J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 Apr;49(4):696-700. 10.3341/jkos.2008.49.4.696.
Intraviteal Bevacizumab (Avastin(R)) Injection for the Treatment of Early-Stage Neovascular Glaucoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cwkee@skku.edu
- KMID: 2211506
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.49.4.696
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: This case is conducted to assess the short term safety and efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab injection in patient with early stage of the neovascular glaucoma (NVG) without peripheral anterior synechiae.
CASE SUMMARY
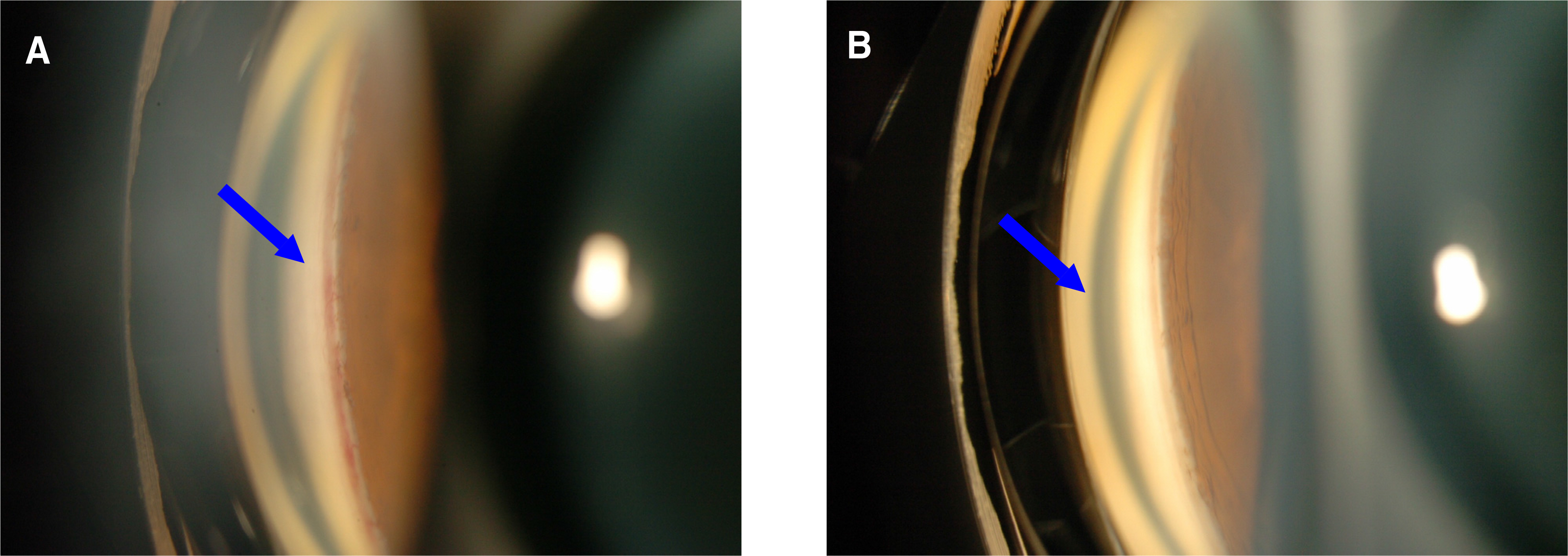
A 66 year old patient with a history of proliferative diabetic retinopathy presented with neovascularization of the iris and the angle and high intraocular pressure of 30 mmHg. The patient received a single injection of bevacizumab (1.25 mg /0.05 mg) intravitreally. The visual acuity (VA), intraocular pressure (IOP), regression of the iris and the angle neovascularization were measured up to the twenty ninth week after injection. Regression of the iris and angle neovascularization were confirmed from the second week after injection. The visual acuity had continued stable and the IOP had been controlled from 30 mmHg to 20 mmHg from fifth week without the need for topical antiglaucoma medications until the twenty ninth week.
CONCLUSIONS
Bevacizumab may be an effective medication for the treatment of neovascular glaucoma. Bevacizumab seems to be a useful adjunct or an advantageous treatment option to panretinal photocoagulation in the treatment of neovascular glaucoma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Brown GC, Magargal LE, Schachat A, Shah H. Neovascular glaucoma. Etiologic considerations. Ophthalmology. 1984; 91:315–20.2. Loffler KU. Neovascular glaucoma: aetiology, pathogenesis and treatment. Ophthalmologe. 2006; 103:1057–63.3. Kahook MY, Schuman JS, Noecker RJ. Intravitreal bevacizumab in a patient with neovascular glaucoma. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2006; 37:144–6.
Article4. Iliev ME, Domig D, Wolf-Schnurrbursch U, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) in the treatment of neovascular glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:1054–6.
Article5. Sivak-Callcott JA, O'Day DM, Gass JD, Tsai JC. Evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of neovascular glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:1767–79.6. Lee KW. Management of Neovascular glaucomas. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1988; 29:596–603.7. Magargal LE, Brown GC, Augsburger JJ, Donoso LA. Efficacy of panretinal photocoagulation in preventing neovascular glaucoma following ischemic central retinal vein obstruction. Ophthalmology. 1982; 89:780–4.
Article8. Duker JS, Brown GC. The efficacy of panretinal photocoagulation for neovascularization of the iris after central retinal artery obstruction. Ophthalmology. 1989; 96:92–5.
Article9. Brooks AM, Gillies WE. The development and management of neovascular glaucoma. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol. 1990; 18:179–85.10. Avery RL, Pieramici DJ, Rabena MD, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for neovascular age‐ related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:363–72.11. Silva Paula J, Jorge R, Alves Costa R, et al. Short-term results of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) on anterior segment neovascularization in neovascular glaucoma. Acta Opthalmol Scand. 2006; 84:556–7.
Article12. Zweng HC, Little LH. Argon laser photocoagulation. St. Louis: The CV. Mosby;1977. p. 263–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Regression of Iris Neovascularization after Subconjunctival Injection of Bevacizumab
- Intravitreal Bevacizumab (Avastin) Treatment of Neovascular Glaucoma in Ocular Ischemic Syndrome
- Effect of Simultaneous Intravitreal Bevacizumab and Retrobulbar Triamcinolone Injection in Refractory Neovascular Glaucoma
- Intravitreal Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Neovascular Glaucoma Associated With Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
- Long-Term Results of Ahmed Valve Implantation in Neovascular Glaucoma and the Effects of Intracameral Bevacizumab