J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Feb;54(2):185-191. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.2.185.
Clinical Features and Results of Steroid Therapy for Orbital Inflammatory Pseudotumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. kcyoon@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2216651
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.2.185
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical features and treatment outcomes of steroid therapy for orbital inflammatory pseudotumor.
METHODS
Sixty-four patients diagnosed with orbital inflammatory pseudotumor were reviewed retrospectively. Patients with a follow-up period of less than 6 months were excluded from the study. The pseudotumor was classified into myositic, lacrimal, anterior, diffuse, or apical type according to orbital computed tomography findings. All patients were initially treated with systemic corticosteroids and evaluated for response to the treatment. Treatment outcome was considered a "success" if the patient had complete relief of symptoms with no recurrence, and a "failure" if the patient had no or only partial relief of symptoms or showed relapse. Factors affecting the treatment outcome were analyzed.
RESULTS
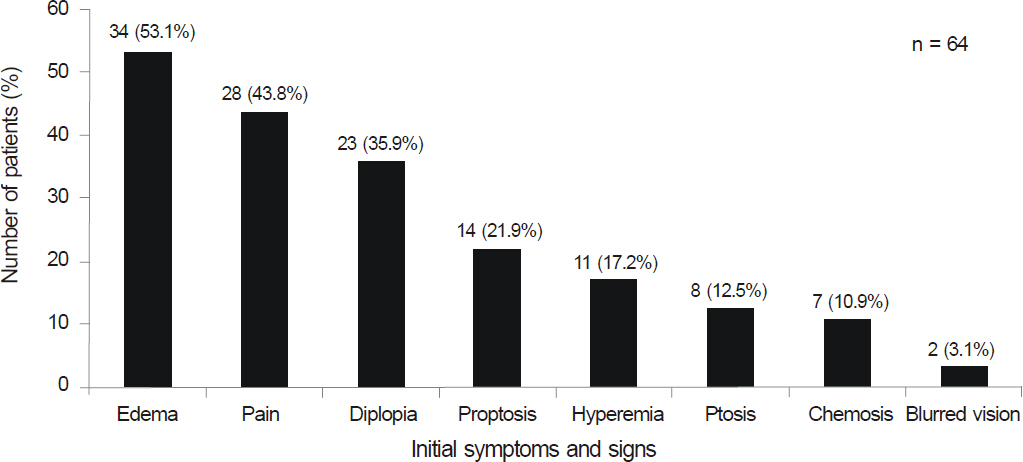
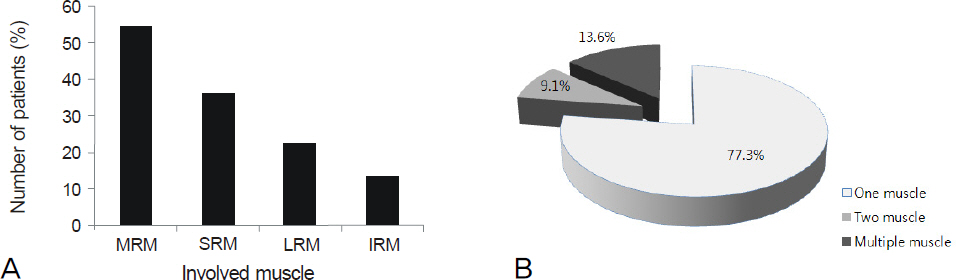
The most frequent lesion subtype was myositis. Periorbital edema was the most common symptom and was evident in 53.1% of the patients. Thirty-eight patients (59.4%) showed treatment success. Age, sex, bilaterality, and mean follow-up length did not correlate with the treatment outcome. A short interval from symptom onset to treatment time and apical subtype were significantly associated with good steroid response (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
In orbital inflammatory pseudotumor, myositis was the most common subtype. A short interval from symptom onset to treatment time and apical subtype were associated with good steroid response.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
A Case of Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation Presenting with Isolated Myositis of the Superior Oblique Muscle
Seung Soo Han, Hye Young Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(8):1213-1217. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.8.1213.A Case of Surgical Diagnosis and Treatment of Idiopathic Orbital Myositis with Sudden Vision Loss
Dong Eun Lee, Byung Gun Park, Sung Hyuk Moon, Jae Wook Yang
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2017;58(10):1183-1188. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.10.1183.Clinical Characteristics of Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation Accompanied with Paranasal Sinusitis
Ka Hyun Lee, Jin Sook Yoon
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2017;58(7):776-781. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.7.776.
Reference
-
References
1. Birch-Hirschfeld A. Zur diagnostic and pathologic der orbital tumoren. Ber Zusammenkunft Dtsch Ophthamol Ges. 1905; 32:127–35.2. Ding ZX, Lip G, Chong V. Idiopathic orbital pseudotumor. Clin Radiol. 2011; 66:886–92.3. Rubin PA, Foster CS. Etiology and management of idiopathic orbital inflammation. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 138:1041–3.
Article4. Weber AL, Jakobiec FA, Sabates NR. Pseudotumor of the orbit. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1996; 6:73–92.
Article5. Shields JA, Shields CL, Scartozzi R. Survey of 1264 patients with orbital tumors and simulating lesions: The 2002 Montgomery Lecture, Part 1. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:997–1008.6. Mombaerts I, Goldschmeding R, Schlingemann RO, Koornneef L. What is orbital pseudotumor? Surv Ophthalmol. 1996; 41:66–78.
Article7. Rootman J, McCarthy M, White V, et al. Idiopathic sclerosing inflammation of the orbit. A distinct clinicopathologic entity. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:570–84.
Article8. Jacobs D, Galetta S. Diagnosis and management of orbital pseudotumor. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2002; 13:347–51.
Article9. Yuen SJ, Rubin PA. Idiopathic orbital inflammation: distribution, clinical features, and treatment outcome. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003; 121:491–9.10. Hatton MP, Rubin PA, Foster CS. Successful treatment of idiopathic orbital inflammation with mycophenolate mofetil. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 140:916–8.
Article11. Garrity JA, Coleman AW, Matteson EL, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant idiopathic orbital inflammation (chronic orbital myositis) with infliximab. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 138:925–30.
Article12. Mombaerts I, Schlingemann RO, Goldschmeding R, Koornneef L. Are systemic corticosteroids useful in the management of orbital pseudotumors? Ophthalmology. 1996; 103:521–8.
Article13. Swamy BN, McCluskey P, Nemet A, et al. Idiopathic orbital inflammatory syndrome: clinical features and treatment outcomes. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007; 91:1667–70.
Article14. Chirapapaisan N, Chuenkongkaew W, Pornpanich K, Vangveeravong S. Orbital pseudotumor: clinical features and outcomes. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2007; 25:215–8.15. Park SJ, Sin SJ, Lee DG, Jang JW. Pseudotumor: distribution, clinical features, treatment outcomes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1379–86.16. Lee H, Kim SJ, Lee SY. Classification and treatment efficacy of orbital pseudotumor. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:1647–54.17. Cho KR, Kim JH. Diagnosis of idiopathic inflammatory pseudotumor of the orbit. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1991; 32:134–42.18. Rootman J, Nugent R. The classification and management of acute orbital pseudotumors. Ophthalmology. 1982; 89:1040–8.
Article19. Scott IU, Siatkowski RM. Idiopathic orbital myositis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1997; 9:504–12.
Article20. Gordon LK. Orbital inflammatory disease: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20:1196–206.
Article21. Sitakowski RM, Capó H, Byrne SF, et al. Clinical and echographic findings in idiopathic orbital myositis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994; 118:343–50.22. McNicholas MM, Power WJ, Griffin JF. Idiopathic inflammatory pseudotumour of the orbit: CT features correlated with clinical outcome. Clin Radiol. 1991; 44:3–7.
Article23. Henderson JW, Farrow GM. Orbital tumors. New York: Brian C. Decker;1980. p. 512.24. Brannan PA. A review of sclerosing idiopathic orbital inflammation. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2007; 18:402–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Atypical Inflammatory Orbital Pseudotumor with Acute Pneumonic Infiltrates
- A Case of Orbital Pseudotumor
- A Case of Inflammatory Pseudotumor in Temporal Bone Treated with Methotraxate
- Effect of Corticosteroid on Orbital Pseudotumor Caused by Orbital Myositis
- A Case of Temporal Posterior Ciliary Artery Obstruction in Patient with Orbital Pseudotumor