J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2007 Sep;14(3):242-250. 10.4078/jkra.2007.14.3.242.
Anti-TNF-alpha Therapy in Rheumatic Diseases with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. scbae@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2202173
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2007.14.3.242
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To assess the safety of anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha therapy in patients with rheumatic disease and chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
METHODS
We used infliximab or etanercept therapy in patients with rheumatic disease and chronic HBV infection. Records concerning these patients were retrospectively reviewed for the duration of disease, treatment, serological status and biological data.
RESULTS
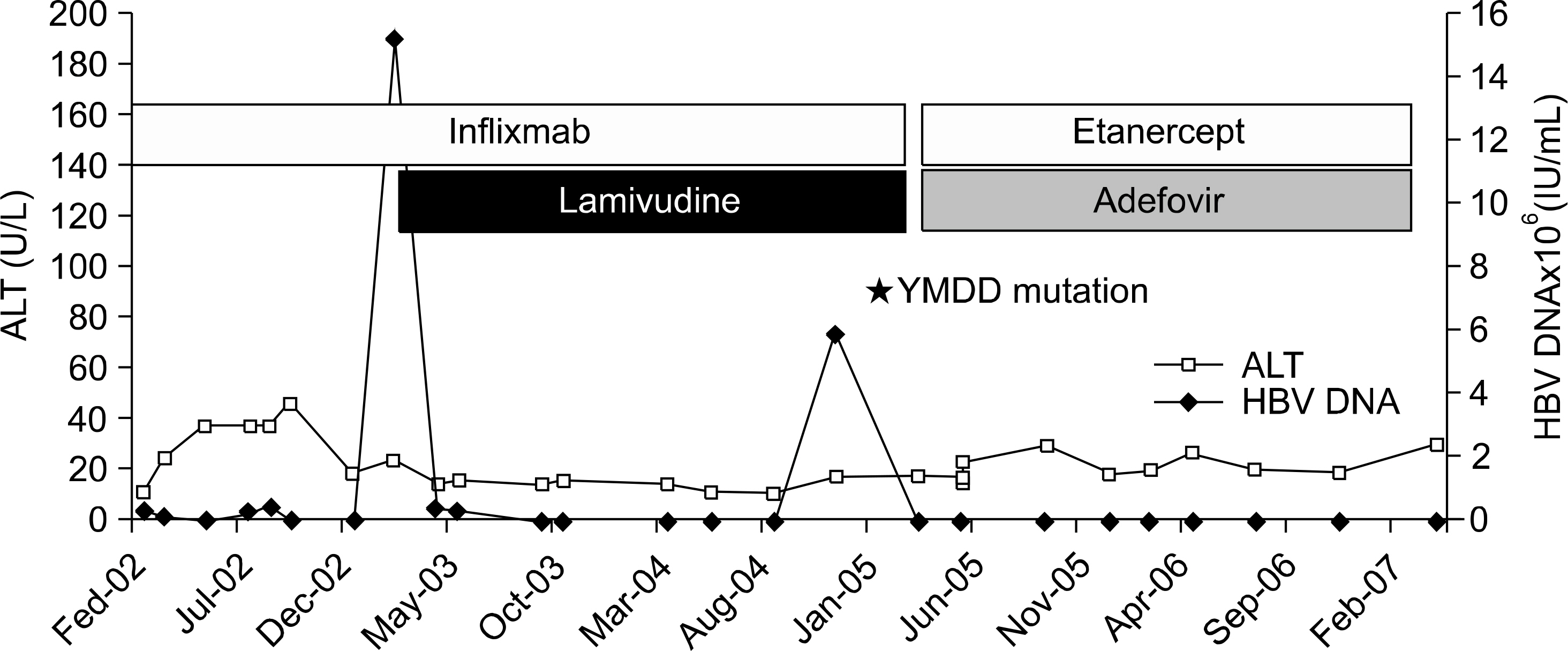
Six relevant cases with chronic HBV infection were identified: three of RA; three of AS. Four patients had received etanercept; two had been given etanercept after infliximab. One of the cases treated with lamivudine before anti-TNF-alpha therapy for chronic hepatitis B treatment. His hepatitis status was maintained stable after he initiated anti-TNF-alpha therapy. Five of the cases started anti-TNF-alpha therapy without lamivudine. Two of these five cases were received lamivudine during anti-TNF-alpha therapy due to elevation of HBV DNA titer without liver function test abnormality and then HBV DNA was normalized. Three cases without lamivudine continued to show the stable level of liver enzyme but, one of the three cases showed persistently elevated HBV DNA titer.
CONCLUSION
Prophylactic or early intervention strategies with anti-viral agent and regular monitoring of aminotransferases and viral load are needed for patient with evidence of chronic HBV infection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Anti-TNF-α Therapy for Ankylosing Spondylitis
Jung-Hwan Son, Sang-Won Cha
Clin Orthop Surg. 2010;2(1):28-33. doi: 10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.28.
Reference
-
1). Ellerin T., Rubin RH., Weinblatt ME. Infections and anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:3013–22.2). Guidotti LG., Chisari FV. Noncytolytic control of viral infections by the innate and adaptive immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. 19:65–91.3). Herbein G., O'Brien WA. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and TNF receptors in viral pathogenesis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 2000. 223:241–57.
Article4). Kasahara S., Ando K., Saito K., Sekikawa K., Ito H., Ishikawa T, et al. Lack of tumor necrosis factor alpha induces impaired proliferation of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 2003. 77:2469–76.
Article5). Arnett FC., Edworthy SM., Bloch DA., McShane DJ., Fries JF., Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988. 31:315–24.
Article6). van der Linden S., Valkenburg HA., Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984. 27:361–8.7). Goie The HS., Steven MM., van der Linden SM., Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison of the Rome, New York and modified New York criteria in patients with a positive clinical history screening test for ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1985. 24:242–9.8). Lok AS., McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2007. 45:507–39.
Article9). Liaw YF. Hepatitis viruses under immunosuppressive agents. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998. 13:14–20.
Article10). Tamori A., Nishiguchi S., Tanaka M., Kurooka H., Fujimoto S., Nakamura K, et al. Lamivudine therapy for hepatitis B virus reactivation in a patient receiving intra-arterial chemotherapy for advanced hepato-cellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 2003. 26:77–80.
Article11). ᄋksuzoglu B., Kilickap S., Yalcin S. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus infection in pancreatic cancer: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002. 32:543–5.12). Steinberg JL., Yeo W., Zhong S., Chan JY., Tam JS., Chan PK, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy for solid tumours: precore/core mutations may play an important role. J Med Virol. 2000. 60:249–55.
Article13). Haanen JB., Bieger R., van't Wout JW. Acute hepatic injury after discontinuation of chemotherapy in a patient with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Neth J Med. 1996. 49:239–43.
Article14). Lau JY., Lai CL., Lin HJ., Lok AS., Liang RH., Wu PC, et al. Fatal reactivation of chronic hepatitis B virus infection following withdrawal of chemotherapy in lymphoma patients. Q J Med. 1989. 73:911–7.15). Esteve M., Saro C., Gonzalez-Huix F., Suarez F., Forne M., Viver JM. Chronic hepatitis B reactivation following infliximab therapy in Crohn's disease patients: need for primary prophylaxis. Gut. 2004. 53:1363–5.
Article16). Ueno Y., Tanaka S., Shimamoto M., Miyanaka Y., Hiyama T., Ito M, et al. Infliximab therapy for Crohn's disease in a patient with chronic hepatitis B. Dig Dis Sci. 2005. 50:163–6.
Article17). Roux CH., Brocq ᄋ., Breuil V., Albert C., Euller-Ziegler L. Safety of anti-TNF-alpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and spondylarthropathies with concurrent B or C chronic hepatitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006. 45:1294–7.18). Michel M., Duvoux C., Hezode C., Cherqui D. Fulminant hepatitis after infliximab in a patient with hepatitis B virus treated for an adult onset still's disease. J Rheumatol. 2003. 30:1624–5.19). Nathan DM., Angus PW., Gibson PR. Hepatitis B and C virus infections and anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy: guidelines for clinical approach. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. 21:1366–71.20). ᄋstuni P., Botsios C., Punzi L., Sfriso P., Todesco S. Hepatitis B reactivation in a chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab and low dose methotrexate. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003. 62:686–7.21). Lai CL., Dienstag J., Schiff E., Leung NW., Atkins M., Hunt C, et al. Prevalence and clinical correlates of YMDD variants during lamivudine therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. 36:687–96.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reactivation of Hepatitis B Virus Following Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Therapy
- Reactivation of Hepatitis B Virus in Patients with Rheumatologic Disease Treated with Biologic Disease Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs: Screening and Treatment
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- Use of TNF Inhibitor in Particular Clinical Settings
- Reactivation of Hepatitis B Virus and Its Prevention in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases Receiving Immunosuppressive Therapy