J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2009 Jun;16(2):156-160. 10.4078/jkra.2009.16.2.156.
IgA Multiple Myeloma Presenting with Pathologic Fracture at Clavicle in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea. kiefe@fatima.or.kr
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2202132
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2009.16.2.156
Abstract
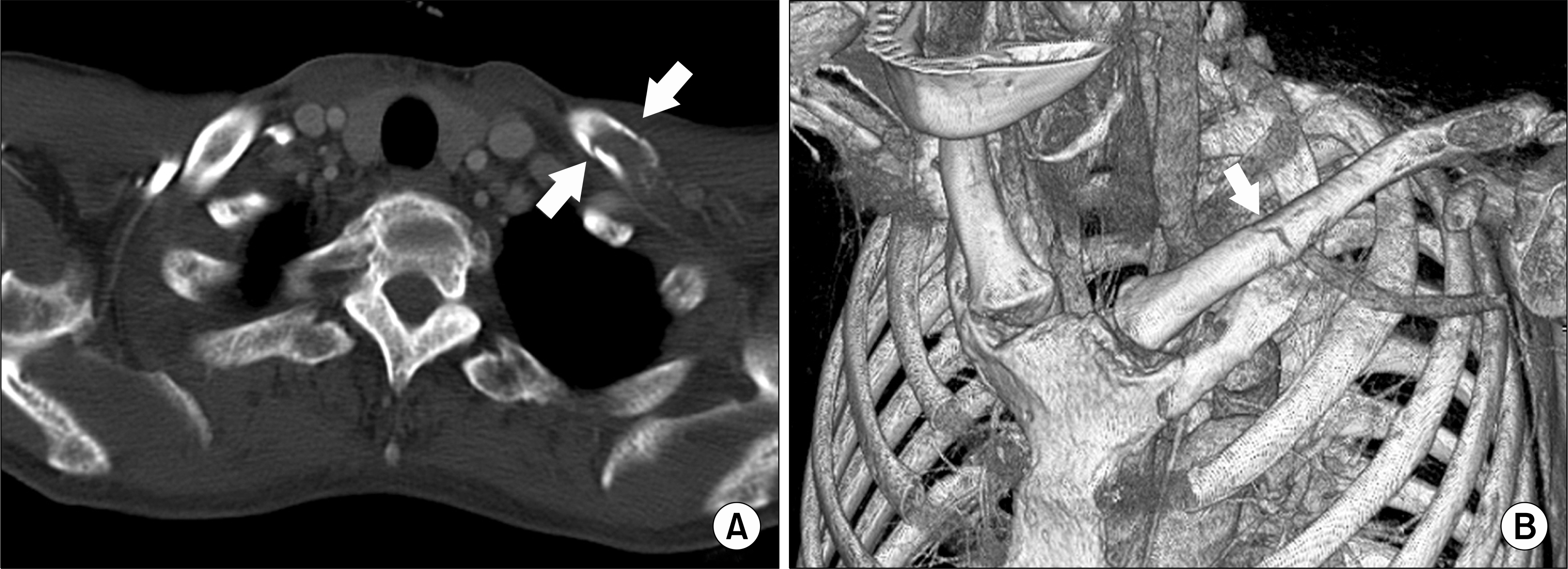
- Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells that commonly causes pathologic fractures in the vertebrae, femur, humerus and rib. Although the association of MM and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) has rarely been reported, most of MM patients with AS share the characteristic of IgA type paraproteinemia, which suggests the presence of mechanisms that possibly connect the two conditions. In this report, we describe a 47-year-old man with a 25-year history of AS, and he was diagnosed as having IgA kappa type MM with a pathologic fracture at the left clavicle. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of IgA myeloma presenting with a pathologic fracture in a patient with AS. We report here on this case along conducting a review of the relevant medical literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Shimizu K, Nagura E, Takatsuki K. Management of patients with multiple myeloma in Japan: data of 1,383 patients from 16 hospitals and 1 treatment group. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 45:2465–9.
Article2. Kyle RA. Multiple myeloma: review of 869 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1975; 50:29–40.3. Sonmez M, Akagun T, Topbas M, Cobanoglu U, Sonmez B, Yilmaz M, et al. Effect of pathologic fractures on survival in multiple myeloma patients: a case control study. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 27:11.
Article4. Blanc AP, Gastaut JA, Sebahoun G, Carcassonne Y. Association for ankylosing spondylarthritis multiple myeloma. A case history (author's transl). Sem Hop. 1979; 55:1335–7.5. Gualandi M, Trotta F, Faggioli M, Vanini A, Tassinari MC. Association of non-secreting myeloma and ankylosing spondylitis. Considerations on a clinical case. Minerva Med. 1981; 72:2631–7.6. Lam SM, Ho HH, Dunn P, Luo SF. Association of ankylosing spondylitis with IgA-multiple myeloma: report of a case and pathogenetic considerations. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1989; 88:726–8.7. O'Neill TW, Harrison BJ, Yin AL, Holt PJ. Ankylosing spondylitis associated with IgA lambda chain myeloma. Br J Rheumatol. 1997; 36:401–2.8. Brown LM, Gridley G, Check D, Landgren O. Risk of multiple myeloma and monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance among white and black male United States veterans with prior autoimmune, infectious, inflammatory, and allergic disorders. Blood. 2008; 111:3388–94.
Article9. Yang CH, Jeong MK, Lee HJ, Lee YH, Yoon KW, Kim CS. Multiple Myeloma Combined with Ankylosing Spondylitis-A case report. Korean J Med. 1985; 28:560–7.10. Franssen MJ, van de Putte LB, Gribnau FW. IgA serum levels and disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis: a prospective study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985; 44:766–71.
Article11. Feltelius N, Hvatum M, Brandtzaeg P, Knutson L, Hallgren R. Increased jejunal secretory IgA and IgM in ankylosing spondylitis: normalization after treatment with sulfasalazine. J Rheumatol. 1994; 21:2076–81.12. Montenegro V, Chiamolera M, Launay P, Goncalves CR, Monteiro RC. Impaired expression of IgA Fc receptors (CD89) by blood phagocytic cells in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 2000; 27:411–7.13. Lentzsch S, Ehrlich LA, Roodman GD. Pathophysiology of multiple myeloma bone disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2007; 21:1035–49. iii.
Article14. Gratacos J, Collado A, Filella X, Sanmarti R, Canete J, Llena J, et al. Serum cytokines (IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta and IFN-gamma) in ankylosing spondylitis: a close correlation between serum IL-6 and disease activity and severity. Br J Rheumatol. 1994; 33:927–31.15. Berenson JR, Rajdev L, Broder M. Bone complications in multiple myeloma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006; 5:1082–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Association between Multiple Myeloma and Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Report of Two Cases
- A Case of Multiple Myeolma with Huge Tumor Mass in Clavicle
- Ankylosing Spondylitis associated with Plasmacytoma: a Case Report
- IgA nephropathy in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis well controlled with etanercept
- Delayed Traumatic Diaphragm Hernia after Thoracolumbar Fracture in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis