J Korean Hip Soc.
2011 Mar;23(1):32-38. 10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.1.32.
The Result of Osteosynthesis for Femur Neck Fracture in Old Age Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Ilsan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Koyang, Korea. osd11@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Jung Ang Janglim Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2190773
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.1.32
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We wanted to investigate the radiographic and clinical results of internal fixation with cannulated screws in elderly patients with femoral neck fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
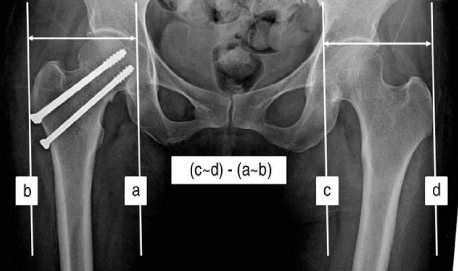
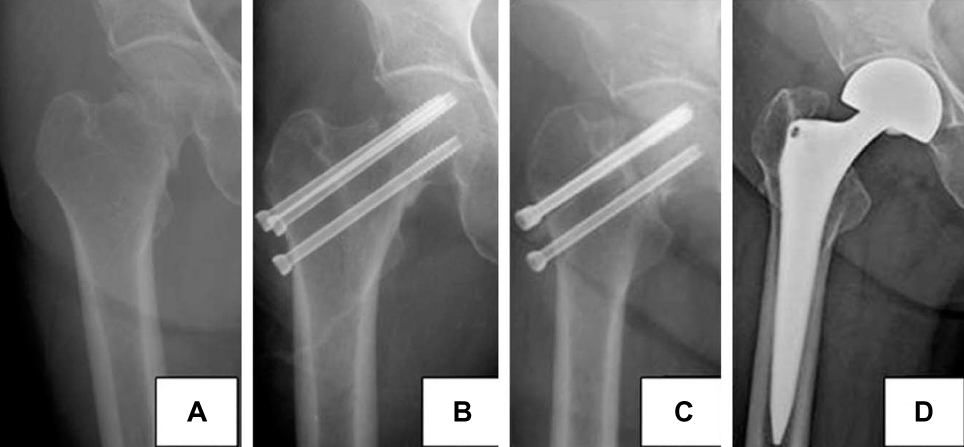
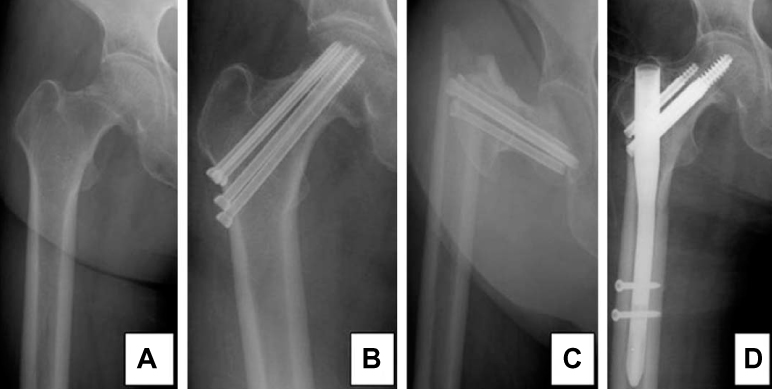
We reviewed the results of 47 cases of elderly patients with femoral neck fractures that were treated by osteosynthesis from May 2000 and March 2009 and these patients could be followed up for more than one year. There were 11 males and 36 females with a median age of 72 years (65~85 years). They were classified by the Garden stage. The number of stage I and II fractures was 34 and 16, respectively. The postoperative follow up period was 24 months (12~84 months). The union time, horizontal shortening and complications were investigated. Walking ability was evaluated by Koval's scoring system and the quality of life was measured by the Korean EQ-5D.
RESULTS
The average union time was 4.4 months. The complications were one case of nonunion, 6 cases of avascular necrosis and one case of subtrochanteric fracture. The average of the horizontal shortening was 6.815 mm (0~20 mm) in the fracture site. The walking ability was on average 1 step down and it was possible to walk independently using a walker for 69% of the patients. The Korean EQ-5D quality of life was reduced from 0.856 to 0.561 (P <0.01).
CONCLUSION
In elderly patients with femur neck fracture, the decreased abductor moment arm may reduce the quality of life and walking ability after cannulated screw fixation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Result of Internal Fixation for Stable Femoral Neck Fractures in Elderly Patients
Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Ki-Cheor Bae, Si-Wuk Lee, Seok-Jung Lee, Jung-Hoon Choi
Hip Pelvis. 2016;28(1):43-48. doi: 10.5371/hp.2016.28.1.43.The Result of Total Hip Arthroplasty after Failure of Multiple Screw Fixation for Femoral Neck Fracture
Min-Cheol Kim, Kyung-Soon Park, Taek-Rim Yoon
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2015;50(4):280-289. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.4.280.
Reference
-
1. Rogmark C, Flensburg L, Fredin H. Undisplaced femoral neck fractures--no problems--A consecutive study of 224 patients treated with internal fixation. Injury. 2009. 40:274–276.
Article2. Hui AC, Anderson GH, Choudhry R, Boyle J, Gregg PJ. Internal fixation or hemiarthroplasty for undisplaced fractures of the femoral neck in octogenarians. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994. 76:891–894.
Article3. Leighton RK, Schmidt AH, Collier P, Trask K. Advances in the treatment of intracapsular hip fractures in the elderly. Injury. 2007. 38:Suppl 3. S24–S34.
Article4. Eisler J, Cornwall R, Strauss E, Koval K, Siu A, Gilbert M. Outcomes of elderly patients with nondisplaced femoral neck fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. 399:52–58.
Article5. McGrory BJ, Morrey BF, Cahalan TD, An KN, Cabanela ME. Effect of femoral offset on range of motion and abductor muscle strength after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995. 77:865–869.
Article6. Benedetti MG, Catani F, Benedetti E, Berti L, Gioia A, Giannini S. To what extent does leg length discrepancy impair motor activity in patients after total hip arthroplasty? Int Orthop. 2010. 34:1115–1121.
Article7. Zlowodzki M, Ayieni O, Petrisor BA, Bhandari M. Femoral neck shortening after fracture fixation with multiple cancellous screws: incidence and effect on function. J Trauma. 2008. 64:163–169.
Article8. Zlowodzki M, Brink O, Switzer J, et al. The effect of shortening and varus collapse of the femoral neck on function after fixation of intracapsular fracture of the hip: a multi-centre cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008. 90:1487–1494.9. Tidermark J, Zethraeus N, Svensson O, Törnkvist H, Ponzer S. Quality of life related to fracture displacement among elderly patients with femoral neck fractures treated with internal fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2002. 16:34–38.
Article10. Min BW, Bae KC, Kang CH, Song KS, Kim SY, Won YY. Valgus intertrochanteric osteotomy for non-union of femoral neck fracture. Injury. 2006. 37:786–790.
Article11. Kang EJ, Shin HS, Park HJ, Jo MW, Kim NY. A valuation of health status using EQ-5D. Korean J Health Econ Policy. 2006. 12:19–43.12. Haidukewych GJ, Rothwell WS, Jacofsky DJ, Torchia ME, Berry DJ. Operative treatment of femoral neck fractures in patients between the ages of fifteen and fifty years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86-A:1711–1716.
Article13. Swiontkowski MF, Winquist RA, Hansen ST Jr. Fractures of the femoral neck in patients between the ages of twelve and forty-nine years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:837–846.
Article14. Sendtner E, Renkawitz T, Kramny P, Wenzl M, Grifka J. Fractured neck of femur--internal fixation versus arthroplasty. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010. 107:401–407.15. Crossman PT, Khan RJ, MacDowell A, Gardner AC, Reddy NS, Keene GS. A survey of the treatment of displaced intracapsular femoral neck fractures in the UK. Injury. 2002. 33:383–386.
Article16. Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, Swiontkowski MF, et al. Interal fixation compared with arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. 85-A:1673–1681.17. Bryant DM, Sanders DW, Coles CP, Petrisor BA, Jeray KJ, Laflamme GY. Selection of outcome measures for patients with hip fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2009. 23:434–441.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of femur neck fracture : Attributing factor of postoperative collapse & avascular necrosis
- Femur neck fracture during open intramedullary nailing of femur shaft fracture: a report of one case
- Femur Neck Fracture during Closed Medullary Nailing of Femur Shaft Fracture: A Report of Two Cases
- Fracture of Femur Neck with Heterotopic Ossification in Spinal Cord Injured Patient
- Bilateral Femoral Neck Fractures in a Young Adult: A Case Report