J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2016 May;59(3):296-301. 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.3.296.
Infantile Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Transverse Sinus Presenting with Ocular Symptoms, Case Reports and Review of Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Alexandria University School of Medicine, Alexandria, Egypt. ahmed.sultan@alexmed.edu.eg
- KMID: 2192110
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.3.296
Abstract
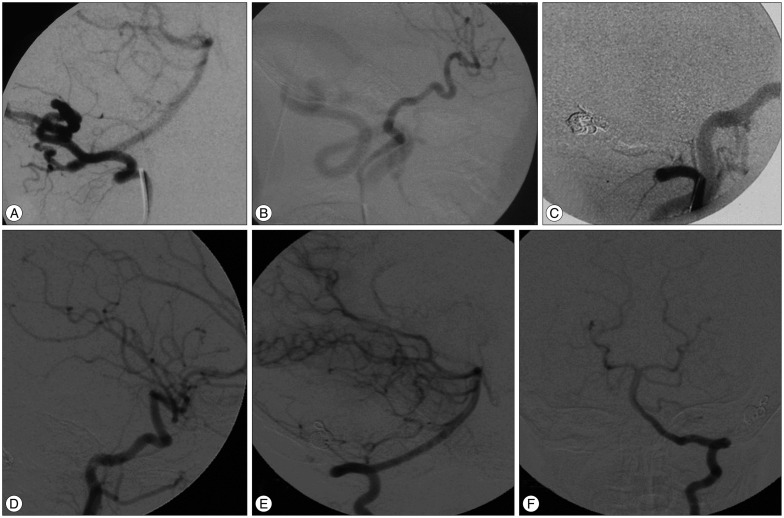
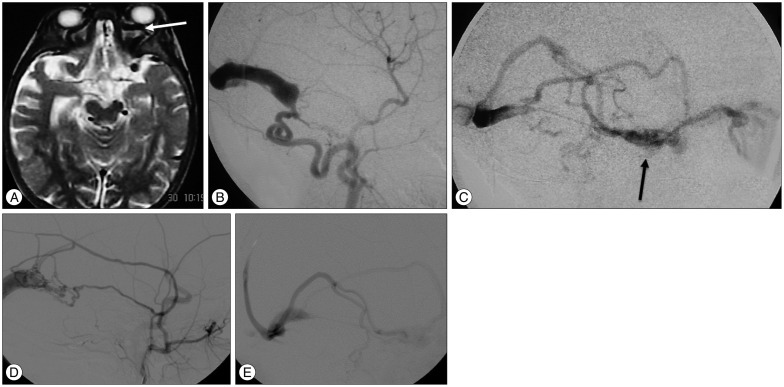
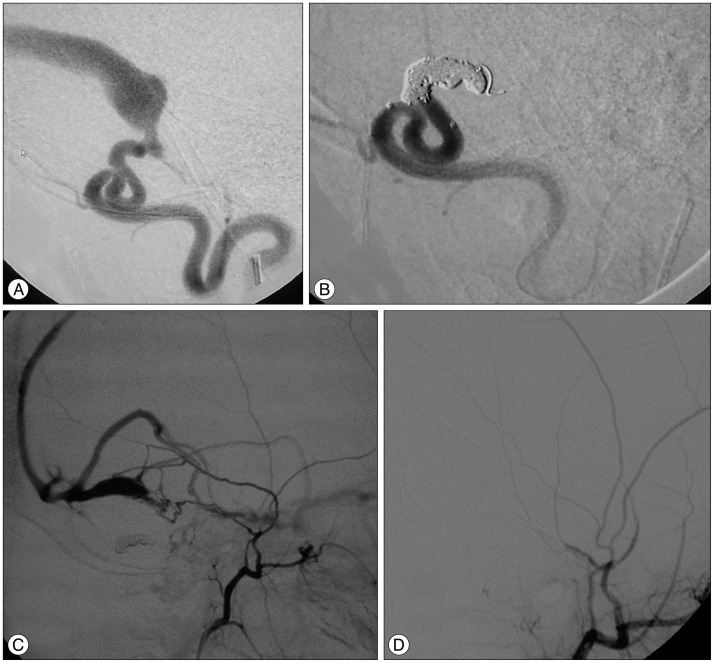
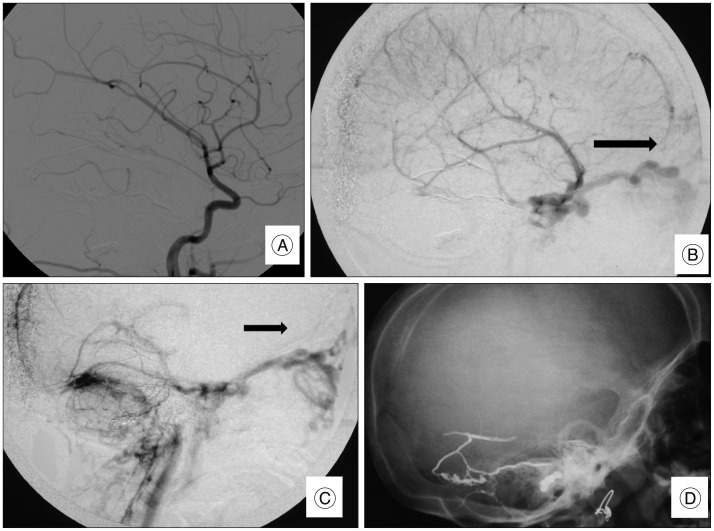
- Dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) of the transverse sinus with ophthalmic manifestations in young children are rare. We reviewed two cases of direct AVF of the transverse sinus with ocular manifestations managed at our institution. The first, a 2.5 years old male child presented with left exophthalmos. Angiography revealed AVF between the occipital artery and the transverse sinus. The second, a 2 years old female child, complained of left exophthalmos. Imaging studies showed bilateral direct AVFs of the transverse sinus with bilateral dysmaturation of the sigmoid sinus. Transarterial embolization was done in both cases. Clinical and radiological follow up revealed complete cure.This report suggests that DAVF of the transverse sinus supplied by the external carotid branches can present with ophthalmic manifestations especially if there is distal venous stenosis or obliteration involving sigmoid sinus. Transarterial embolization using coils and liquid embolic agents could be safe and feasible to obliterate the fistula.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berenstein A, Lasjaunias PL, TerBrugge KG. Vol 3 : Clinical and Interventional Aspects in Children. Dural arteriovenous shunts. Surgical Neuroangiography. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg;2006. p. 389–453.2. Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA. A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg. 1995; 82:166–179. PMID: 7815143.
Article3. Cataltepe O, Berker M, Gürçay O, Erbengi A. An unusual dural arteriovenous fistula in an infant. Neuroradiology. 1993; 35:394–397. PMID: 8327121.
Article4. Chaudhary MY, Sachdev VP, Cho SH, Weitzner I Jr, Puljic S, Huang YP. Dural arteriovenous malformation of the major venous sinuses : an acquired lesion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1982; 3:13–19. PMID: 6800236.5. Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, et al. Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas : clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology. 1995; 194:671–680. PMID: 7862961.
Article6. Davies MA, TerBrugge K, Willinsky R, Coyne T, Saleh J, Wallace MC. The validity of classification for the clinical presentation of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg. 1996; 85:830–837. PMID: 8893721.
Article7. Harrigan MR, Deveikis JP, Ardelt AA. Dural arteriovenous fistulas. In : Harrigan MR, Deveikis JP, editors. Handbook of Cerebrovascular Disease and Neurointerventional Technique. New York: Humana Press;2009. p. 539–560.8. Herman JM, Spetzler RF, Bederson JB, Kurbat JM, Zabramski JM. Genesis of a dural arteriovenous malformation in a rat model. J Neurosurg. 1995; 83:539–545. PMID: 7666234.
Article9. Houdart E, Gobin YP, Casasco A, Aymard A, Herbreteau D, Merland JJ. A proposed angiographic classification of intracranial arteriovenous fistulae and malformations. Neuroradiology. 1993; 35:381–385. PMID: 8327118.
Article10. Ihn YK, Kim MJ, Shin YS, Kim BS. Dural arteriovenous fistula involving an isolated sinus treated using transarterial onyx embolization. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 52:480–483. PMID: 23323170.
Article11. Liu HM, Shih HC, Huang YC, Wang YH. Posterior cranial fossa arteriovenous fistula with presenting as caroticocavernous fistula. Neuroradiology. 2001; 43:405–408. PMID: 11396747.
Article12. McDougall CG, Halbach VV, Dowd CF, Higashida RT, Larsen DW, Hieshima GB. Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the marginal sinus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997; 18:1565–1572. PMID: 9296201.
Article13. Mironov A. Dural arteriovenous fistula of the inferior petrosal sinus producing contralateral exophthalmus. Neuroradiology. 1994; 36:619–621. PMID: 7862279.
Article14. Morita A, Meyer FB, Nichols DA, Patterson MC. Childhood dural arteriovenous fistulae of the posterior dural sinuses : three case reports and literature review. Neurosurgery. 1995; 37:1193–1199. discussion 1199-1200. PMID: 8584161.15. Nakamura M, Tamaki N, Hara Y, Nagashima T. Two unusual cases of multiple dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurgery. 1997; 41:288–292. discussion 292-293. PMID: 9218321.
Article16. Souza MP, Willinsky RA, Terbrugge KG. Intracranial dural arteriovenous shunts in children. The toronto experience. Interv Neuroradiol. 2003; 9(Suppl 2):47–52. PMID: 20591280.
Article17. Spittau B, Millán DS, El-Sherifi S, Hader C, Singh TP, Motschall E, et al. Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the hypoglossal canal : systematic review on imaging anatomy, clinical findings, and endovascular management. J Neurosurg. 2015; 122:883–903. PMID: 25415064.
Article18. Toledo MM, Wilson TJ, Dashti S, McDougall CG, Spetzler RF. Dural arteriovenous fistula associated with superior sagittal sinus occlusion secondary to invasion by a parafalcine meningioma : case report. Neurosurgery. 2010; 67:205–207. discussion 207. PMID: 20559067.19. Wang TJ, Jou JR, Woung LC, Shih YF, Lin LLK. Ophthalmic manifestations of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula - report of four cases. Tzu Chi Med J. 2005; 17:93–99.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Contralateral Transverse Sinus Occlusion After Treatment of Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
- Borden Type I Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting as Subarachnoid Hemorrhage from a Feeding Artery Aneurysm of the Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery: A Case Report
- Occurrence of De Novo Dural Arteriovenous Fistula after Transvenous Embolization of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula : Case Reports of Two Patients
- Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Involving Transverse Sinus: Successful Embolization Using Onyx(R)
- A Case of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Multitudinous Feeders Treated by Transvenous Embolization