who underwent MH surgery and were followed-up more than 12 months. Distance between the parafoveal edge of the outer plexiform layer (OPL) was defined as the inter-OPL distance and measured using optical coherence tomography images at 5 to 8 months postoperatively and at the last follow-up. The horizontal and vertical inter-OPL distances were compared between the 2 defined time points. In addition, further elongation of the foveal tissue in certain directions was defined as asymmetric elongation and was compared between the defined time points.
RESULTS
The early and late postoperative examination was performed at 6.3 +/- 1.1 (mean +/- standard deviation) months and 22.7 +/- 7.8 months, respectively. The horizontal inter-OPL distance was 552.3 +/- 130.5 microm and 502.8 +/- 139.3 microm at the defined time points, respectively and the vertical inter-OPL distance was 478.9 +/- 107.2 microm and 447.5 +/- 107.1 microm, respectively. Both horizontal and vertical inter-OPL distances were significantly shortened at the last postoperative examination (p < 0.001, p = 0.002, respectively). The degree of asymmetric elongation was 10.8 +/- 6.5% and 11.8 +/- 7.9% at the defined time points, respectively, and was not different between the defined time points (p = 0.426).
CONCLUSIONS
The long-term shortening of foveal tissue after MH surgery without progression of asymmetry may partially contribute to the long-term recovery of visual function after MH surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
ILM Peeling Size and Postoperative Foveal Tissue Elongation in Macular Hole Surgery
Jae Hong Park, Hye Min Jeon, Hee Seong Yoon
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(12):1860-1867. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1860.
Reference
-
References
1. Wang S, Xu L, Jonas JB. Prevalence of full-thickness macular holes in urban and rural adult Chinese: the Beijing Eye Study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 141:589–91.
Article2. Kelly NE, Wendel RT. Vitreous surgery for idiopathic macular holes. Results of a pilot study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991; 109:654–9.
Article3. Choi M, Kim H, Yun I. Surgical outcome of epiretinal membrane and internal limiting membrane removal for macular hole retinal detachment. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1491–7.4. Kim HK, Hong SB, Kwon OW. The effect of vitrectomy for the treatment of macular holes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:1797–802.5. Nassif N, Cense B, Park BH, et al. In vivo human retinal imaging by ultrahigh-speed spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett. 2004; 29:480–2.
Article6. Bottoni F, De Angelis S, Luccarelli S, et al. The dynamic healing process of idiopathic macular holes after surgical repair: a spec- tral-domain optical coherence tomography study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:4439–46.7. Christensen UC, Kroyer K, Sander B, et al. Prognostic significance of delayed structural recovery after macular hole surgery. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:2430–6.
Article8. Wakabayashi T, Fujiwara M, Sakaguchi H, et al. Foveal micro- structure and visual acuity in surgically closed macular holes: spec- tral-domain optical coherence tomographic analysis. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:1815–24.9. Kang SW, Lim JW, Chung SE, Yi CH. Outer foveolar defect after surgery for idiopathic macular hole. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 150:551–7.
Article10. Kim JH, Kang SW, Park DY, et al. Asymmetric elongation of foveal tissue after macular hole surgery and its impact on metamorphopsia. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:2133–40.
Article11. Leonard RE 2nd, Smiddy WE, Flynn HW Jr, Feuer W. Long-term visual outcomes in patients with successful macular hole surgery. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104:1648–52.
Article12. Scott IU, Moraczewski AL, Smiddy WE, et al. Long-term anatomic and visual acuity outcomes after initial anatomic success with mac- ular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 135:633–40.13. Haritoglou C, Reiniger IW, Schaumberger M, et al. Five-year fol- low-up of macular hole surgery with peeling of the internal limiting membrane: update of a prospective study. Retina. 2006; 26:618–22.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of the Macular Curvature on Foveal Migration after Macular Hole Surgery
- Postoperative Changes in Vessel Density according to Macular Hole and Macular Pseudohole Subtypes
- Long-Term Visual Outcomes and Prognostic Factors for Successful Idiopathic Macular Hole
- Relationship between Visual Acuity and Photoreceptor Layer or Foveal Thickness on Optical Coherence Tomography after Macular Hole Surgery
- Eccentric Macular Hole Formation After Macular Hole Surgery