J Korean Surg Soc.
2012 Jul;83(1):60-64. 10.4174/jkss.2012.83.1.60.
Synchronous T-cell lymphoma in patient with colon cancer: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. cosmo021@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2212281
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.83.1.60
Abstract
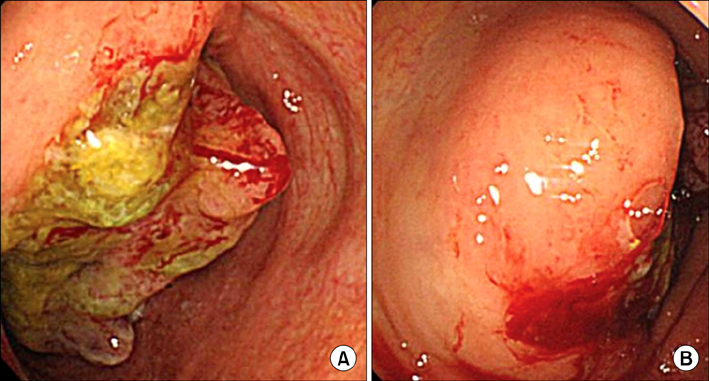
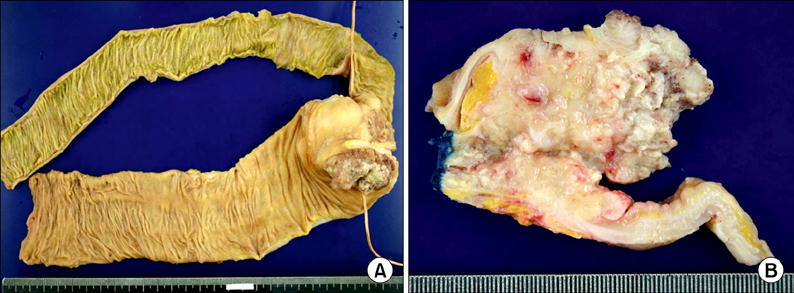
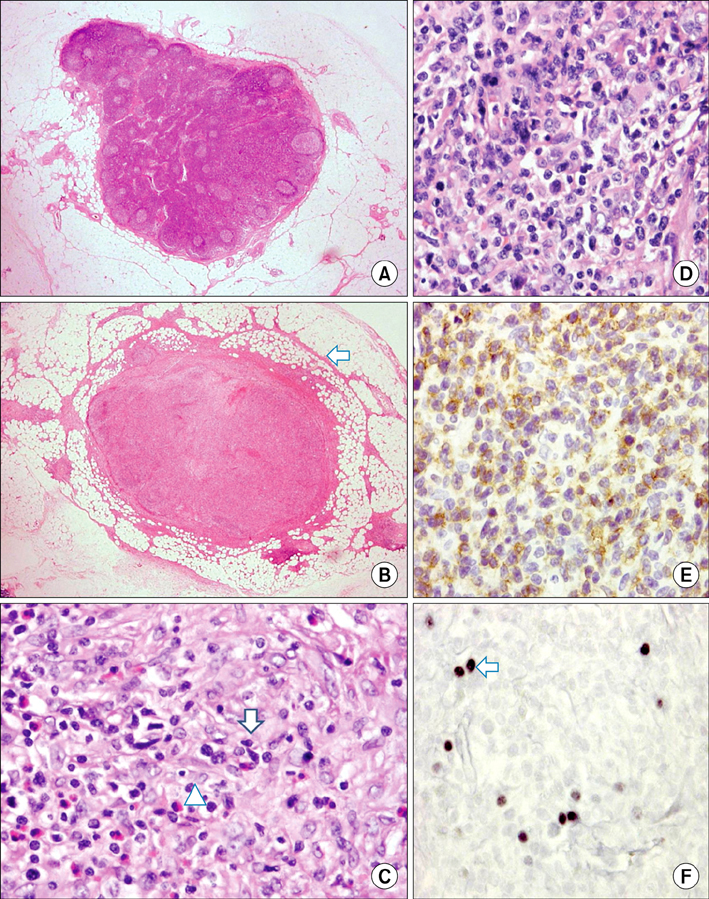
- Colorectal cancer is the third most common malignancy in Korea. In contrast, pericolic or mesenteric lymphoma is relatively rare. We experienced an extremely rare case of synchronous primary colon cancer in the ascending colon with T-cell lymphoma in the pericolic lymph node. A 79-year-old woman presented with complaints of epigastric and right lower abdominal pain combined with anorexia and nausea. Colonoscopic evaluation and biopsy were performed, and the diagnosis was cecal adenocarcinoma. She underwent right hemicolectomy with lymph node dissection. The pathology report revealed adenocarcinoma in cecum with metastasis to 1 regional lymph node out of 37 lymph nodes. In addition, there was malignant angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma in 1 pericolic lymph node. There was no evidence of lymphoma in ileum, cecum and ascending colon, so the possibility of early phase of lymphoma was suggested.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Koh SJ, Kim JS. The reasons for the increased incidence of colorectal cancer in Korea. Korean J Med. 2010. 79:97–103.2. Barron BA, Localio SA. A statistical note on the association of colorectal cancer and lymphoma. Am J Epidemiol. 1976. 104:517–522.3. Romaguera J, Hagemeister FB. Lymphoma of the colon. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005. 21:80–84.4. Nishimura Y, Takenaka H, Yoshidome K, Iwase K, Oshima S, Tanaka T. Primary mesenteric tumor of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: report of a case. Surg Today. 1994. 24:263–267.5. Shepherd NA, Hall PA, Coates PJ, Levison DA. Primary malignant lymphoma of the colon and rectum. A histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of 45 cases with clinicopathological correlations. Histopathology. 1988. 12:235–252.6. Kidd LR, Evans MD, Williams NW, Beynon J. Synchronous diagnosis of colorectal malignancy and lymphoma. Colorectal Dis. 2011. 13:1107–1109.7. Dogan A, Gaulard P, Jaffe ES, Ralfkiaer E, Muller-Hermelink HK. Swerdlow S, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, editors. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 2008. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC;309–311.8. Mourad N, Mounier N, Briere J, Raffoux E, Delmer A, Feller A, et al. Clinical, biologic, and pathologic features in 157 patients with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma treated within the Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte (GELA) trials. Blood. 2008. 111:4463–4470.9. Longo D, Fauci A, Kasper D, Hauser S, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2011. 18th ed. New York: McGraw Hill.10. Quilon JM, Day S, Lasker JC. Synchronous tumors: Hodgkin disease presenting in mesenteric lymph nodes from a right hemicolectomy for colon carcinoma. South Med J. 2004. 97:1133–1135.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Synchronous double cancer of rectal non-Hodgkin lymphoma and lung cancer: 1 case report
- Double Primary Cancer Patient with Sigmoid Colon Adenocarcinoma and Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Rectal Mucosal Metastasis A case report
- Primary Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of the Breast with Synchronous Contralateral Invasive Breast Cancer: A Case Report
- A Case of Cecal Colon Cancer Causing Intussusception and Synchronous Sigmoid Colon Cancer
- Synchronous Primary Low-grade Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of Colon and Stomach