J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Aug;79(2):116-121. 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.2.116.
Early Experience of Treatment for Symptomatic Hemorrhoids with Doppler Guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and Recto-anal Repair
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wonkkang@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2211981
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.79.2.116
Abstract
- PURPOSE
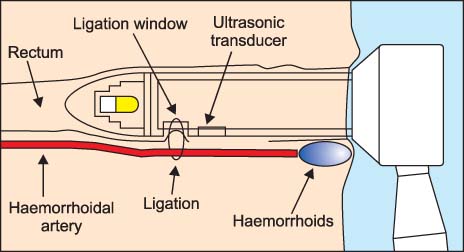
Despite all developments in recent years, the choice of an adequate treatment for hemorrhoids remains a problem. Hemorrhoidal artery ligation and recto-anal repair (HAL-RAR) is a nonexcisional surgical technique for the treatment of hemorrhoids, consisting in the ligation of the distal branches of the superior rectal artery, resulting in a reduction of blood flow and decongestion of the hemorrhoidal plexus. The aim of this study was to present the early experience of treating hemorrhoids with HAL-RAR.
METHODS
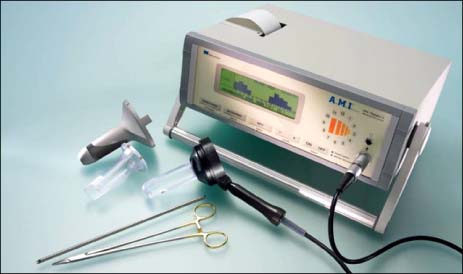
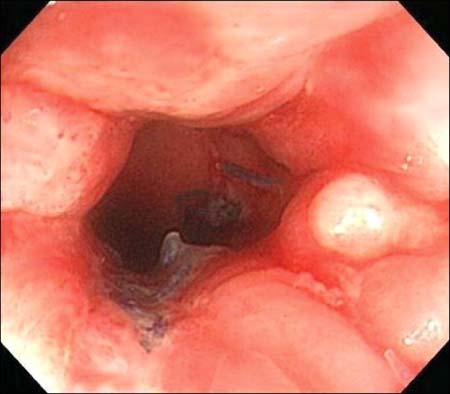
Between December 2008 and November 2009, 70 consecutive patients with symptomatic hemorrhoids were treated with HAL-RAR. The patients underwent sonographic identification and suture ligation of 4 to 8 terminal branches of the superior rectal artery above the dentate line.
RESULTS
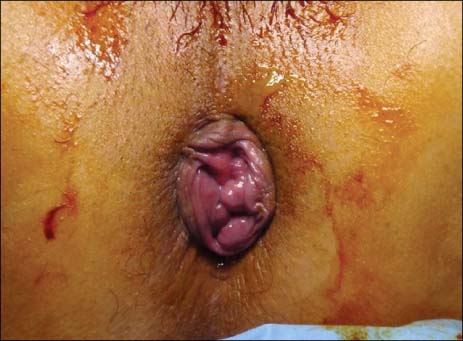
There were 33 males and 37 females (mean age, 49.72+/-14.1 years). The mean operative time was 43.8 minutes (25~80 min). Most patients (=61, 87%) were without any complaint upon follow-up at 1 week. Nine patients presented with early complication: isolated pain in 1, anemia in 1, isolated bleeding in 1, voiding difficulty (over 1 day) in 2 and tenesmus (over 2 weeks) in 4.
CONCLUSION
Based on our results we may conclude that HAL-RAR is a minimally invasive, safe and effective method and may offer an important alternative for the treatment of hemorrhoids. It may offer minimally postoperative pain, and early return of patients to their normal activities.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Morinaga K, Hasuda K, Ikeda T. A novel therapy for internal hemorrhoids: ligation of the hemorrhoidal artery with a newly devised instrument (Moricorn) in conjunction with a Doppler flowmeter. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995. 90:610–613.2. Longo A. Treatment of hemorrhoids disease by reduction of mucosa and hemorrhoidal prolapse with a circular suturing device: a new procedure. 1998. In : Proceedings of the 6th World Congress of Endoscopic Surgery; 1998 Jun 3-6; Rome, Italy. Rome: Manduzzi;777–784.3. Kolbert GW, Raulf F. Evaluation of Longo's technique for haemorrhoidectomy by doppler ultrasound measurement of the superior rectal artery. Zentralbl Chir. 2002. 127:19–21.4. Dal Monte PP, Tagariello C, Sarago M, Giordano P, Shafi A, Cudazzo E, et al. Transanal haemorrhoidal dearterialisation: nonexcisional surgery for the treatment of haemorrhoidal disease. Tech Coloproctol. 2007. 11:333–338.5. Greenberg R, Karin E, Avital S, Skornick Y, Werbin N. First 100 cases with Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation. Dis Colon Rectum. 2006. 49:485–489.6. Lim MH, Kim KH, Chung SS, Nam SY, Lee RA. Early experience with Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2009. 25:215–220.7. Cho SW, Lee RA, Chung SS, Kim KH. Early experience of Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation and rectoanal repair (DG-HAL & RAR) for the treatment of symptomatic hemorrhoids. J Korean Surg Soc. 2010. 78:23–28.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early Experience of Doppler-Guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and Rectoanal Repair (DG-HAL & RAR) for the Treatment of Symptomatic Hemorrhoids
- One Year Follow-up Result of Doppler-guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and Recto-Anal Repair in 97 Consecutive Patients
- Early Experience with Doppler-guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation
- Submucosal Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation Technique and Shortening Suture Technique for a Hemorrhoidectomy
- Modified Anal Cushion Preserving Hemorrhoidectomy