J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Nov;56(11):1783-1788. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.11.1783.
The Surgical Outcomes of Unilateral Lateral Rectus Recession in Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia after Unilateral Recession-Resection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. lsy3379@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Uijeongbu, Korea.
- KMID: 2214188
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.11.1783
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the surgical outcomes of unilateral lateral rectus (LR) recession on the contralateral eye for recurrent intermittent exotropia after unilateral recession-resection (R & R).
METHODS
A retrospective analysis of 43 patients was performed. The patients were classified into 2 groups, 18 patients who underwent unilateral LR recession for intermittent exotropia of 18 to 20 prism diopters (PD) after unilateral R & R (reoperation group) and 25 patients who had primary unilateral LR recession (primary operation group).
RESULTS
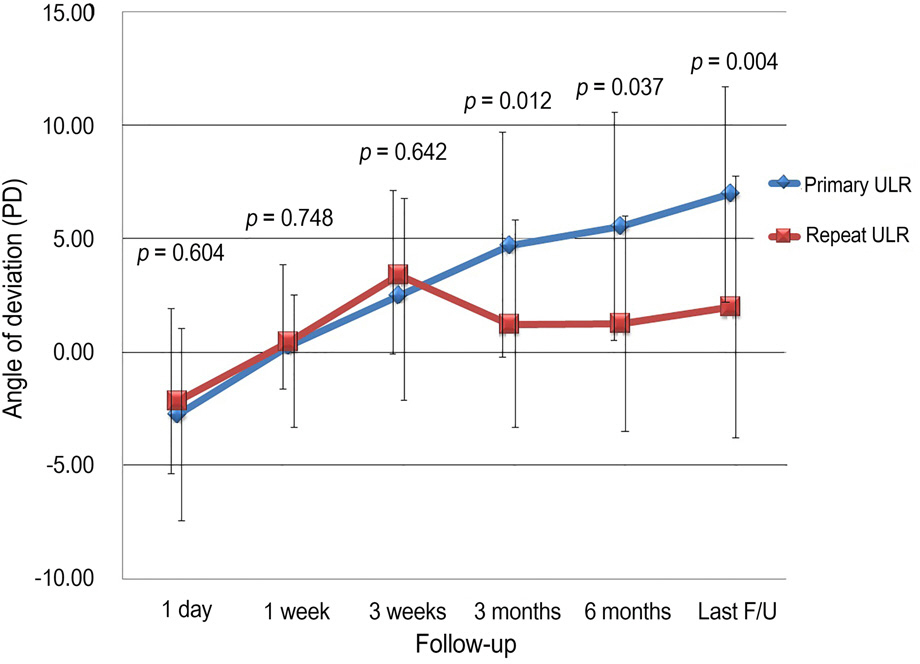
Significant differences in age, gender, refractive error, preoperative deviation, and near stereoacuity were not observed between the 2 groups (p > 0.05). The mean follow-up duration was 14.28 +/- 14.98 months in the reoperation group and 14.68 +/- 12.15 months in the primary operation group. Postoperative deviations were 1.11 +/- 3.89 PD at near distance and 2.00 +/- 4.70 PD at far distance in the reoperation group and 6.44 +/- 5.26 PD at near distance and 7.00 +/- 5.77 PD at far distance in the primary operation group on the final follow-up (p = 0.000, p = 0.004). The final surgical successful rates were 94.4% in the reoperation group and 64.0% in the primary group (p = 0.021).
CONCLUSIONS
The long-term surgical results of unilateral LR recession on the contralateral eye was better in patients with recurrent intermittent exotropia of 18 to 20 PD after unilateral R & R than patients who had primary unilateral LR recession.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Burian HM, Spivey BE. The surgical management of exodevia-tions. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965; 59:603–20.2. Binion WW. The surgical treatment of intermittent exotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966; 61:(5 Pt 1). 869–74.
Article3. Deutsch JA, Nelson LB, Sheppard RW, Burke MJ. Unilateral later-al rectus recession for the treatment of exotropia. Ann Ophthalmol. 1992; 24:111–3.4. Nelson LB, Bacal DA, Burke MJ. An alternative approach to the surgical management of exotropia-the unilateral lateral rectus recession. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1992; 29:357–60.
Article5. Spierer A, Ben-Simon GJ. Unilateral and bilateral lateral rectus re-cession in exotropia. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2005; 36:114–7.
Article6. Wang L, Nelson LB. Outcome study of unilateral lateral rectus re-cession for small to moderate angle intermittent exotropia in children. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2010; 47:242–7.
Article7. Weakley DR Jr, Stager DR. Unilateral lateral rectus recessions in exotropia. Ophthalmic Surg. 1993; 24:458–60.
Article8. Oh JY, Hwang JM. Survival analysis of 365 patients with exotropia after surgery. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20:1268–72.
Article9. Maruo T, Kubota N, Sakaue T, Usui C. Intermittent exotropia sur-gery in children: long term outcome regarding changes in binocular alignment. A study of 666 cases. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q. 2001; 16:265–70.10. Moon KJ, Choi WC, Park C. The long-term effect of unilateral lat-eral rectus muscle recession for moderate angle exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:1885–90.11. Kim JY, Chang BL. The effect of unilateral lateral rectus recession in recurrent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:2261–5.12. Lee K, Shin KS, Kim Y, Choi MY. Comparison of outcomes of uni-lateral lateral rectus recession for exotropia between first and sec-ond operations. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2011; 25:329–33.
Article13. Wright KW. Practical aspects of the adjustable suture technique for strabismus surgery. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1989; 29:10–5.
Article14. Kim HJ, Kim D, Choi DG. Long-term outcomes of unilateral later-al rectus recession versus recess-resect for intermittent exotropia of 20-25 prism diopters. BMC Ophthalmol. 2014; 14:46.
Article15. Dadeya S, Kamlesh . Long-term results of unilateral lateral rectus recession in intermittent exotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2003; 40:283–7.
Article16. Ekdawi NS, Nusz KJ, Diehl NN, Mohney BG. Postoperative out-comes in children with intermittent exotropia from a population-based cohort. J AAPOS. 2009; 13:4–7.
Article17. Feretis D, Mela E, Vasilopoulos G. Excessive single lateral rectus muscle recession in the treatment of intermittent exotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1990; 27:315–6.
Article18. Sohn JH, Chang BL. Management for reoperation in recurrent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:580–4.19. Kim WJ, Kim MM. The clinical course of recurrent intermittent exotropia after previous unilateral recess-resection surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1386–91.
Article20. Lee SY. The effect of unilateral lateral rectus muscle recession over 11mm in the treatment of intermittent exotropia of 15-20PD. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:550–4.21. Olitsky SE, Kelly C, Lee H, Nelson LB. Unilateral rectus resection in the treatment of undercorrected or recurrent strabismus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2001; 38:349–53.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Analysis after Reoperation for Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia
- The Effect of Unilateral Lateral Rectus Muscle Recession over 11mm in the Treatment of Intermittent Exotropia of 15-20PD
- Comparison of Surgical Results Between Bilateral Recession and Unilateral Resection-Recession in Intermittent Exotropia
- How to Better Treat Patients with Intermittent Exotropia: A Review of Surgical Treatment of Intermittent Exotropia
- Comparison of Surgical Results Between Bilateral Recession and Unilateral Recession-Resection in Intermittent Exotropia