J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2016 Feb;42(1):51-54. 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.1.51.
Anterior tympanic plate fracture following extraction of the lower molar
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. omfs1ksh@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2189416
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.1.51
Abstract
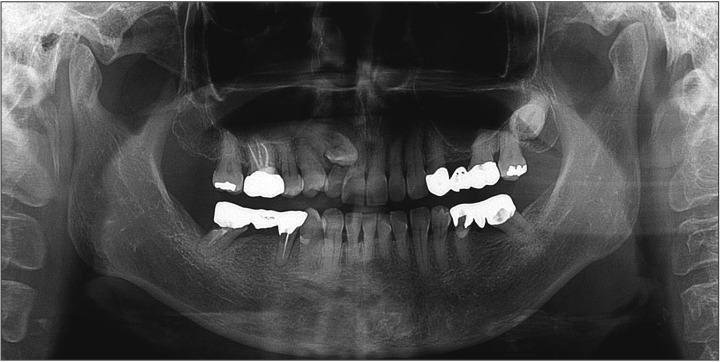
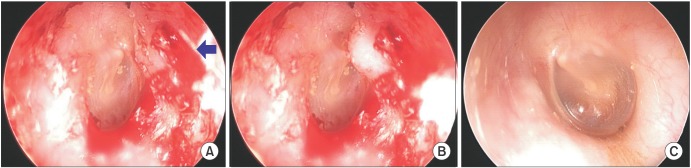
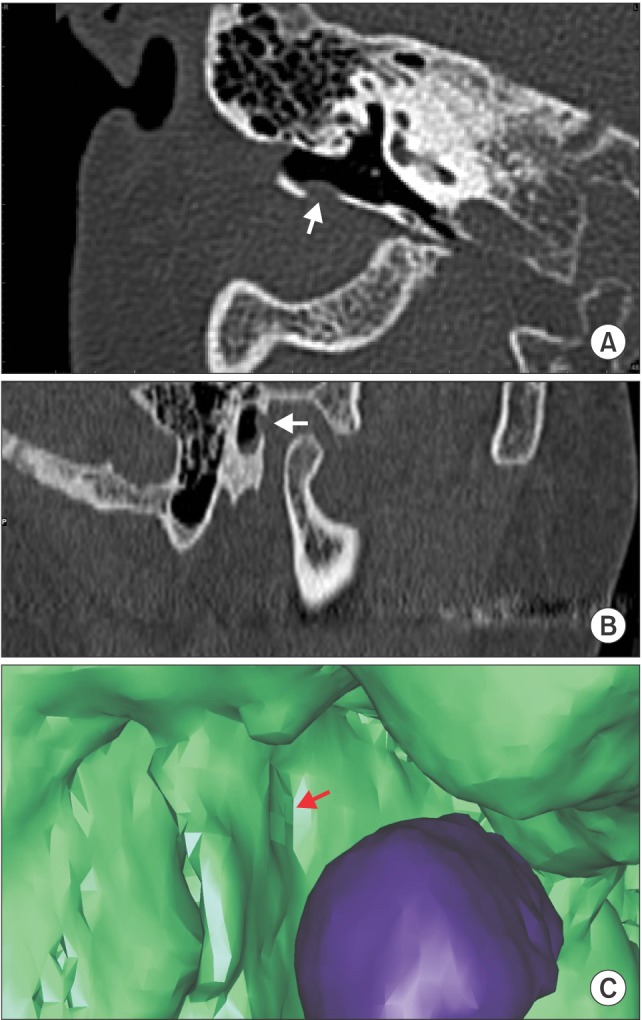
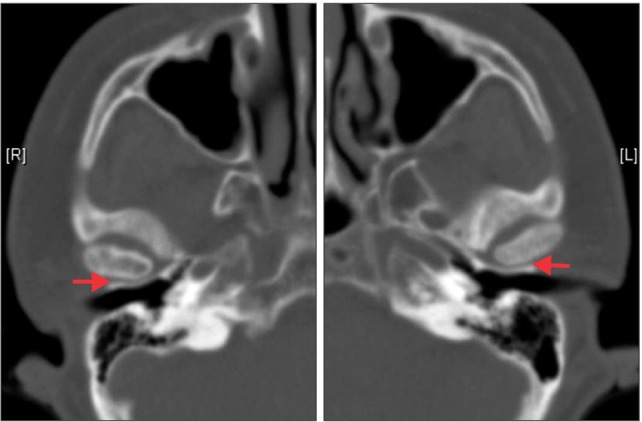
- The present case report describes an external auditory canal injury following extraction of the lower molar. The external auditory canal was torn in the same fashion that occurs in an anterior tympanic plate fracture. This case demonstrates one of the rare complications associated with dental extractions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Isolated tympanic plate fracture detected by cone-beam computed tomography: report of four cases with review of literature
Ashita Ritesh Kalaskar, Ritesh Kalaskar
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;43(5):356-360. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.5.356.
Reference
-
1. Lim JS, Yoon HJ, Lee SH. Injury of submandibular gland and lingual nerve as complication third molar tooth extraction in mandible: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 37:137–141.2. Marciani RD. Complications of third molar surgery and their management. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2012; 20:233–251. PMID: 23021398.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Study on the eruption of the lower third molar in the cases of non-extraction and the extraction of first premolar
- A study on treatment effects of Class III cases by second molar extraction
- A study on the pre-eruptive positional change of the lower third molar following orthodontic treatment
- Isolated tympanic plate fracture detected by cone-beam computed tomography: report of four cases with review of literature
- Effect of Third Molar on Postoperative Infection after Reduction of the Mandibular Angle Fracture