The Present State of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea Univerisity College of Medicine, Korea. k50367@korea.ac.kr, cdongs@kmuc.or.kr
- KMID: 2185956
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2008.51.9.791
Abstract
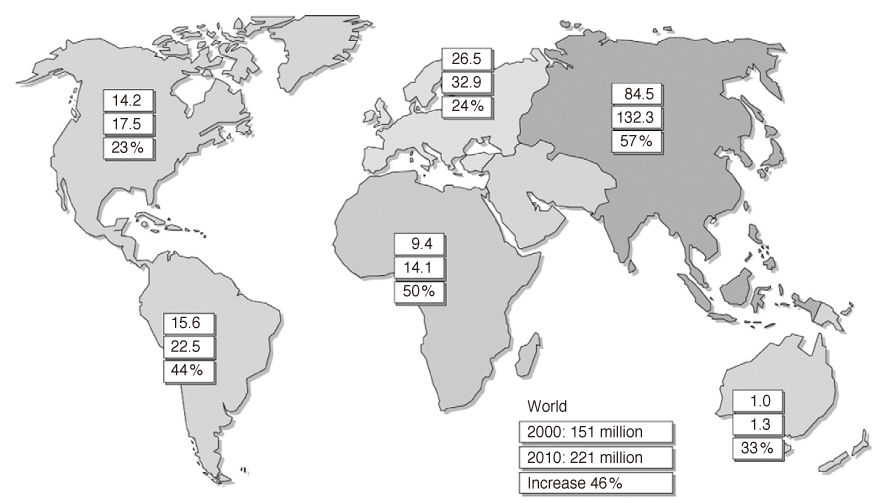
- Diabetes mellitus has approached to us as a social epidemic in Korea. The prevalence of diabetes in Korea has increased five to six-fold from 1.5% to 7~9% during the past 30 years. This increasing rate is remarkably high in comparison with those of developed countries such as the USA- doubled during the past 30 years. In addition, diabetic complication is very common in Korean diabetic patients. For example, a total of 70.5% among new patients who were started with renal replacement therapy had diabetes mellitus. Furthermore, diabetes-related mortality has rapidly increased over the last 20 years. The age-sex adjusted mortality rate of diabetic patients was about three-fold higher than those of general population. As a result, medical cost of diabetes mellitus covered by the national health insurance corporation was 3.2 trillion won and accounted for 19.2% of all medical costs. On the other hand, the rate of awareness and treatment in diabetic patients has improved from 1998 to 2005. However, the proportion of adequate glycemic control (HbA1c < 7%) among the treated diabetic patients was only 40%. The comprehensive and integrated health intervention including public approach is urgently needed to control the increasing prevalence of diabetes mellitus and its related undesirable outcomes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 12 articles
-
Response: Cause-of-Death Trends for Diabetes Mellitus over 10 Years (Korean Diabetes J 33(1):65-72, 2009)
Su Kyung Park, Duk Kyu Kim
Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(2):166-166. doi: 10.4093/kdj.2009.33.2.166.Risk Factor Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed with Non-mydriatic Fundus Camera: KNHANES V
Jung Suk Yoon, Seung-Kook Baek, Young Hoon Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2019;60(6):555-568. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.6.555.The effects of weight loss by a low-calorie diet and a low-calorie plus exercise in overweight undergraduate students
Gun-Ae Yoon, Hyun-Ho Ahn, Bo-Hae Park, Danbi Yoo, Sunmin Park
Korean J Nutr. 2012;45(4):315-323. doi: 10.4163/kjn.2012.45.4.315.Prevention and management of the diabetic foot
Ho Seong Lee
J Korean Med Assoc. 2013;56(3):220-228. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2013.56.3.220.Performance Evaluation of the ARKRAY ADAMS A1c HA-8180
Eun-Hyung Yoo, Byung-In Kim, Hyun-Jung Cho
Lab Med Online. 2014;4(3):164-167. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2014.4.3.164.Current Treatments on Obesity
Chul Jin Lee, Min-Jeong Kim, Sang Joon An
Korean J Health Promot. 2019;19(4):171-185. doi: 10.15384/kjhp.2019.19.4.171.Physician-Directed Diabetes Education without a Medication Change and Associated Patient Outcomes
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hae-Kyung Yang, Eun Young Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In Young Choi, Hyeon Woo Yim, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(3):187-194. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.187.The Epidemiology of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jin Hwa Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2013;14(1):11-14. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2013.14.1.11.Role of Sphingolipid Metabolites in Metabolic Disease
Hyeonjin Kim, Tae-Sik Park
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(3):156-161. doi: 10.3803/jkes.2009.24.3.156.A Placebo-Controlled, Single and Multiple Dose Study to Investigate the Appropriate Parameters for Evaluation of Phannacodynamic Equivalence of Voglibose in Healthy Korean Volunteers
Kyungho Jang, Sang-Heon Cho, Jung-Ryul Km, Jae-Yong Chung, Kyoung Soo Lim, In-Jin Jang, Kyung-Sang Yu
J Korean Soc Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013;21(1):63-70. doi: 10.12793/jkscpt.2013.21.1.63.Association between Diabetes Education Status and Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Analysis of the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V)
Jun Sung Kwon, Won Jun Kim, Yang Hee Han, Hyun Joong Kim, Sa Young Shin, Kyoo Ho Choi, Jae Hyuck Jun, Myoung Sook Shim, Jin Yeob Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2014;15(4):236-243. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2014.15.4.236.Impact of Hyperglycemia on Survival and Infection-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Who Were Receiving Palliative Chemotherapy
Yong Joo Hong, Hye-Suk Han, Yusook Jeong, Jiwon Jeong, Sung-Nam Lim, Hyung Jin Choi, Hyun-Jung Jeon, Tae-Keun Oh, Sang-Jeon Lee, Ki Hyeong Lee
Cancer Res Treat. 2014;46(3):288-296. doi: 10.4143/crt.2014.46.3.288.
Reference
-
1. Kim KS, Choi CH, Lee DY, Kim EJ. Epidermiological study on diabetes mellitus among rural Korean. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1972. 1:17–24.2. Kim DJ, Park HM. Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey - the 3rd Report (2005). 2007. asessed on July 12, 2008. The Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;131–166. http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/result/Result_03.aspx/.3. Korean Diabetes Association Task Force Team for Basic Statistical Study of Korean Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetes in Korea. 2007.4. Death rate for the 10 leading causes of death. 2006. asessed on July 12, 2008. Korea National Statistical Office; http://www.nso.go.kr/.5. Park Y, Lee H, Koh CS, Min H, Yoo K, Kim Y, Shin Y. Prevalence of diabetes and IGT in Yonchon County, South Korea. Diabetes Care. 1995. 18:545–548.
Article6. Song KH, Nam-Goomg IS, Han SM, Kim MS, Lee EJ, Lee YS, Lee MS, Yoon S, Lee KU, Park JY. Change in prevalence and 6-year incidence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Korean subjects living in a rural area. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. 78:378–384.
Article7. Kwon JW, Song YM, Park H, Sung J, Kim H, Cho SI. Effects of age, time period, and birth cohort on the prevalence of diabetes and obesity in Korean men. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:255–260.
Article8. International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas, 2nd ed. 2003. accessed on July 12, 2008. Available at: www.eatlas.idf.org.9. Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001. 13:782–787.
Article10. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, Zimmet P, Son HY. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006. 11:1681–1688.
Article11. Gregg EW, Cadwell BL, Cheng YJ, Cowie CC, Williams DE, Geiss L, Engelgau MM, Vinicor F. Trends in the prevalence and ratio of diagnosed to undiagnosed diabetes according to obesity levels in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:2806–2812.
Article12. Choi YJ, Cho YM, Park CK, Jang HC, Park KS, Kim SY, Lee HK. Rapidly increasing diabetes-related mortality with socio-environmental changes in South Korea during the last two decades. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006. 74:295–300.
Article13. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Heine RJ, Holman RR, Sherwin R, Zinman B. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: A consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:1963–1972.
Article14. Kim DJ, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim HC, Kim HJ, Lee KW. Trends in the prevalence and management status of diabetes in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008. 79:S. 21.